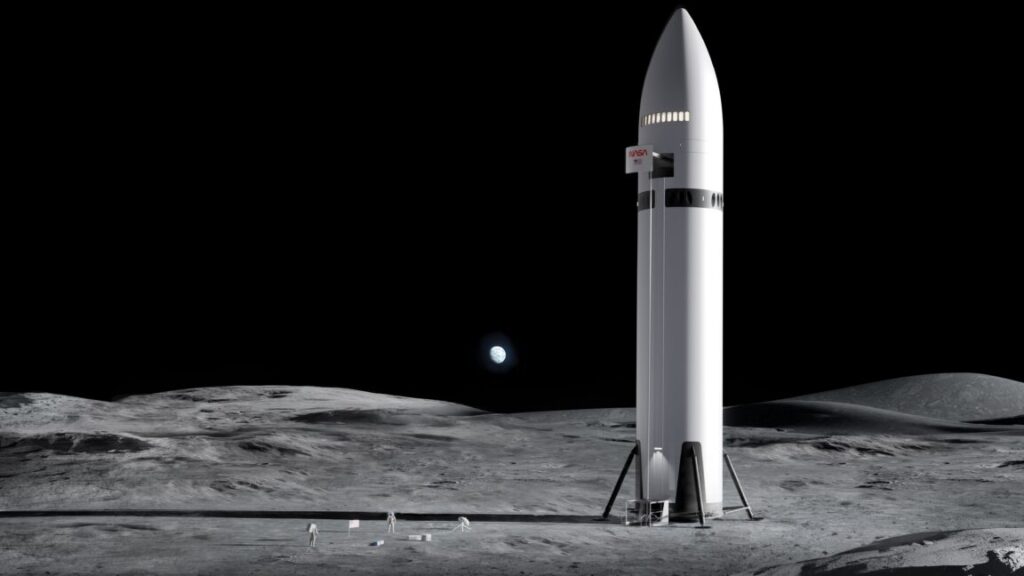
NASA and SpaceX disagree about manual controls for lunar lander
The report notes that during every one of the Apollo program’s crewed lunar landings, astronauts engaged the backup manual control method. (Of course, this occurred six decades ago, when flight software was considerably less sophisticated than today.)
As NASA and SpaceX near a key decision point, known as Critical Design Review, the issue remains unresolved. The new report suggests that this may result in automation being the only landing method.
A similar fight over Dragon
The space agency and SpaceX engaged in a similar back-and-forth during the design process for the Crew Dragon spacecraft a decade ago. SpaceX initially wanted touchscreens only, with limited flight commands available to astronauts. NASA pushed back and wanted what were essentially joysticks for astronauts to fly the vehicles like previous spacecraft. A former NASA astronaut then working at SpaceX, Garret Reisman, helped broker a compromise by which astronauts could manually fly the vehicles using controls on touchscreens.
However, the new report says the flight controls for Dragon were built on many successful missions by a cargo version of the vehicle that flew to the International Space Station.
“Starship will not have the same level of proven flight heritage in the actual operating environment for its crewed lunar missions,” the report states. “Incorporating this system capability is a key element of HLS’s human-rating certification and part of an essential crew survival strategy.”
A design for Blue Origin’s manual control has not yet been made, according to the inspector general.
There is other interesting information in the report, including details on the uncrewed demonstration flights that SpaceX and Blue Origin are both required to fly before human missions can take place. The inspector general notes that these flights will not require life support systems and airlocks, as human missions will. Nor will the tall Starship vehicle be required to test an elevator to bring crew down to the surface.
There will also be a limited ability to test the abrasive impact of lunar dust, expected to be returned inside the vehicles after Moonwalks, on life support equipment during these uncrewed demonstrations.
NASA and SpaceX disagree about manual controls for lunar lander Read More »