TikTok deal is done; Trump wants praise while users fear MAGA tweaks
US will soon retrain TikTok
“I am so happy”: Trump closes deal that hands TikTok US to his allies.
The TikTok deal is done, and Donald Trump is claiming a win, although it remains unclear if the joint venture he arranged with ByteDance and the Chinese government actually resolves Congress’ national security concerns.
In a press release Thursday, TikTok announced the “TikTok USDS Joint Venture LLC,” an entity established to keep TikTok operating in the US.
Giving Americans majority ownership, ByteDance retains 19.9 percent of the joint venture, the release said, which has been valued at $14 billion. Three managing investors—Silver Lake, Oracle, and MGX—each hold 15 percent, while other investors, including Dell Technologies CEO Michael Dell’s investment firm, Dell Family Office, hold smaller, undisclosed stakes.
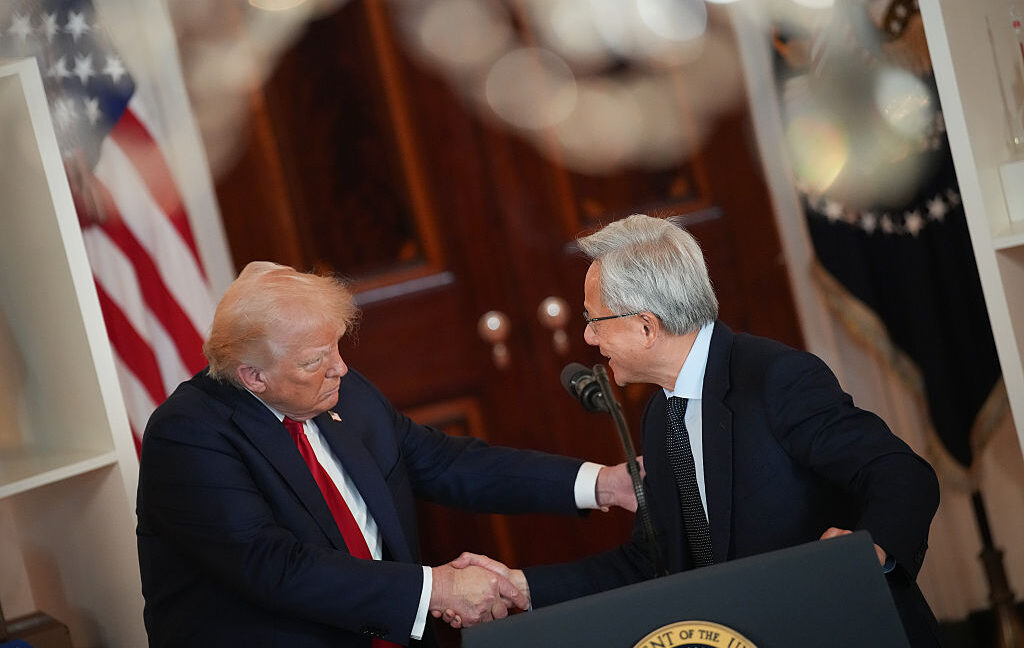
Americans will also have majority control over the joint venture’s seven-member board. TikTok CEO Shou Chew holds ByteDance’s only seat. Finalizing the deal was a “great move,” Chew told TikTok employees in an internal memo, The New York Times reported.
Two former TikTok employees will lead the joint venture. Adam Presser, who previously served as TikTok’s global head of Operations and Trust & Safety, has been named CEO. And Kim Farrell, TikTok’s former global head of Business Operations Protection, will serve as chief security officer.
Trump has claimed the deal meets requirements for “qualified divestiture” to avoid a TikTok ban otherwise required under the Protecting Americans from Foreign Adversary Controlled Applications Act. However, questions remain, as lawmakers have not yet analyzed the terms of the deal to determine whether that’s true.
The law requires the divestment “to end any ‘operational relationship’ between ByteDance and TikTok in the United States,” critics told the NYT. That could be a problem, since TikTok’s release makes it clear that ByteDance will maintain some control over the TikTok US app’s operations.
For example, while the US owners will retrain the algorithm and manage data security, ByteDance owns the algorithm and “will manage global product interoperability and certain commercial activities, including e-commerce, advertising, and marketing.” The Trump administration seemingly agreed to these terms to ensure that the US TikTok isn’t cut off from the rest of the world on the app.
“Interoperability enables the Joint Venture to provide US users with a global TikTok experience, ensuring US creators can be discovered and businesses can operate on a global scale,” the release said.
Perhaps also concerning to Congress, Slate noted, while ByteDance may be a minority owner, it remains the largest individual shareholder.
Michael Sobolik, an expert on US-China policy and senior fellow at the right-leaning think tank the Hudson Institute, told the NYT that the Trump administration “may have saved TikTok, but the national security concerns are still going to continue.”
Some critics, including Republicans, have vowed to scrutinize the deal.
On Thursday, Senator Edward Markey (D-Mass.) complained that the White House had repeatedly denied requests for information about the deal. They’ve provided “virtually no details about this agreement, including whether TikTok’s algorithm is truly free of Chinese influence,” Markey said.
“This lack of transparency reeks,” Markey said. “Congress has a responsibility to investigate this deal, demand transparency, and ensure that any arrangement truly protects national security while keeping TikTok online.”
In December, Representative John Moolenaar (R-Mich.), chair of the House Select Committee on China, said that he wants to hold a hearing with TikTok leadership to discuss how the deal addresses national security concerns. On Thursday, Moolenaar said he “has two specific questions for TikTok’s new American owners,” Punchbowl News reported.
“Can we ensure that the algorithm is not influenced by the Chinese Communist Party?” Moolenaar said. “And two, can we ensure that the data of Americans is secure?”
Moolenaar may be satisfied by the terms, as the NYT suggested that China hawks in Washington appeared to trust that Trump’s arrangement is a qualified divestiture. TikTok’s release said that Oracle will protect US user data in a secure US cloud data environment that will regularly be audited by third-party cybersecurity experts. The algorithm will be licensed from ByteDance and retrained on US user data, the release said, and Vice President JD Vance has confirmed that the joint venture “will have control over how the algorithm pushes content to users.”
Last September, a spokesperson for the House China Committee told Politico that “any agreement must comply with the historic bipartisan law passed last year to protect the American people, including the complete divestment of ByteDance control and a fully decoupled algorithm.”
Users brace for MAGA tweaks to algorithm
“I am so happy to have helped in saving TikTok!” Trump said on Truth Social after the deal was finalized. “It will now be owned by a group of Great American Patriots and Investors, the Biggest in the World, and will be an important Voice.”
However, it’s unclear to TikTokers how the app might change as Trump allies take control of the addictive algorithm that drew millions to the app. Lawmakers had feared the Chinese Communist Party could influence the algorithm to target US users with propaganda, and Trump’s deal was supposed to mitigate that.
Not only do critics worry that if ByteDance maintains ownership of the algorithm, it could allow the company to continue to influence content, but there is now concern that the app’s recommendations could take a right-leaning slant under US control.
Trump has already said that he’d like to see TikTok go “100 percent MAGA,” and his allies will now be in charge of “deciding which posts to leave up and which to take down,” the NYT noted. Anupam Chander, a law and technology professor at Georgetown University, told the NYT that the TikTok deal offered Trump and his allies “more theoretical room for one side’s views to get a greater airing.”
“My worry all along is that we may have traded fears of foreign propaganda for the reality of domestic propaganda,” Chander said.
For business owners who rely on the app, there’s also the potential that the app could be glitchy after US owners start porting data and retraining the algorithm.
Trump clearly hopes the deal will endear him to TikTok users. He sought praise on Truth Social, writing, “I only hope that long into the future I will be remembered by those who use and love TikTok.”
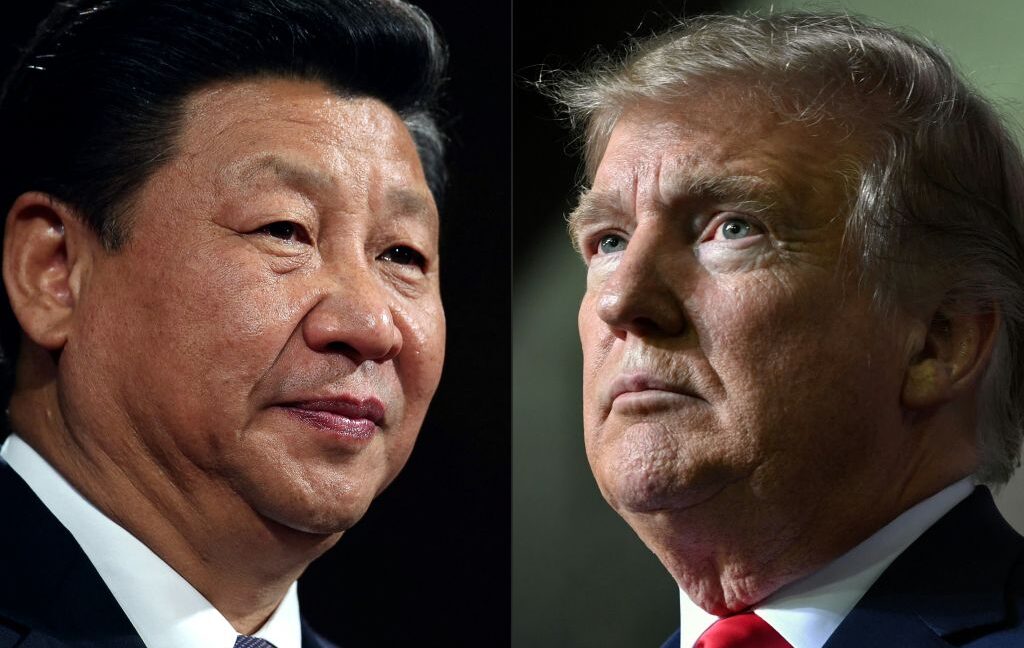
China “played” Trump, expert says
So far, the Chinese government has not commented on the deal’s finalization, but Trump thanked Chinese President Xi Jinping in his Truth Social post “for working with us and, ultimately, approving the Deal.”
“He could have gone the other way, but didn’t, and is appreciated for his decision,” Trump said.
Experts have suggested that China benefits from the deal by keeping the most lucrative part of TikTok while the world watches it export its technology to the US.
When Trump first announced the deal in September, critics immediately attacked him for letting China keep the algorithm. One US advisor close to the deal told the Financial Times that “Trump always chickens out,” noting that “after all this, China keeps the algorithm.”
On Thursday, Sobolik told Politico that Trump “got played” by Xi after taking “terrible advice from his staff” during trade negotiations that some critics said gave China the upper hand.
Trump sees things differently, writing on Truth Social that the TikTok deal came to “a very dramatic, final, and beautiful conclusion.”
Whether the deal is “dramatic,” “final,” or “beautiful” depends on who you ask, though, as it could face legal challenges and disrupt TikTok’s beloved content feeds. The NYT suggested that the deal took so long to finalize that TikTokers don’t even care anymore, while several outlets noted that Trump’s deal is very close to the Project Texas arrangement that Joe Biden pushed until it was deemed inadequate to address national security risks.
Through Project Texas, Oracle was supposed to oversee TikTok US user data, auditing for security risks while ByteDance controlled the code. The joint venture’s “USDS” “coinage even originated from Project Texas,” Slate noted.
Lindsay Gorman, a former senior advisor in the Biden administration, told NYT that “we’ve gone round and round and ended up not too far from where we started.”
TikTok deal is done; Trump wants praise while users fear MAGA tweaks Read More »