Windows 11’s Steam Deck-ish, streamlined Xbox gaming UI comes to all PCs in April
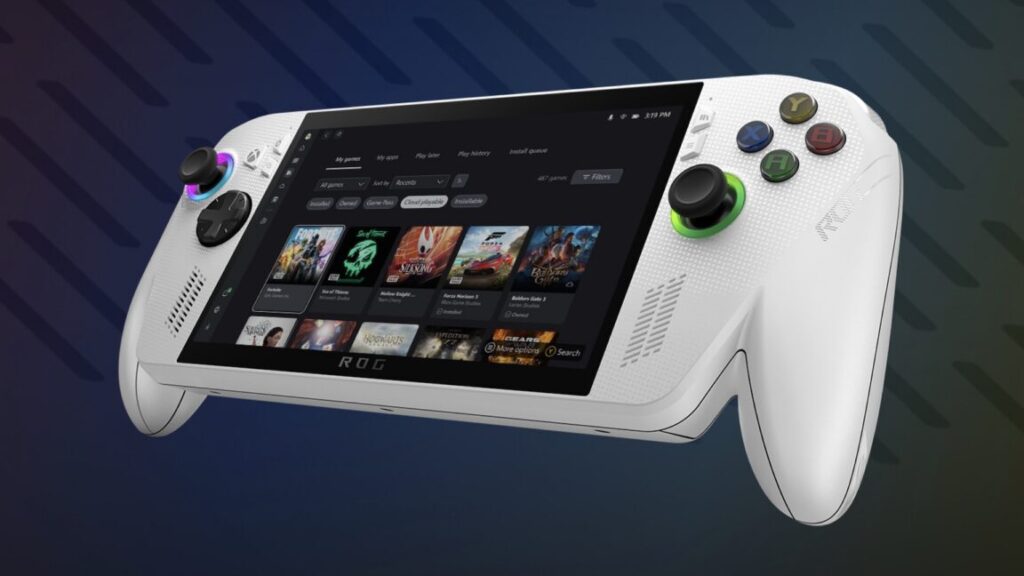
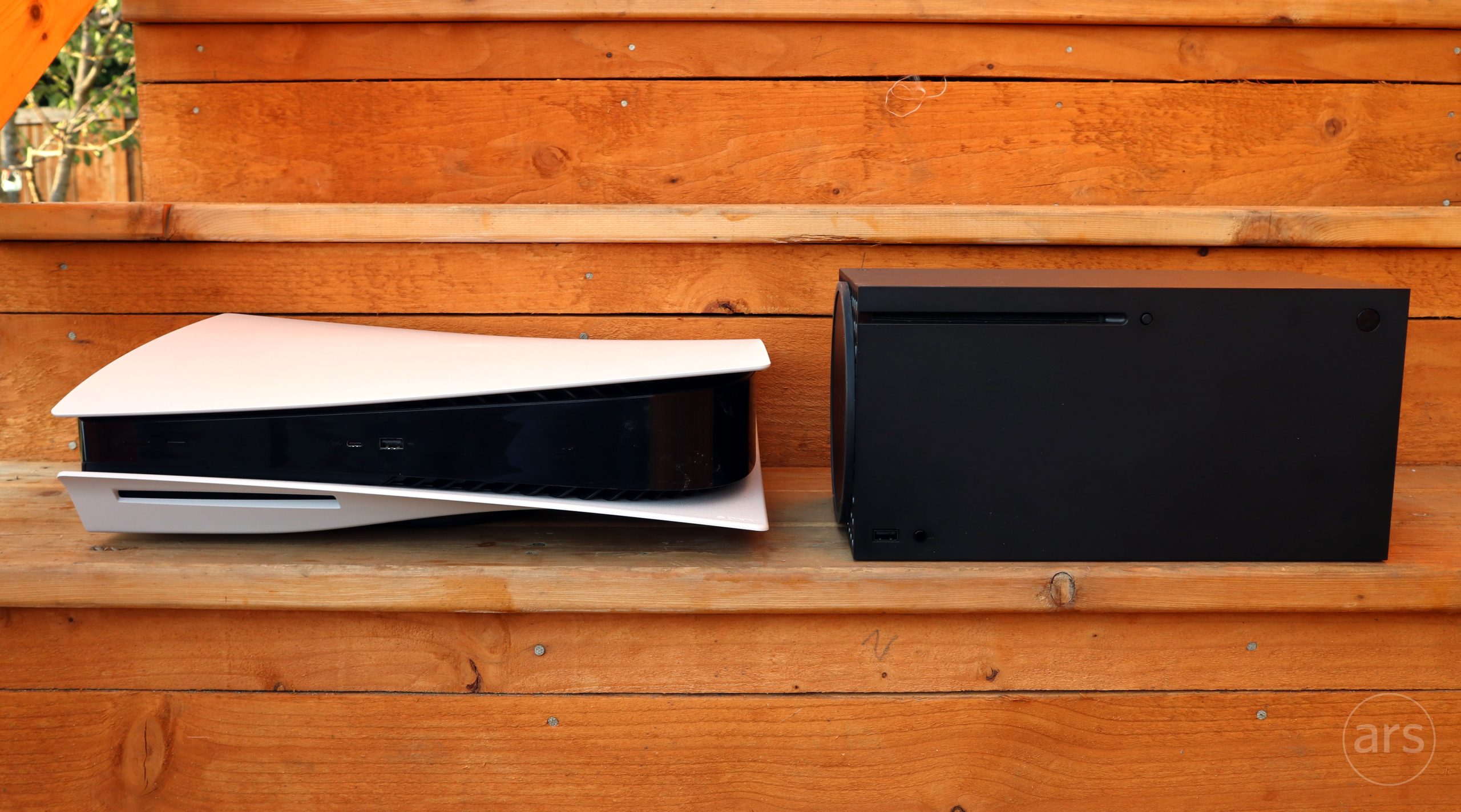
When Asus and Microsoft launched the ROG Xbox Ally X last summer, it came with a bespoke controller-driven full-screen interface running on top of Windows 11. The handheld was still running Windows under the hood, and you could bring up the typical Windows desktop any time, but it defaulted to the full-screen gaming UI.
Then called either the “Xbox Experience for Handheld” or the “Xbox Full-Screen Experience (FSE)” depending on who you asked and when, Microsoft said it would be available on all Windows PCs at some point in 2026. That point has apparently arrived: Microsoft announced this week at the Game Developers Conference that other Windows 11 PCs “in select markets” would be getting what’s now being called “Xbox mode” starting in April.
Under the hood, a PC running in Xbox mode is still running regular-old Windows, with the same capabilities as any other PC. But there are system services and UI elements (like the standard Start menu and taskbar) that don’t launch when the system is in Xbox mode, something Microsoft claims can save a gigabyte or two of RAM while also allowing systems to use less energy. Users can return to Windows’ traditional desktop mode whenever they want, though.
Our experience with Xbox mode on the ROG Xbox Ally X was mixed; a Windows PC in Xbox mode is still a Windows PC, with both the broad game/app compatibility and the messiness that entails.
The seams between the controller-friendly interface and the mouse-and-keyboard version of Windows were the most visible when trying to download and launch games from third-party game stores like Steam and the Epic Games Store, which generally required you to use those store apps to buy and download games before they could be launched from the comfort of Xbox mode. We’ll have to test the update on other PCs after it rolls out to see whether Microsoft has made substantial improvements.
Windows 11’s Steam Deck-ish, streamlined Xbox gaming UI comes to all PCs in April Read More »