Eleven things to know about in the Windows 11 2024 Update
The Windows 11 2024 Update, also known as Windows 11 24H2, started rolling out last week. Your PC may have even installed it already!
The continuous feature development of Windows 11 (and Microsoft’s phased update rollouts) can make it a bit hard to track exactly what features you can expect to be available on any given Windows PC, even if it seems like it’s fully up to date.
This isn’t a comprehensive record of all the changes in the 2024 Update, and it doesn’t reiterate some basic but important things like Wi-Fi 7 or 80Gbps USB4 support. But we’ve put together a small list of new and interesting changes that you’re guaranteed to see when your version number rolls over from 22H2 or 23H2 to 24H2. And while Microsoft’s announcement post spent most of its time on Copilot and features unique to Copilot+ PCs, here, we’ll only cover things that will be available on any PC you install Windows 11 on (whether it’s officially supported or not).
Quick Settings improvements
The Quick Settings panel sees a few nice quality-of-life improvements. The biggest is a little next/previous page toggle that makes all of the Quick Settings buttons accessible without needing to edit the menu to add them. Instead of clicking a button and entering an edit menu to add and remove items from the menu, you click and drag items between pages. The downside is that you can’t see all of the buttons at once across three rows as you could before, but it’s definitely more handy if there are some items you want to access sometimes but don’t want to see all the time.
A couple of individual Quick Settings items see small improvements: a refresh button in the lower-right corner of the Wi-Fi settings will rescan for new Wi-Fi networks instead of making you exit and reopen the Wi-Fi settings entirely. Padding in the Accessibility menu has also been tweaked so that all items can be clearly seen and toggled without scrolling. If you use one or more VPNs that are managed by Windows’ settings, it will be easier to toggle individual VPN connections on and off, too. And a Live Captions accessibility button to generate automatic captions for audio and video is also present in Quick Settings starting in 24H2.
More Start menu “suggestions” (aka ads)
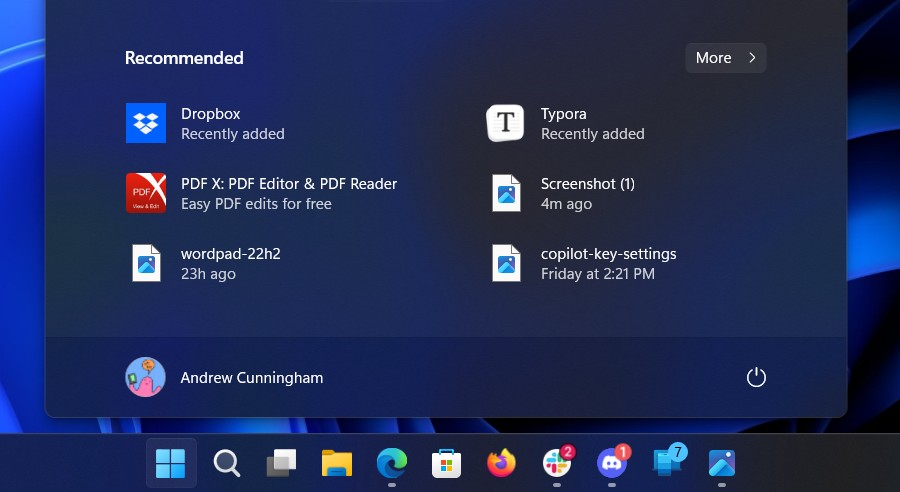
Amid apps I’ve recently installed and files I’ve recently opened, the “recommended” area of the Start menu will periodically recommend apps to install. These change every time I open the Start menu and don’t seem to have anything to do with my actual PC usage. Credit: Andrew Cunningham
One of the first things a fresh Windows install does when it connects to the Internet is dump a small collection of icons into your Start menu, things grabbed from the Microsoft Store that you didn’t ask for and may not want. The exact apps change from time to time, but these auto-installs have been happening since the Windows 10 days.
The 24H2 update makes this problem subtly worse by adding more “recommendations” to the lower part of the Start menu below your pinned apps. This lower part of the Start menu is usually used for recent files or newly (intentionally) installed apps, but with recommendations enabled, it can also pull recommended apps from the Microsoft Store, giving Microsoft’s app store yet another place to push apps on you.
These recommendations change every time you open the Start menu—sometimes you’ll see no recommended apps at all, and sometimes you’ll see one of a few different app recommendations. The only thing that distinguishes these items from the apps and files you have actually interacted with is that there’s no timestamp or “recently added” tag attached to the recommendations; otherwise, you’d think you had downloaded and installed them already.
These recommendations can be turned off in the Start menu section of the Personalization tab in Settings.
Context menu labels
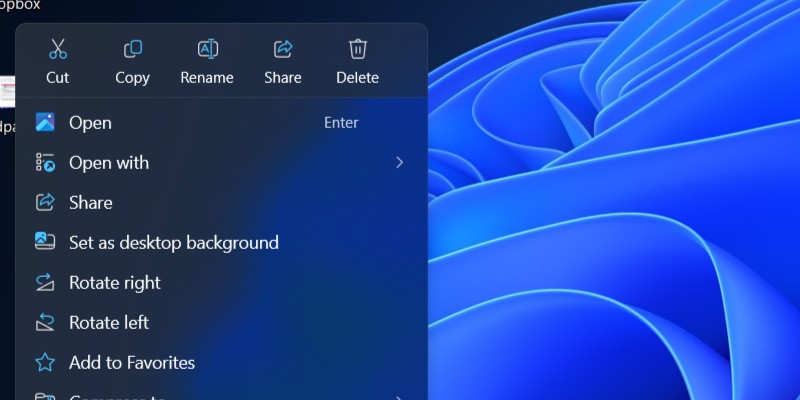
Text labels added to the main actions in the right-click/context menu. Credit: Andrew Cunningham
When Windows 11 redesigned the right-click/context menu to help clean up years of clutter, it changed basic commands like copy and paste from text labels to small text-free glyphs. The 2024 Update doesn’t walk this back, but it does add text labels back to the glyphs, just in case the icons by themselves didn’t accurately communicate what each button was used for.
Windows 11’s user interface is full of little things like this—stuff that was changed from Windows 10, only to be changed back in subsequent updates, either because people complained or because the old way was actually better (few text-free glyphs are truly as unambiguously, universally understood as a text label can be, even for basic commands like cut, copy, and paste).
Smaller, faster updates
The 24H2 update introduces something that Microsoft calls “checkpoint cumulative updates.”
To recap, each annual Windows update also has a new major build number; for 24H2, that build number is 26100. In 22H2 and 23H2, it was 22621 and 22631. There’s also a minor build number, which is how you track which of Windows’ various monthly feature and security updates you’ve installed. This number starts at zero for each new annual update and slowly increases over time. The PC I’m typing this on is running Windows 11 build 26100.1882; the first version released to the Release Preview Windows Insider channel in June was 26100.712.
In previous versions of Windows, any monthly cumulative update that your PC downloads and installs can update any build of Windows 11 22H2/23H2 to the newest build. That’s true whether you’re updating a fresh install that’s missing months’ worth of updates or an actively used PC that’s only a month or two out of date. As more and more updates are released, these cumulative updates get larger and take longer to install.
Starting in Windows 11 24H2, Microsoft will be able to designate specific monthly updates as “checkpoint” updates, which then become a new update baseline. The next few months’ worth of updates you download to that PC will contain only the files that have been changed since the last checkpoint release instead of every single file that has been changed since the original release of 24H2.
If you’re already letting Windows do its update thing automatically in the background, you probably won’t notice a huge difference. But Microsoft says these checkpoint cumulative updates will “save time, bandwidth, and hard drive space” compared to the current way of doing things, something that may be more noticeable for IT admins with dozens or hundreds of systems to keep updated.
Sudo for Windows
A Windows version of the venerable Linux sudo command—short for “superuser do” or “substitute user do” and generally used to grant administrator-level access to whatever command you’re trying to run—first showed up in experimental Windows builds early this year. The feature has formally been added in the 24H2 update, though it’s off by default, and you’ll need to head to the System settings and then the “For developers” section to turn it on.
When enabled, Sudo for Windows (as Microsoft formally calls it) allows users to run software as administrator without doing the dance of launching a separate console window as an administrator.
By default, using Sudo for Windows will still open a separate console window with administrator privileges, similar to the existing runas command. But it can also be configured to run inline, similar to how it works from a Linux or macOS Terminal window, so you could run a mix of elevated and unelevated software from within the same window. A third option, “with input disabled,” will run your software with administrator privileges but won’t allow additional input, which Microsoft says reduces the risk of malicious software gaining administrator privileges via the sudo command.
One thing the runas command supports that Sudo for Windows doesn’t is the ability to run software as any local user—you can run software as the currently-logged-in user or as administrator, but not as another user on the machine, or using an account you’ve set up to run some specific service. Microsoft says that “this functionality is on the roadmap for the sudo command but does not yet exist.”
Protected print mode
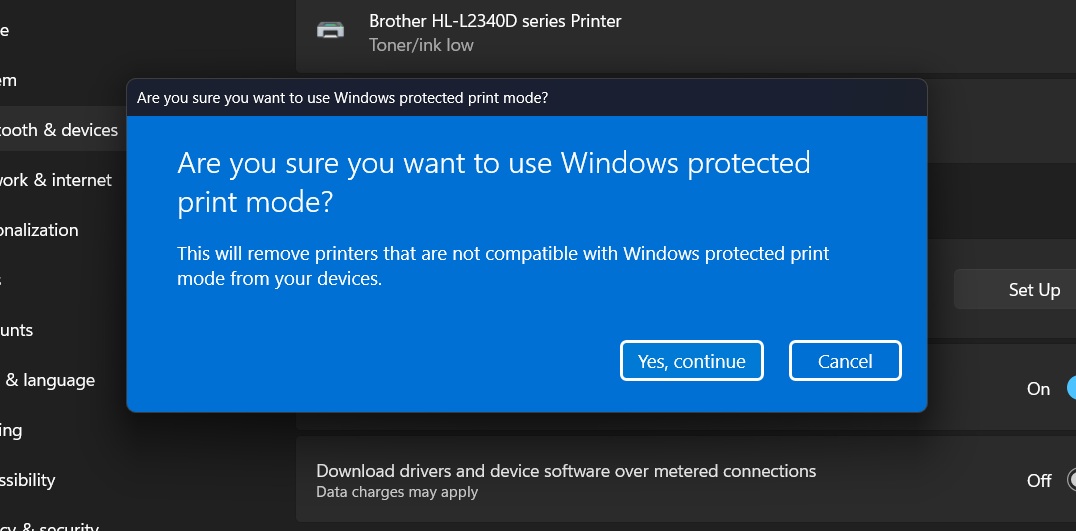
Enabling the (currently optional) protected print mode in Windows 11 24H2. Credit: Andrew Cunningham
Microsoft is gradually phasing out third-party print drivers in Windows in favor of more widely compatible universal drivers. Printer manufacturers will still be able to add things on top of those drivers with their own apps, but the drivers themselves will rely on standards like the Internet Printing Protocol (IPP), defined by the Mopria Alliance.
Windows 11 24H2 doesn’t end support for third-party print drivers yet; Microsoft’s plan for switching over will take years. But 24H2 does give users and IT administrators the ability to flip the switch early. In the Settings app, navigate to “Bluetooth & devices” and then to “Printers & scanners” and enable Windows protected print mode to default to the universal drivers and disable compatibility. You may need to reconnect to any printer you had previously set up on your system—at least, that was how it worked with a network-connected Brother HL-L2340D I use.
This isn’t a one-way street, at least not yet. If you discover your printer won’t work in protected print mode, you can switch the setting off as easily as you turned it on.
New setup interface for clean installs
When you create a bootable USB drive to install a fresh copy of Windows—because you’ve built a new PC, installed a new disk in an existing PC, or just want to blow away all the existing partitions on a disk when you do your new install—the interface has stayed essentially the same since Windows Vista launched back in 2006. Color schemes and some specific dialog options have been tweaked, but the interface itself has not.
For the 2024 Update, Microsoft has spruced up the installer you see when booting from an external device. It accomplishes the same basic tasks as before, giving you a user interface for entering your product key/Windows edition and partitioning disks. The disk-partitioning interface has gotten the biggest facelift, though one of the changes is potentially a bit confusing—the volumes on the USB drive you’re booted from also show up alongside any internal drives installed in your system. For most PCs with just a single internal disk, disk 0 should be the one you’re installing to.
Wi-Fi drivers during setup
Microsoft’s obnoxious no-exceptions Microsoft account requirement for all new PCs (and new Windows installs) is at its most obnoxious when you’re installing on a system without a functioning network adapter. This scenario has come up most frequently for me when clean-installing Windows on a brand-new PC with a brand-new, as-yet-unknown Wi-Fi adapter that Windows 11 doesn’t have built-in drivers for. Windows Update is usually good for this kind of thing, but you can’t use an Internet connection to fix not having an Internet connection.
Microsoft has added a fallback option to the first-time setup process for Windows 11 that allows users to install drivers from a USB drive if the Windows installer doesn’t already include what you need. As a failover, would we prefer to see an easy-to-use option that didn’t require Microsoft account sign-in? Sure. But this is better than it was before.
To bypass this entirely, there are still local account workarounds available for experts. Pressing Shift + F10, typing OOBEBYPASSNRO in the Command Prompt window that opens, and hitting Enter is still there for you in these situations.
Boosted security for file sharing
The 24H2 update has boosted the default security for SMB file-sharing connections, though, as Microsoft Principal Program Manager Ned Pyle notes, it may result in some broken things. In this case, that’s generally a good thing, as they’re only breaking because they were less secure than they ought to be. Still, it may be dismaying if something suddenly stops functioning when it was working before.
The two big changes are that all SMB connections need to be signed by default to prevent relay attacks and that Guest access for SMB shares is disabled in the Pro edition of Windows 11 (it had already been disabled in Enterprise, Education, and Pro for Workstation editions of Windows in the Windows 10 days). Guest fallback access is still available by default in Windows 11 Home, though the SMB signing requirement does apply to all Windows editions.
Microsoft notes that this will mainly cause problems for home NAS products or when you use your router’s USB port to set up network-attached storage—situations where security tends to be disabled by default or for ease of use.
If you run into network-attached storage that won’t work because of the security changes to 24H2, Microsoft’s default recommendation is to make the network-attached storage more secure. That usually involves configuring a username and password for access, enabling signing if it exists, and installing firmware updates that might enable login credentials and SMB signing on devices that don’t already support it. Microsoft also recommends replacing older or insecure devices that don’t meet these requirements.
That said, advanced users can turn off both the SMB signing requirements and guest fallback protection by using the Local Group Policy Editor. Those steps are outlined here. That post also outlines the process for disabling the SMB signing requirement for Windows 11 Home, where the Local Group Policy Editor doesn’t exist.
Windows Mixed Reality is dead and gone
Several technology hype cycles ago, before the Metaverse and when most “AI” stuff was still called “machine learning,” Microsoft launched a new software and hardware initiative called Windows Mixed Reality. Built on top of work it had done on its HoloLens headset in 2015, Windows Mixed Reality was meant to bring in app developers and the PC makers and allowed them to build interoperable hardware and software for both virtual reality headsets that covered your eyes entirely and augmented reality headsets that superimpose objects over the real world.
But like some other mid-2010s VR-related initiatives, both HoloLens and Windows Mixed Reality kind of fizzled and flailed, and both are on their way out. Microsoft officially announced the end of HoloLens at the beginning of the month, and Windows 11 24H2 utterly removes everything Mixed Reality from Windows.
Microsoft announced this in December of 2023 (in a message that proclaims “we remain committed to HoloLens”), though this is a shorter off-ramp than some deprecated features (like the Android Subsystem for Windows) have gotten. Users who want to keep using Windows Mixed Reality can continue to use Windows 23H2, though support will end for good in November 2026 when support for the 23H2 update expires.
WordPad is also dead
WordPad running in Windows 11 22H2. It will continue to be available in 22H2/23H2, but it’s been removed from the 2024 update. Credit: Andrew Cunningham
We’ve written plenty about this already, but the 24H2 update is the one that pulls the plug on WordPad, the rich text editor that has always existed a notch above Notepad and many, many notches below Word in the hierarchy of Microsoft-developed Windows word processors.
WordPad’s last update of any real substance came in 2009, when it was given the then-new “ribbon” user interface from the then-recent Office 2007 update. It’s one of the few in-box Windows apps not to see some kind of renaissance in the Windows 11 era; Notepad, by contrast, has gotten more new features in the last two years than it had in the preceding two decades. And now it has been totally removed, gone the way of Internet Explorer and Encarta.
Andrew is a Senior Technology Reporter at Ars Technica, with a focus on consumer tech including computer hardware and in-depth reviews of operating systems like Windows and macOS. Andrew lives in Philadelphia and co-hosts a weekly book podcast called Overdue.
Eleven things to know about in the Windows 11 2024 Update Read More »