Never-before-seen data wiper may have been used by Russia against Ukraine
KREMLIN FINGERPRINTS —
AcidRain, discovered in 2022, is tied to AcidPour. Both are attributed to Russia.

Getty Images
Researchers have unearthed never-before-seen wiper malware tied to the Kremlin and an operation two years ago that took out more than 10,000 satellite modems located mainly in Ukraine on the eve of Russia’s invasion of its neighboring country.
AcidPour, as researchers from security firm Sentinel One have named the new malware, has stark similarities to AcidRain, a wiper discovered in March 2022 that Viasat has confirmed was used in the attack on its modems earlier that month. Wipers are malicious applications designed to destroy stored data or render devices inoperable. Viasat said AcidRain was installed on more than 10,000 Eutelsat KA-SAT modems used by the broadband provider seven days prior to the March 2022 discovery of the wiper. AcidRain was installed on the devices after attackers gained access to the company’s private network.
Sentinel One, which also discovered AcidRain, said at the time that the earlier wiper had enough technical overlaps with malware the US government attributed to the Russian government in 2018 to make it likely that AcidRain and the 2018 malware, known as VPNFilter, were closely linked to the same team of developers. In turn, Sentinel One’s report Thursday noting the similarities between AcidRain and AcidPour provides evidence that AcidPour was also created by developers working on behalf of the Kremlin.
Technical similarities include:
- Use of the same reboot mechanism
- The exact logic of recursive directory wiping
- The same IOCTL-based wiping mechanism.
AcidPour also shares programming similarities with another piece of malware attributed to Sandworm: CaddyWiper, which was used against various targets in Ukraine.
“AcidPour is programmed in C without relying on statically compiled libraries or imports,” Thursday’s report noted. “Most functionality is implemented via direct syscalls, many called through the use of inline assembly and opcodes.” Developers of CaddyWiper used the same approach.
Bolstering the theory that AcidPour was created by the same Russian threat group behind previous attacks on Ukraine, a representative with Ukraine’s State Service of Special Communications and Information Protection told Cyberscoop that AcidPour was linked to UAC-0165, a splinter group associated with Sandworm (a much larger threat group run by Russia’s military intelligence unit, GRU). Representatives with the State Service of Special Communications and Information Protection of Ukraine didn’t immediately answer an email seeking comment for this post.
Sandworm has a long history of targeting Ukrainian critical infrastructure. Ukrainian officials said last September that UAC-0165 regularly props up fake hacktivist personas to take credit for attacks the group carries out.
Sentinel One researchers Juan Andrés Guerrero-Saade and Tom Hegel went on to speculate that AcidPour was used to disrupt multiple Ukrainian telecommunications networks, which have been down since March 13, three days before the researchers discovered the new wiper. They point to statements a persona known as SolntsepekZ made on Telegram that took responsibility for hacks that took out Triangulum, a consortium providing telephone and Internet services under the Triacom brand, and Misto TV.
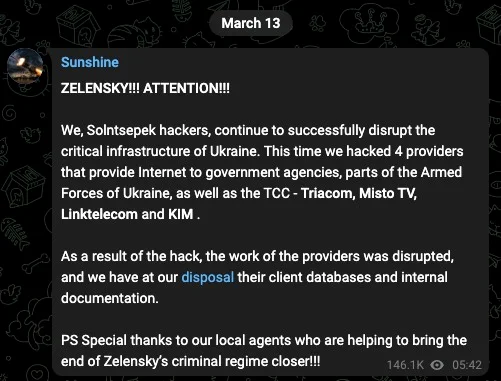
A message a persona known as SolntsepekZ posted to Telegram.
Sentinel One
The weeklong outage has been confirmed anecdotally and by Network intelligence firm Kentik and content delivery network Cloudflare, with the latter indicating the sites remained inoperable at the time this post went live on Ars. As of Thursday afternoon California time, Misto-TV’s website displayed the following network outage notice:
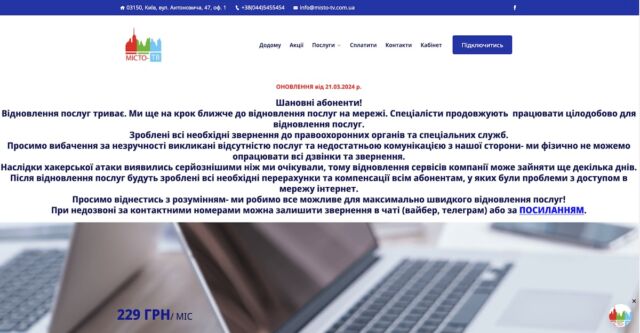
Enlarge / Outage notice displayed on Misto-TV’s website.
“At this time, we cannot confirm that AcidPour was used to disrupt these ISPs,” Guerrero-Saade and Hegel wrote in Thursday’s post. “The longevity of the disruption suggests a more complex attack than a simple DDoS or nuisance disruption. AcidPour, uploaded 3 days after this disruption started, would fit the bill for the requisite toolkit. If that’s the case, it could serve as another link between this hacktivist persona and specific GRU operations.”
The researchers added:
“The transition from AcidRain to AcidPour, with its expanded capabilities, underscores the strategic intent to inflict significant operational impact. This progression reveals not only a refinement in the technical capabilities of these threat actors but also their calculated approach to select targets that maximize follow-on effects, disrupting critical infrastructure and communications.”
Never-before-seen data wiper may have been used by Russia against Ukraine Read More »