Ghost forests are growing as sea levels rise
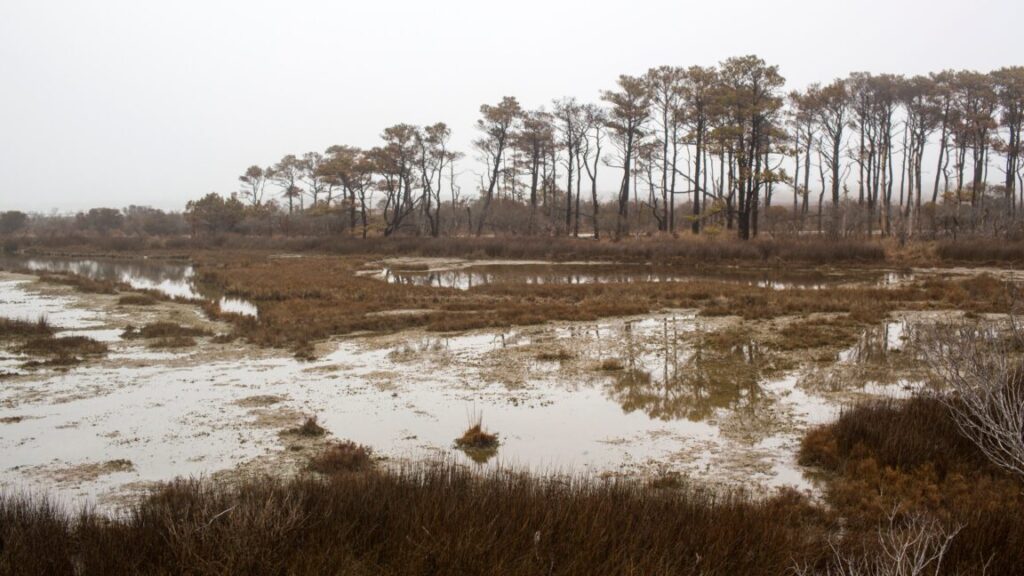
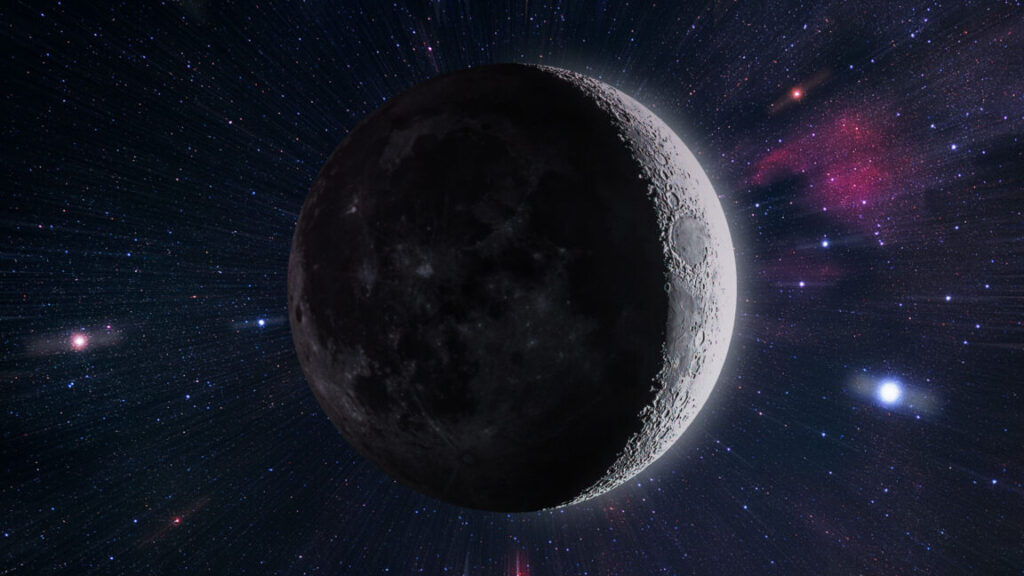
Like giant bones planted in the earth, clusters of tree trunks, stripped clean of bark, are appearing along the Chesapeake Bay on the United States’ mid-Atlantic coast. They are ghost forests: the haunting remains of what were once stands of cedar and pine. Since the late 19th century, an ever-widening swath of these trees have died along the shore. And they won’t be growing back.
These arboreal graveyards are showing up in places where the land slopes gently into the ocean and where salty water increasingly encroaches. Along the United States’ East Coast, in pockets of the West Coast, and elsewhere, saltier soils have killed hundreds of thousands of acres of trees, leaving behind woody skeletons typically surrounded by marsh.
What happens next? That depends. As these dead forests transition, some will become marshes that maintain vital ecosystem services, such as buffering against storms and storing carbon. Others may become home to invasive plants or support no plant life at all—and the ecosystem services will be lost. Researchers are working to understand how this growing shift toward marshes and ghost forests will, on balance, affect coastal ecosystems.
Many of the ghost forests are a consequence of sea level rise, says coastal ecologist Keryn Gedan of George Washington University in Washington, DC, coauthor of an article on the salinization of coastal ecosystems in the 2025 Annual Review of Marine Science. Rising sea levels can bring more intense storm surges that flood saltwater over the top of soil. Drought and sea level rise can shift the groundwater table along the coast, allowing saltwater to journey farther inland, beneath the forest floor. Trees, deprived of fresh water, are stressed as salt accumulates.
Yet the transition from living forest to marsh isn’t necessarily a tragedy, Gedan says. Marshes are important features of coastal ecosystems, too. And the shift from forest to marsh has happened throughout periods of sea level rise in the past, says Marcelo Ardón, an ecosystem ecologist and biogeochemist at North Carolina State University in Raleigh.
“You would think of these forests and marshes kind of dancing together up and down the coast,” he says.
Marshes provide many ecosystem benefits. They are habitats for birds and crustaceans, such as salt marsh sparrows, marsh wrens, crabs, and mussels. They are also a niche for native salt-tolerant plants, like rushes and certain grasses, which provide food and shelter for animals.
Ghost forests are growing as sea levels rise Read More »