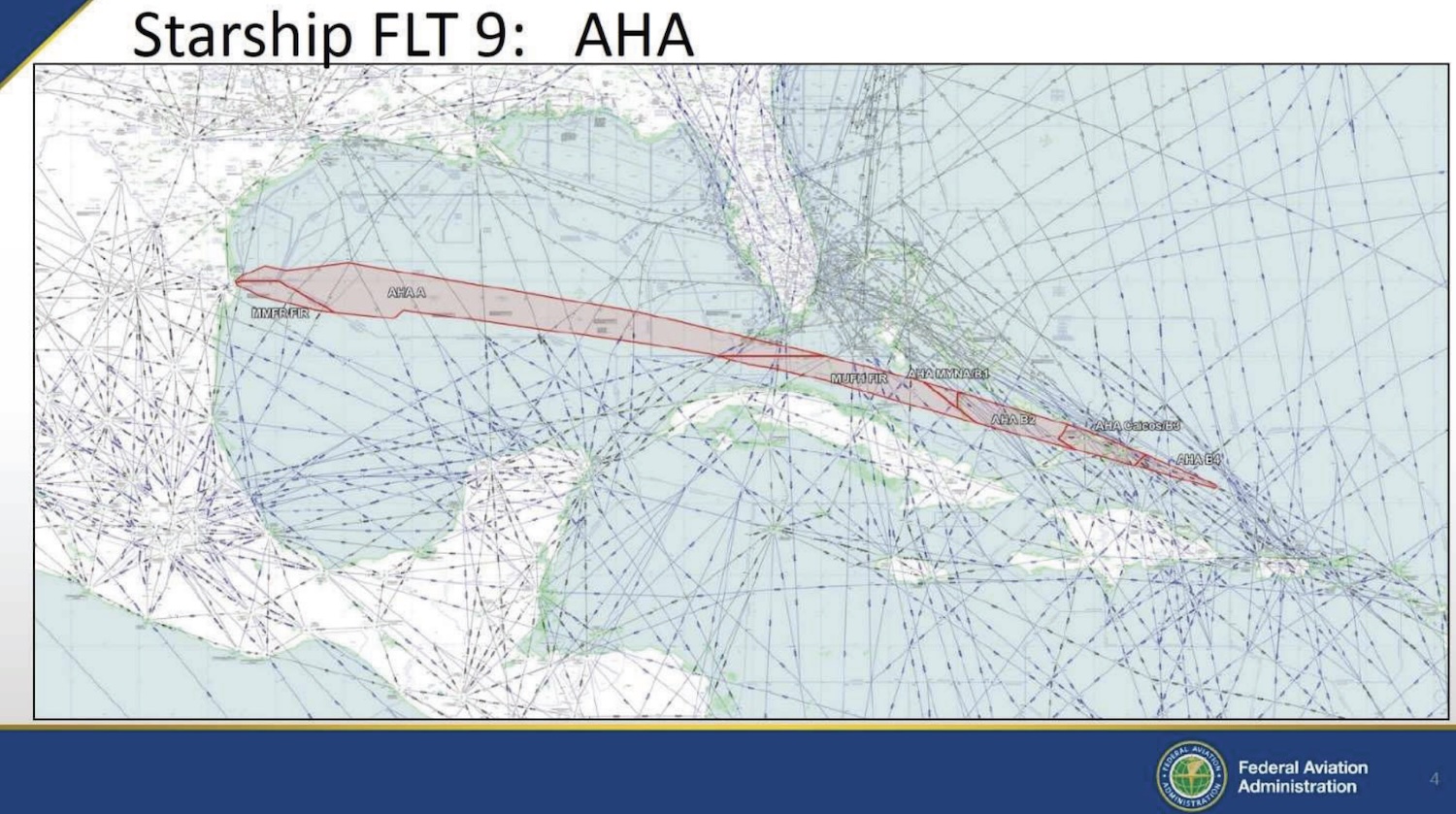
Have we finally solved mystery of magnetic moon rocks?
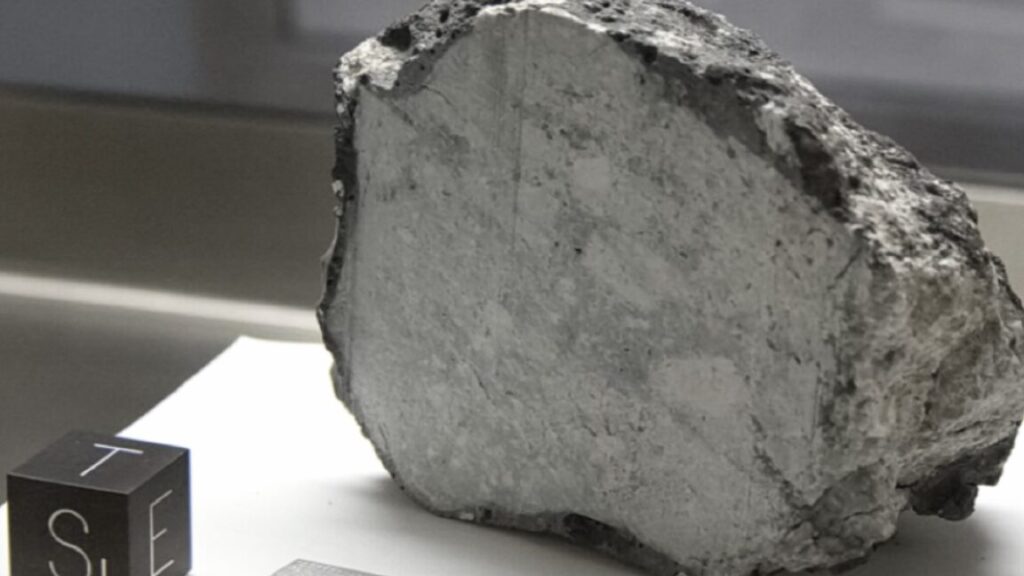
NASA’s Apollo missions brought back moon rock samples for scientists to study. We’ve learned a great deal over the ensuing decades, but one enduring mystery remains. Many of those lunar samples show signs of exposure to strong magnetic fields comparable to Earth’s, yet the Moon doesn’t have such a field today. So, how did the moon rocks get their magnetism?
There have been many attempts to explain this anomaly. The latest comes from MIT scientists, who argue in a new paper published in the journal Science Advances that a large asteroid impact briefly boosted the Moon’s early weak magnetic field—and that this spike is what is recorded in some lunar samples.
Evidence gleaned from orbiting spacecraft observations, as well as results announced earlier this year from China’s Chang’e 5 and Chang’e 6 missions, is largely consistent with the existence of at least a weak magnetic field on the early Moon. But where did this field come from? These usually form in planetary bodies as a result of a dynamo, in which molten metals in the core start to convect thanks to slowly dissipating heat. The problem is that the early Moon’s small core had a mantle that wasn’t much cooler than its core, so there would not have been significant convection to produce a sufficiently strong dynamo.
There have been proposed hypotheses as to how the Moon could have developed a core dynamo. For instance, a 2022 analysis suggested that in the first billion years, when the Moon was covered in molten rock, giant rocks formed as the magma cooled and solidified. Denser minerals sank to the core while lighter ones formed a crust.
Over time, the authors argued, a titanium layer crystallized just beneath the surface, and because it was denser than lighter minerals just beneath, that layer eventually broke into small blobs and sank through the mantle (gravitational overturn). The temperature difference between the cooler sinking rocks and the hotter core generated convection, creating intermittently strong magnetic fields—thus explaining why some rocks have that magnetic signature and others don’t.
Or perhaps there is no need for the presence of a dynamo-driven magnetic field at all. For instance, the authors of a 2021 study thought earlier analyses of lunar samples may have been altered during the process. They re-examined samples from the 1972 Apollo 16 mission using CO2 lasers to heat them, thus avoiding any alteration of the magnetic carriers. They concluded that any magnetic signatures in those samples could be explained by the impact of meteorites or comets hitting the Moon.
Have we finally solved mystery of magnetic moon rocks? Read More »