What’s it like to be 70 years old in space? “All those little aches and pains heal up.”
Not many people celebrate their birthday by burning a fiery arc through the atmosphere, pulling 4.4gs in freefall back to planet Earth, thudding into the ground, and emptying their stomach on the steppes of Kazakhstan.
No one has ever done it on their 70th birthday.
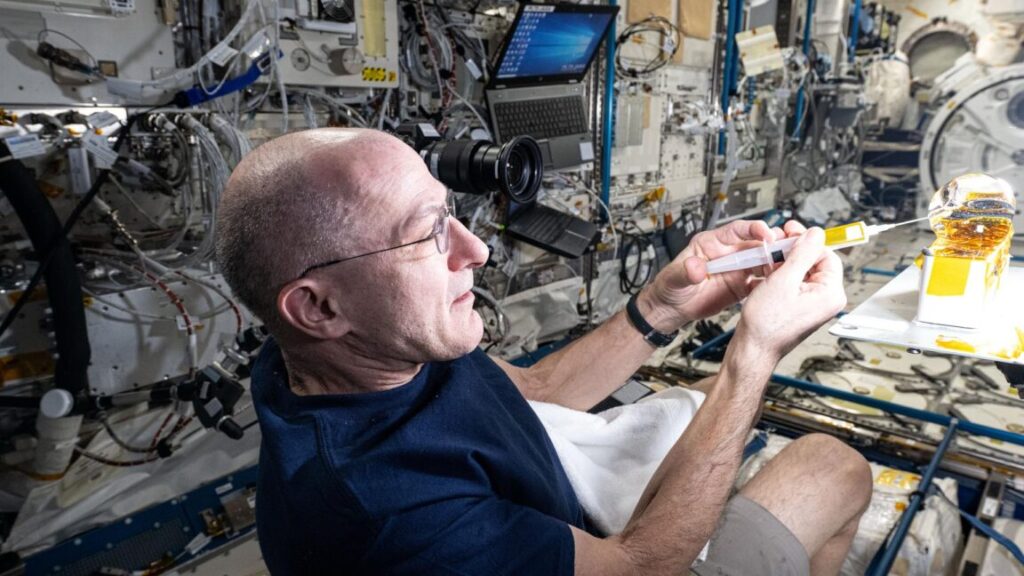
Perhaps this is appropriate because NASA astronaut Don Pettit is a singular individual. His birthday is April 20, and when the Soyuz spacecraft carrying him landed at dawn in Kazakhstan, the calendar had turned over to that date. John Glenn, then 77, was older when he went to space. But no one as old as Pettit had spent as long as he had in orbit, 220 days, on a mission.
On Monday, a little more than a week after returning from orbit, Pettit met with reporters at Johnson Space Center. “It’s good to be back on planet Earth,” he said. “As much as I love exploring space, going into the frontier, and making observations, you do reach a time when it’s time to come home.”
Flying in space at 70 years old
Pettit first went into space at the age of 47 for his first of three long-duration missions to the International Space Station. Since then, he has flown a shorter shuttle mission and two more space station increments. All told, he has lived in space for 590 days, the third-most all-time among NASA astronauts.
“I’ve got a few creaks and groans in my body, but basically I feel the same as I did 20 years ago, and coming back to gravity is provocative,” he said.
After every one of his missions, Pettit said the readjustment to gravity for him has been a challenge. He added that the surprising thing about spaceflight is that it’s not so much your large muscles that ache, but the smaller ones.
What’s it like to be 70 years old in space? “All those little aches and pains heal up.” Read More »