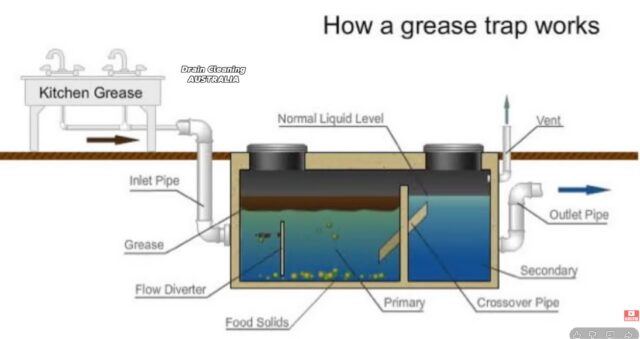
If there’s several things this blog endorses, one of them would be going meta.
It’s time. The big picture awaits.
The most important meta question is location, location, location.
This is the periodic reminder that dating dynamics are very different in different locations, and gender ratios are far more uneven than they appear because a lot of people pair off and aren’t in the pool.
If you are a man seeking to date women, New York City is the place to be.
Churrasco Suadade: when I’m out I notice that tables at restaurants and bars in manhattan are probably around 80-95% women, it’s a new dynamic that no one is talking about.
Fixed Income Guy: Are you at all the poor people places? All the finance guy hang outs are 80% dudes.
I mention Fixed Income Guy to mock him, as in why are you spending a lot more money to hang out with 80% dudes and largely finance dudes at that? I mean, sure, if that’s what you want.
Darrell Owens: Oh this is new? Coming from the Bay Area, the amount of women I see in Manhattan is insane. You rarely see more than few young women partying back in San Francisco. The gender ratio here feels 70: 30 young women to men, its every block in Manhattan!
Noah Smith: In an ideal world, where you live wouldn’t really matter in terms of dating opportunities, but the truth is that one of the easiest ways to get chicks is to just move to New York City.
Having lived in both Tokyo and NYC, I can pretty confidently tell you that while Tokyo is not a tough dating market by any means, NYC is absolutely on another level.
This viral clip (which is viral for a reason, it’s good fun, wait for it) is another endorsement of New York City being a great place to meet women, as you have a wide variety of great and largely successful women to explore. What doesn’t get mentioned in that clip as a key reason things are so great is that the gender ratio in NYC is highly favorable for men.
The interviewer asks about dating women who make more money than then the man, clearly trying to get the guy to say this is a problem, but he isn’t buying it, instead pointing out that successful women are more thoughtful and plan for the future, and it in no way bothers him at all. Right on, but this sidesteps the other half of problem. The man has to be okay with the fact that he earns less money (and often has less formal education or other status markers), which often men aren’t, and also the woman has to be okay with it too.
That’s the rub. As a man, you might (and should be) be actively all for it (this doesn’t make you less successful, it makes you more successful), but if she’s going to be bothered by it anyway, that’s also your problem. So the key is to figure out quickly if she will actually be fine with it or not.
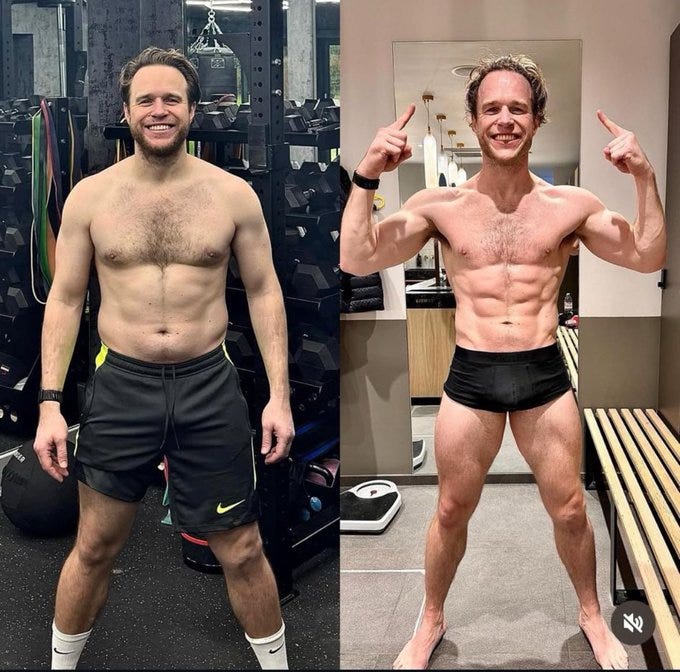
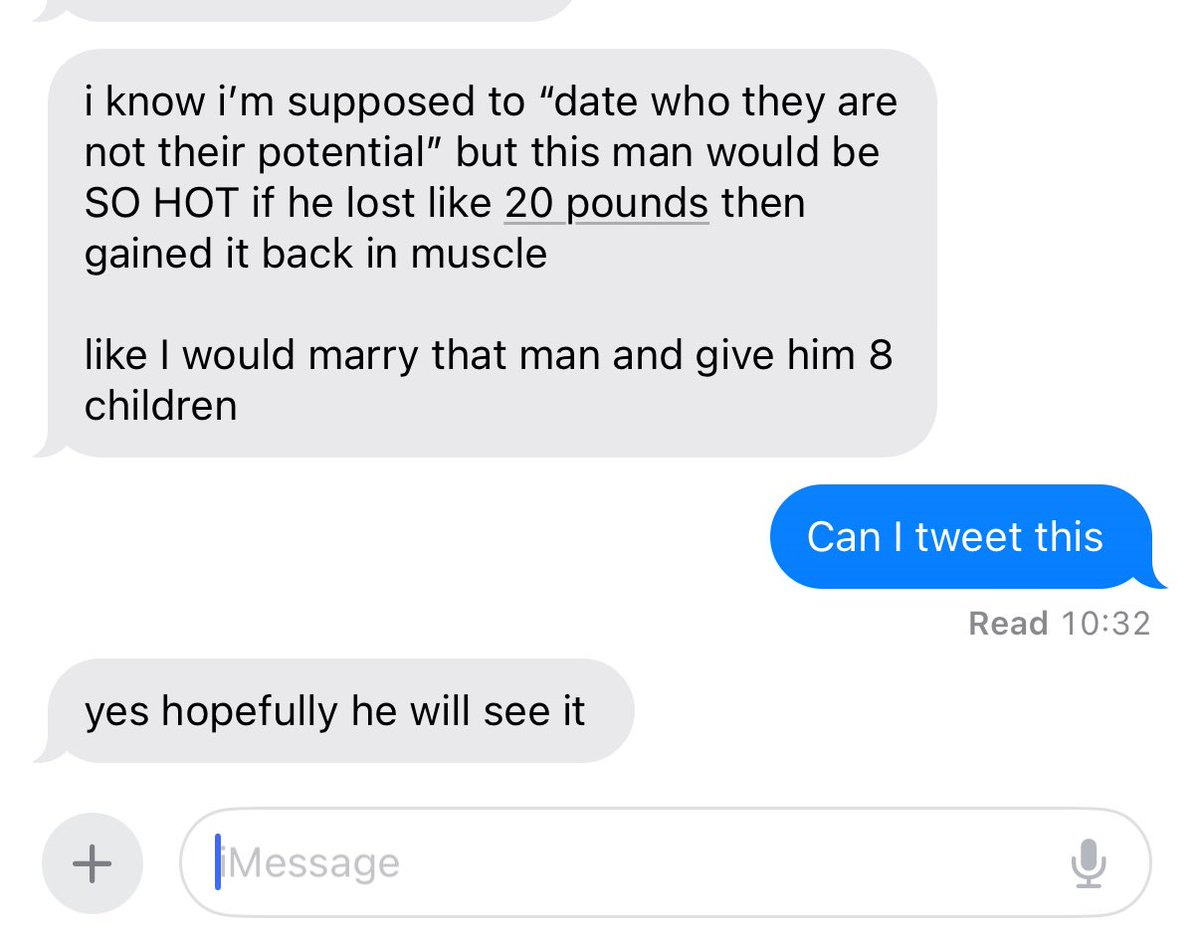
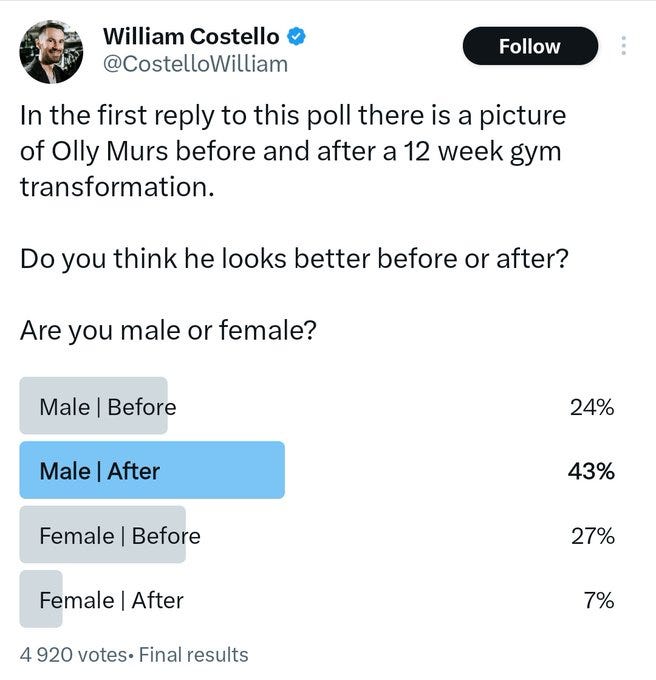
Being in shape is great. Having muscle can be a game changer. By far the worst plausible amount of exercise is none at all.
Lauren Self: Men severely underestimate the power of gaining 20lbs of muscle
Lauren Self (QTing from before): LISTEN UP BOYS.
But don’t go nuts. For most people that is not a problem, but yes it is very possible to go too far. As a man, as I understand preferences in general, you don’t want to go near actual zero fat and you don’t want to look actively skinny.
Taoki: why are women lying about this? like what’s the actual cause?
Lauren Self: 100% of women would choose something in between these two options
Shako: The aesthetics of a man who poses gives them the ick. But if both were shirtless at a beach they’d obviously prefer the fit guy.
Special K: No he does look better in the before. Women are correct on this one I fear. Guys obsess over these supremely tight toned muscles and they shouldn’t.
Liron Shapira: Guy on left looks like he’s a chill dude with a social life, guy on right looks like he’s obsessed with his body. Same body could look better with better social context, although just the extremeness of his rippedness is a little alarming about his life priorities.
Joel: “let’s get a burger?” v “are you really gonna eat that?”
Mason: The male equivalent of the hourglass shape is just “wall”
Teej dv: his smile is nicer in the first one
Taoki: It is actually. We like you guys wide.
LS Vision: Nah this is cap. The women who selected before is def just the insecurity of his value going up afterwards and making them feel insecure he’d cheat or leave. Any man who has went through a gym transformation, you can LITERALLY feel women treat you significantly different after.
Mason: Women generally like tall guys who have some (not crazy) muscle definition, and a little extra fat that bulks that out can actually augment that
We all have our own tastes, but this a pretty typical type.
I don’t know what there is to be mad about here.
For practical purposes, before beats after here. The before guy is already in ordinary, practical good shape. The after guy took things too far, and seems to know it except that he thinks it is good, which makes it worse.
Except one key special case?
Benjamin Ryan: People are going back and forth about whether women think the guy in the right is hot. But people have no idea how extreme the standards are for gay men. In gay culture, the man on the left is considered hopelessly fat. Many gay men have no reservations about informing such a man about his supposed corpulence being anathema.
I wrote about the rare study to examine the toxic qualities of gay culture for The Guardian.
I mean, of course there are hot guys who don’t know they’re hot, even more so than there are hot women who don’t know they’re hot.
Pandora: One surprising takeaway from Slutcon was that apparently there are hot guys who just don’t know they are hot? Guess it’s time to go objectify some more men.
Eneasz Brodski: If you grow up ugly you never really internalize that you are attractive after a glow-up. I still don’t believe it inside, and I hear I’m attractive to a fair percentage of women. Also makes me far more attracted to women w the same experience, but that may be a male universal.
Pandora: This problem seems even more pervasive than I thought.
Sparr: Hot in general, to the average viewer, or hot to you? You seem like someone who can probably tell the difference.
Pandora: I saw examples of guys being clueless about all three at once.
21 Kindness: The whole “men subsist on one compliment a decade thing” is kinda true lol.
Misha: it turns out being hot is not, in and of itself, very useful for men.
Sokoban Hero: No it’s useful.
Misha: I said not VERY useful.
Dissproportionately: I’ve seen men unhot themselves to women within minutes. I don’t think women can unhot themselves to men.
Being hot is in many ways a lot less valuable if you don’t know you are hot, because you don’t get the confidence and you don’t take advantage of opportunities or feel you’re good enough, but contra Misha I believe it is still very useful. There are even some advantages to not knowing, in that some of the behaviors that happen when someone knows they are hot are often effectively arrogant or entitled or demanding or selfish, none of which helps.
This link is almost certainly bait, but things in some spaces have gotten so insane that you can’t be sure people aren’t talking about 28-31 as a problematic age gap. What?
I mean, at minimum it’s good bait, it worked.
I’ve also seen some other examples that look a lot less like bait but still involve obviously totally fine gaps in both directions. As in, I’ve heard talk in places where it definitely wasn’t bait of 24 and 27 being radically different numbers, and I don’t understand why.
Well, maybe. Via Rolf Degen there is a meta-study.
The obvious question is whether this is a causal relationship, or whether it is primarily selection effects. You are on the dating apps for a reason.
Rolf Degen (quoting the study):
Meta-analysis: The use of dating apps is associated with poorer mental health.
Dating apps hold the promising reward of love but have been accused of using perverse incentive structures to profit from those who try to find it. We conducted the first systematic review and quantitative meta-analysis of studies examining average differences in the outcomes of dating app users and non-users.
Our results showed that dating app users had worse psychological health and well-being than dating app non-users across a variety of outcomes including depression, anxiety, affective dysregulation, loneliness, and psychological distress, although cross-sectional design limitations prevent causal interpretation. By aggregating findings from extant studies, we showed that in the nearly 17 years since dating apps have been on the market, users of these platforms have reported poorer psychological health and well-being than non-users.
There are several explanations for why dating app users may be struggling. The first is that dating apps are subject to selection effects, making the people who choose to use these platforms different from those who do not. People who are vulnerable to psychological health and well-being difficulties may prefer dating apps because they can avoid uncomfortable interactions, leading to negative patterns of reinforcement.
A second explanation involves exposure effects; that is, features such as gamification that may provide positive reinforcements that encourage problematic dating app use and keep people swiping.
The differences identified here could explain some of the challenges that users are likely to experience and be part of the reason they eventually burn out and quit dating apps altogether.
My guess is that dating apps are in important ways bad for mental health versus having better ways to find dates, and that sufficiently bad outcomes in terms of ability to find dates or find worthwhile dates is indeed worse for short term reported mental health than not trying. Whereas those who are successful get off the apps or never needed them in the first place.
What is the alternative? If the other choice is ‘do not try’ then for the median user the dating app is probably trading short term pain for chance of long term gain. If the other choice is ‘have uncomfortable real life interactions and make things happen’ and the app is blocking that instead of supplementing or leading into that, then the alternative is plausibly strictly better.
Certainly we could make app variations that are better for mental health controlling for outcomes, and also that give people better outcomes. Solving for the equilibrium, to get people to actually use those apps, is the difficult part, since people will value convenience and ease of use and low cost and avoiding trivial inconveniences dramatically more than they should, and if enough especially women effectively insist on the swiping experience it’s hard to escape from that.
I think this is importantly wrong for both e-girls and also VCs?
Anton: egirl dating takes are worthless for the same reason vc takes on how you should run your company are worthless; if you could do it you would just do it not talk about it
men in particular are truly better off without this kind of “help”
making up egirls in my head to get mad at
If she could be an E-Girl or she could date, what makes you think she would choose to date? What makes you think she isn’t also dating?
Similarly, if you could be a VC or a startup founder, it’s not that suspicious that you would choose VC. At this point in my life I would definitely prefer VC over founder. I don’t want to go through founder mode again. I am totally prepared to eat my words if I end up doing it anyway, and if I’m in then I’m in, but I don’t want to be in.
Division of labor, like dudes and also women, rocks. Matchmakers should be much more of a thing than they are. There is a profound market failure, a failure of the services to be good versions of themselves, or both.
I cannot in any way vouch for the effectiveness of Blaine Anderson’s matchmaking service. I can however vouch for her Twitter feed having consistently insightful and fun things to say. Her price range is ‘usually less than $50k’ and in exchange she goes out and sources to fit your particular criteria (which she will sometimes push back on).
You can also sign up (for free) to be a woman she reached out to for matches, on first principles being on these lists seems to be a good time investment?
There’s a lot of self-promotion, no question, but there are hard-to-fake signals that she is the real version of the thing in various ways, facing reality as it is, looking at the data and actually trying to get good results.
Also this one makes a good case:
Blaine Anderson: Underrated advantage of hiring a matchmaker, if you’re a single man:
• You sound cringe AF when you brag about yourself to women
• You sound amazing when I brag about you to women
One thing that blows my mind is she tells stories where the guy will say ‘get me a date with this specific micro-famous woman’ and she (at least sometimes) goes out and makes that happen. The guys asking this look damn good on paper, which no doubt is a lot of why this can sometimes work, but still, hot damn.
EigenGender: despite being very happily in a long term relationship im always very excited to read a dating doc. they’re some of the most vulnerable and genuine writing you can find and a window into another persons life. if you make fun of them you’re burning the commons and you should stop.
Stephen Fay: I like to read the date me docs, but I also am entertained by what Zizek has to say about them
Zizek (well okay actually Paula Rambles): Ah! You see, this miserable little document, this so-called date-me doc, is our era’s most honest pornography. It pretends to be romance, but what is it really? It is no longer the trembling hand on paper, the confession of desire. It is a spreadsheet of desire. “I am ready. I am six foot four. I have done the work.” What work? Love is precisely the place where work collapses into failure. You study and then you fail the exam.
And look at this language. “Highly agentic, emotionally warm.” Beautiful nonsense. Freedom, yes, but domesticated. Agency, yes, but pointing politely towards him. For Hegel, love is the risky collision of two freedoms. Here, there is no risk. She must arrive pre-formatted.
Then the farce reaches ecstasy. “If she does not appear, I will pursue single fatherhood.” Magnificent. Chance is canceled. Eros becomes procedure. The miracle of two gazes across a smoky room is replaced by paperwork and a receipt. The objet petit a is now a literal baby routed around the Other. And of course, the “monogamish” clause. Pure ideology. Fidelity with a footnote. Like Coke Zero: love without sugar, passion without calories. He wants the experience of devotion, but sterilized of danger.
The document offers no asylum from loneliness. It is loneliness, meticulously formatted, hyperlinked, and begging for comments. He does not whisper “I love you.” He says “I am prepared to love you, conditionally, pending review.”
That’s a funny post, and does an excellent job of mocking those who would make fun of date me docs and other actually intentional stances. Such magnificent flailing.
And thus, you have failed to look at the Date Me doc of Olga Yakimenko.
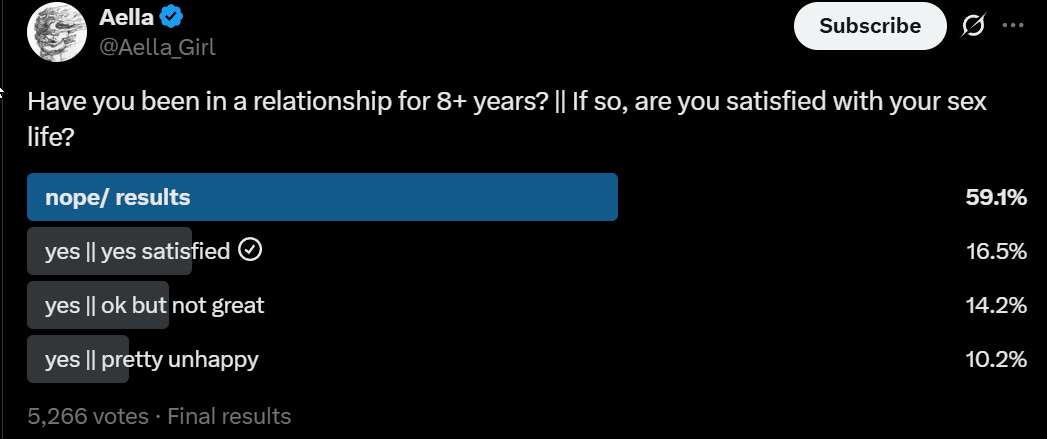
Here, in addition to the intended lede, we have at least 40% of respondents having been in a relationship for fully 8 years.
Aella: wow a whole 40% of people in long-term relationships are satisfied with their sex lives!
Critter: i imagine the numbers are worse for people not in long-term relationships
If anything these results seem potentially ‘too good,’ implying that couples are breaking up over this more than they probably should over the longer term.
One must also note that this is an Aella survey, so some of these relationships will be poly or open, but even accounting for that this says a lot. Selection effects are a lot of this, but that’s part of the point.
Perhaps you especially don’t appreciate marriage.
Raffi Grinberg writes that marriage is sexy, both figuratively that married couples are happier and make more money and have more kids and die less often and all that, and also that they have more sex (even if you only count with each other). And that the lifetime divorce rate is actually only 30% not 50%, average age of marriage is 29 and average first child is 28, despite the implicit cultural message that those numbers are in the 30s.
And yet he says Hollywood is sending us the opposite message. To which I’d say, sometimes, but I wouldn’t oversell this. Yes, in the How I Met Your Mother episode he talks about Barney keeps making fun of Marshall for being married, but the show clearly thinks that Marshall marrying Lily is sexy and awesome and great for both of them throughout and that Barney is ultimately wrong, and also the whole show is Ted trying to meet his wife and mother of his children.
Here’s another backdoor ‘are you in a relationship’ poll, 78% of monogamous heterosexual men reported having a partner for longer than a year.
Alice Playing: monogamous hetero men with 1+ year-long partners: if you could have an affair with a woman of your liking, with absolute, 100% certainty that your partner would never find out, would you do it?
On the question itself, it’s not actually possible, since you’ll know and you can’t be sure you won’t tell them, and you’ll almost certainly act differently even if they never suspect or figure it out. One could even say ‘the only way to have 100% certainty they’ll never find out is if they’re dead, so absolutely not.’
Literal ‘any woman you wanted’ with zero risk of discovery is a stupidly tempting offer. If you treat this in the spirit it was presumably intended, instead, and everyone was being fully honest including with themselves and fully understood what was on offer (as in literally whoever you’d most want), presumably the ratio would be a lot higher.
Unless, of course, the way you know your partner will never find out is that your partner (or you and the woman you’d have the affair with) would be dead, in which case yeah bad deal, but that’s presumably not this meant. mnnn oo
How do we know this? Well, one big data point is this next poll.
Um, guys, are almost none of you in a monogamous relationship? And even if you are single there’s also the issue of risking the friendship. What are you all thinking?
Alice Is Playing: men attracted to women: how many of your female friends would you have a one-night stand with, if they offered?
Only 14% of men attracted to women answering this didn’t have at least one female friend they would have a one night stand with? Presumably many of the others don’t have the right female friend. Which means substantially more than 86% of them are not, for the most important practical purpose, in a monogamous relationship?
Remember that other poll from Aella above, that showed at least 40% of people were in 8+ year relationships? And the one from Alice that 78% of herero men were in a 1+ year nominally monogamous relationship? Rut roh.
Then on top of that, a majority are willing to do this with a majority of their female friends, not only that one they have that crush on.
It doesn’t mean these people don’t think they’re in relationships. As we’ve seen, they very much do think this. They might even be right. But don’t tempt them.
Paper reminds us there is a 34 points gap (+34 versus +0) in net happiness for married versus unmarried people, with cohabitation only worth 10 points, and analyzes how this premium varies (slightly) by demographics.
As the paper readily admits this tells us essentially nothing about what makes someone happy, because the whole thing is unfixibly confounded to hell. Happier, healthier and more successful people have an easier time getting married, and being unhappy leads to divorce. Both effects are epic in size.
We do know the overall situation over a 50+ year time horizon is not good news, because while marrieds are slightly happier, the unmarrieds are somewhat less happy and more importantly are a larger percent of the population.
Beyond that, I don’t know what to do with all these graphs or how to cash it out in useful advice. One might say ‘be the type of person who gets married,’ perhaps.
As usual, never stop Robin Hansoning.
Robin Hanson: You know how in romance stories the main characters hope to find a special relation, better than that which the ordinary people around them settle for? Your relations will probably be more like those of the ordinary folks, less like those of special main characters.
This has to be true, because math.
It’s less true than it appears, because the relations of ‘main characters’ feel special to them the same as everyone else’s feel special. You could totally make a romantic comedy based on what I experienced, and you could also totally have me as a background character in someone else’s romantic comedy, although probably I’d be in a different genre entirely.
To you, it will feel more like that of the special main characters, except that you don’t need to have a false crisis in the third act.
Don’t be whoever Casy Means is being here. Or do, it’s not like it did that much harm, as long as you don’t expect any of it to do anything.
We wish everyone involved the best.
Aella: it’s really unfortunate that having an insane ex turns you personally into a greater liability for others
Grimes: hahaha [trauma laughter].
Aella: 🙁 i wasnt thinking about u when i wrote the tweet but also :(.
Try harder.
A new app lets you pay to crash someone’s wedding and be a legit guest, cost is about $100-$150 per guest. This seems low, given the cost to have a wedding worth crashing, and given you get a full meal, plus buffet and open bar, a unique experience and a reasonable amount of opportunity.
What Jacob learned about sex at the rationalist bloggers’ conference, essentially that with zero integrity you get fuckbois and pickup artists, and when you do the opposite and get sufficiently high integrity and optimize for trust and honesty way above normal levels you get something magical and suddenly many good things are possible.
Here’s another fun bit:
Jacob: My friend “Standard Deviant” gave a talk titled “How I’ve had more sex.” He described the “escalator”: starting a conversation, exchanging compliments, light touch on the arm, etc. The important thing isn’t to rush up the escalator, my friend said, but to move together in synchrony whether you’re taking a step up or a step down.
When women show interest in casual sex, he often asks: do you do this sort of thing often? If they don’t, he often forgoes the opportunity out of an excess of caution.
Afterwards, more women wanted to have sex with him. I joked that women want to have sex not with the tall guy, hot guy, or the famous guy, but with the Schelling point guy.
Someone pointed out that tall, hot, and famous are the usual Schelling points.