Runaway black hole mergers may have built supermassive black holes
The researchers used cosmological simulations to recreate the first 700 million years of cosmic history, focusing on the formation of a single dwarf galaxy. In their virtual galaxy, waves of stars were born in short, explosive bursts as cold gas clouds collapsed inside a dark matter halo. Instead of a single starburst episode followed by a steady drizzle of star formation as Garcia expected, there were two major rounds of stellar birth. Whole swarms of stars flared to life like Christmas tree lights.
“The early Universe was an incredibly crowded place,” Garcia said. “Gas clouds were denser, stars formed faster, and in those environments, it’s natural for gravity to gather stars into these tightly bound systems.”
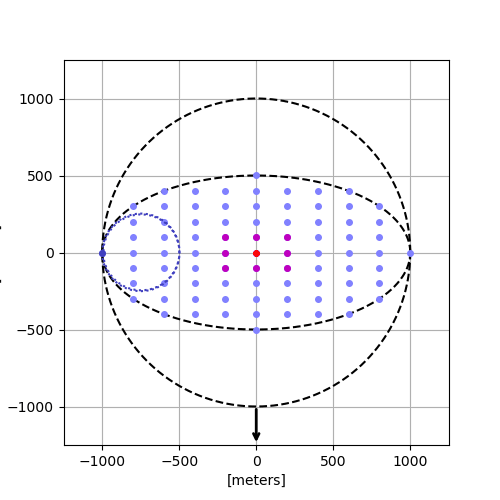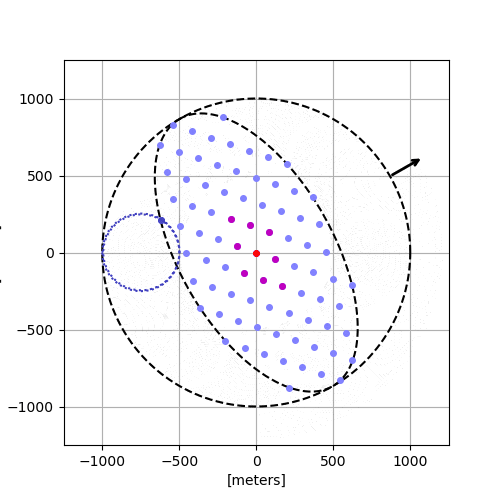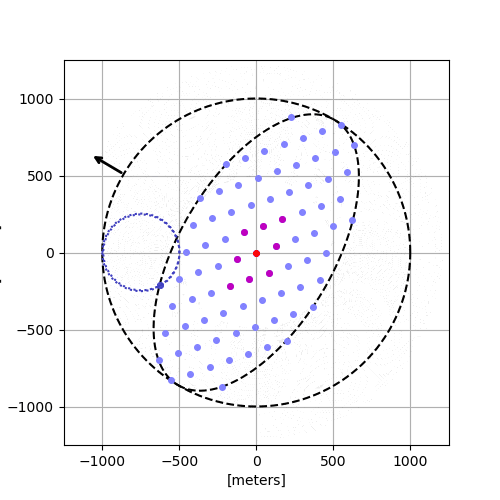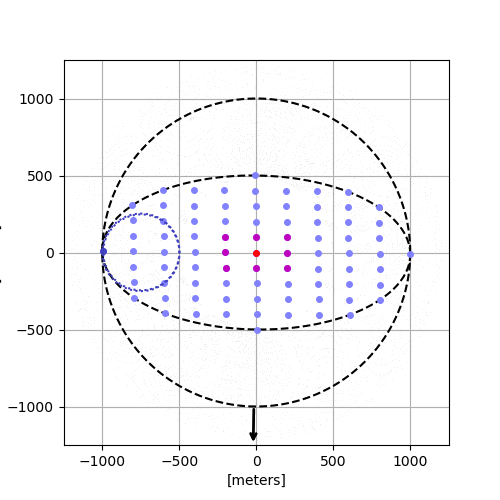
Those clusters started out scattered around the galaxy but fell in toward the center like water swirling down a drain. Once there, they merged to create one megacluster, called a nuclear star cluster (so named because it lies at the nucleus of the galaxy). The young galactic heart shone with the light of a million suns and may have set the stage for a supermassive black hole to form.
A simulation of the formation of the super-dense star clusters.
A seemingly simple tweak was needed to make the simulation more precise than previous ones. “Most simulations simplify things to make calculations more practical, but then you sacrifice realism,” Garcia said. “We used an improved model that allowed star formation to vary depending on local conditions rather than just go at a constant rate like with previous models.”
Using the University of Maryland’s supercomputing facility Zaratan, Garcia accomplished in six months what would have taken 12 years on a MacBook.
Some clouds converted as much as 80 percent of their gas into stars—a ferocious rate compared to the 2 percent typically seen in nearby galaxies today. The clouds sparkled to life, becoming clusters of newborn stars held together by their mutual gravity and lighting a new pathway for supermassive black holes to form extremely early in the Universe.
Chicken or egg?
Most galaxies, including our own, are anchored by a nuclear star cluster nestled around a supermassive black hole. But the connection between the two has been a bit murky—did the monster black hole form and then draw stars close, or did the cluster itself give rise to the black hole?
Runaway black hole mergers may have built supermassive black holes Read More »