Gemini Deep Think learns math, wins gold medal at International Math Olympiad
In the past, making LLMs better at math would involve reinforcement learning with final answers. Luong explained to Ars that models trained in this way can get to the correct answer, but they have “incomplete reasoning,” and part of the IMO grading is based on showing your work. To prepare Deep Think for the IMO, Google used new reinforcement learning techniques with higher-quality “long answer” solutions to mathematical problems, giving the model better grounding in how to handle every step on the way to an answer. “With this kind of training, you can actually get robust, long-form reasoning,” said Luong.
Credit: Google DeepMind
As you might expect, Deep Think takes more time to generate an output compared to the simpler versions you can access in the Gemini app. However, the AI followed the same rules as the flesh-and-blood participants, which was only possible because of its ability to ingest the problems as natural language. Gemini was provided with the problem descriptions and gave its answers within the 4.5-hour time limit of the competition.
Rigorous proofs
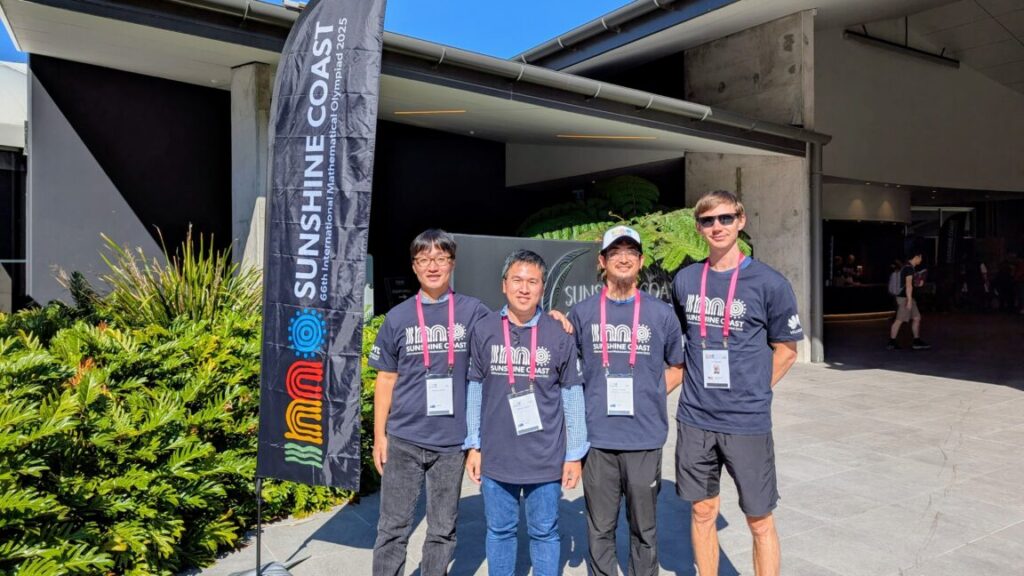
AI firms like DeepMind have taken an interest in the IMO over the past few years because it presents a unique challenge. While the competition is aimed at pre-university mathematicians, the questions require critical thinking and an understanding of multiple mathematical disciplines, including algebra, combinatorics, geometry, and number theory. Only the most advanced AI models have any hope of accurately answering these multi-layered problems.
The DeepMind team has pointed out some interesting aspects of Deep Think’s performance, which they say come from its advanced training. In the third problem (below), for example, many human competitors applied a graduate-level concept called Dirichlet’s Theorem, using mathematics outside the intended scope of the competition. However, Deep Think recognized that it was possible to solve the problem with simpler math. “Our model actually made a brilliant observation and used only elementary number theory to create a self-contained proof of the given problem,” said DeepMind researcher and Brown University professor Junehyuk Jung.
Gemini Deep Think learns math, wins gold medal at International Math Olympiad Read More »