As ABL Space departs launch, the 1-ton rocket wars have a clear winner
“Take a look around,” Piemont wrote. “US rockets fly every couple of days, with perfect success. It’s revolutionary. While there is still a need for more providers in certain market segments, those opportunities are decreasing. To succeed in such a demanding effort as scaling up an orbital launch program, you need deep motivation around your mission and potential impact, from many stakeholders. As the launch market matured, those motivations thinned and our path to making a big contribution as a commercial launch company narrowed considerably.”
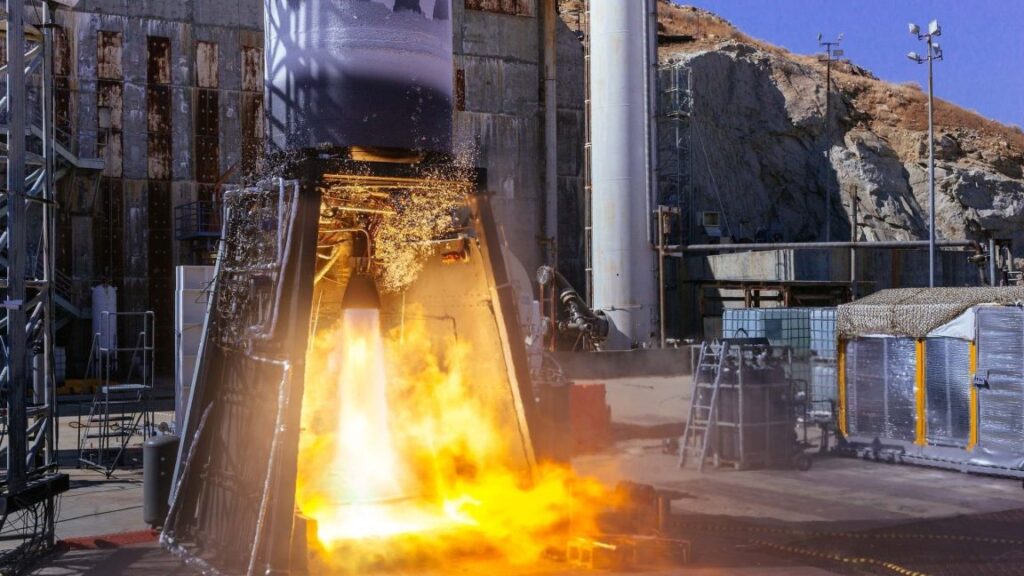
Over the last half decade or so, three US companies have credibly vied to develop rockets in the 1-ton class in terms of lift capacity. ABL has been competing alongside Relativity Space and Firefly to bring its rockets to market. ABL never took off. In March 2023, Relativity reached space with the Terran 1 rocket, but, due to second-stage issues, failed to reach orbit. Within weeks, Relativity announced it was shifting its focus to a medium-lift rocket, Terran R. Since then, the California-based launch company has moved along, but there are persistent rumors that it faces a cash crunch.
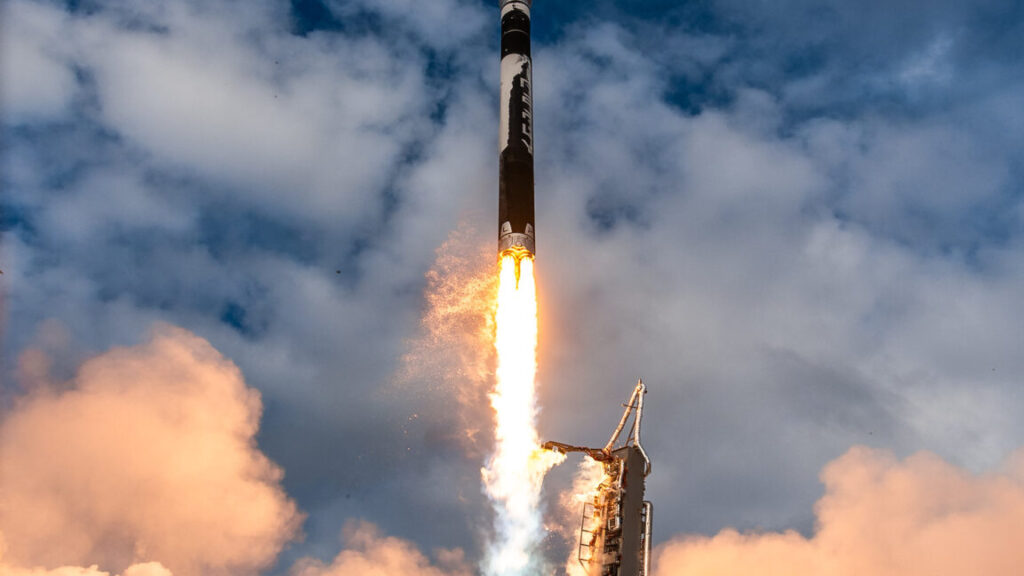
Of the three, only Firefly has enjoyed success. The company’s Alpha rocket has reached orbit on multiple occasions, and just this week Firefly announced that it completed a $175 million Series D fundraising round, resulting in a valuation of more than $2 billion. The 1-ton rocket wars are over: Firefly has won.
Focusing on defense
Just as Relativity pivoted away from this class of rocket, ABL will now also shift its focus—this time in an even more radical direction.
US Defense spending on missile production and defense has skyrocketed since Russia’s invasion of Ukraine in 2022, and ABL will now seek to tap into this potentially lucrative market.
“We have made the decision to focus our efforts on national defense, and specifically on missile defense technologies,” Piemont said. “We’ll have more to share soon on our roadmap and traction in this area. For now, suffice to say we see considerable opportunity to leverage RS1, GS0, the E2 engine, and the rest of the technology we’ve developed to date to enable a new type of research effort around missile defense technologies.”
As ABL Space departs launch, the 1-ton rocket wars have a clear winner Read More »