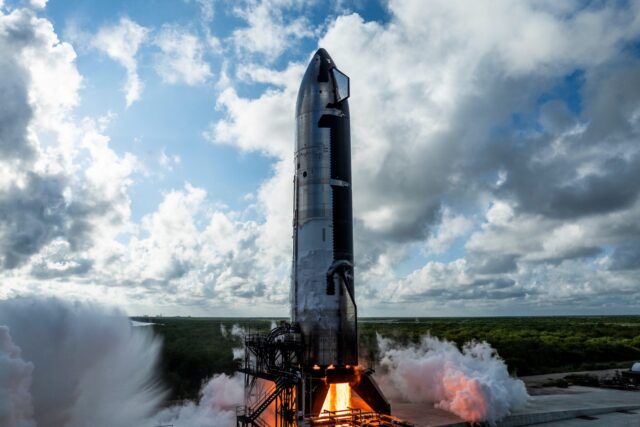
Italy’s plan to buy Starlink data deals a serious blow to European space network
Developed by the European Union and European Space Agency, with Italian participation, this constellation of 290 satellites is planned to come online by 2030 at a development cost of $10.5 billion. During the lengthy negotiations, Italy even managed to secure one of the three primary ground stations in the Abruzzo region of the country.
The response from some Italian and European officials to the potential agreement between Italy and SpaceX has been ferocious.
Antonio Misiani, former deputy finance minister for Italy and senator for the opposition Democratic Party, told Politico that a completed agreement would represent an “unacceptable sell-out of national sovereignty.”
An Atlantic Council senior fellow and former policy advisor to the Italian government, Beniamino Irdi, told the Financial Times, “It sends a political signal to the EU,” Irdi said. “Iris² is a symbol of Europe’s strategic autonomy, and a key EU member shifting to a different solution can be interpreted as a sign of divestment from that.”
There are multiple layers of frustration here beyond Iris². One concerns Musk, who, since the election of Trump, has turned his attention toward advancing far-right political causes in Europe, particularly in Germany and the United Kingdom. Meloni, a conservative leader of Italy, considers Musk a friend and ally. Andrea Stroppa, one of Musk’s advisers in Italy, explained in September that “Elon recognizes Giorgia Meloni’s leadership. And he sees in her the same thing he sees in Donald Trump, someone who can defend Western values in danger.”
Battling with Breton
Musk has also had a long-running feud with French businessman Thierry Breton, who was Commissioner for the Internal Market of the European Union for five years until last September. Breton spearheaded the Iris² initiative to provide secure communications from low-Earth orbit. He also championed the Digital Services Act, which aims to curb misinformation published online in Europe. The European Commission has been energetically investigating Musk’s social media site X under the law.
Italy’s plan to buy Starlink data deals a serious blow to European space network Read More »