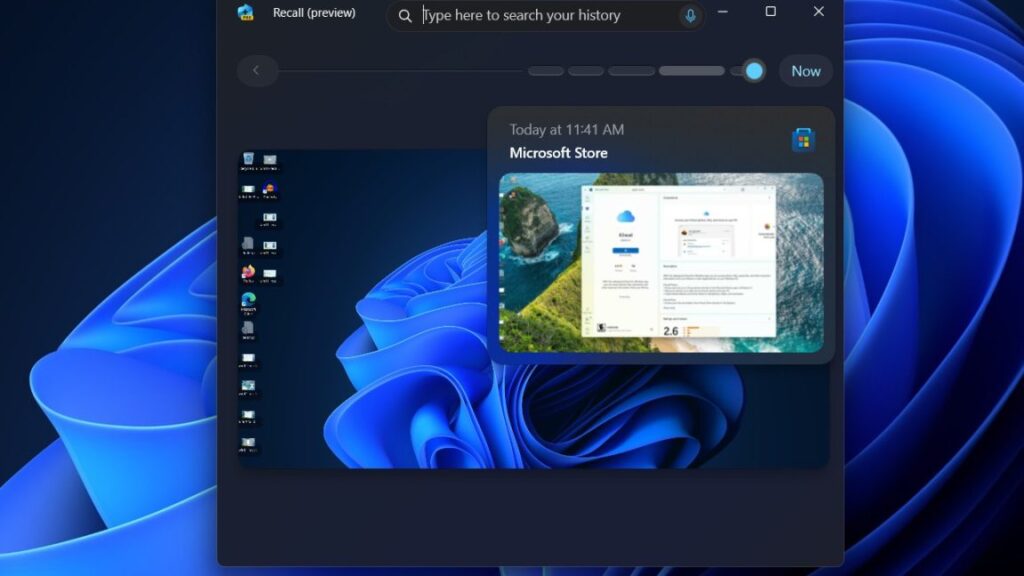
“Microsoft has simply given us no other option,” Signal says as it blocks Windows Recall
But the changes go only so far in limiting the risks Recall poses. As I pointed out, when Recall is turned on, it indexes Zoom meetings, emails, photos, medical conditions, and—yes—Signal conversations, not just with the user, but anyone interacting with that user, without their knowledge or consent.
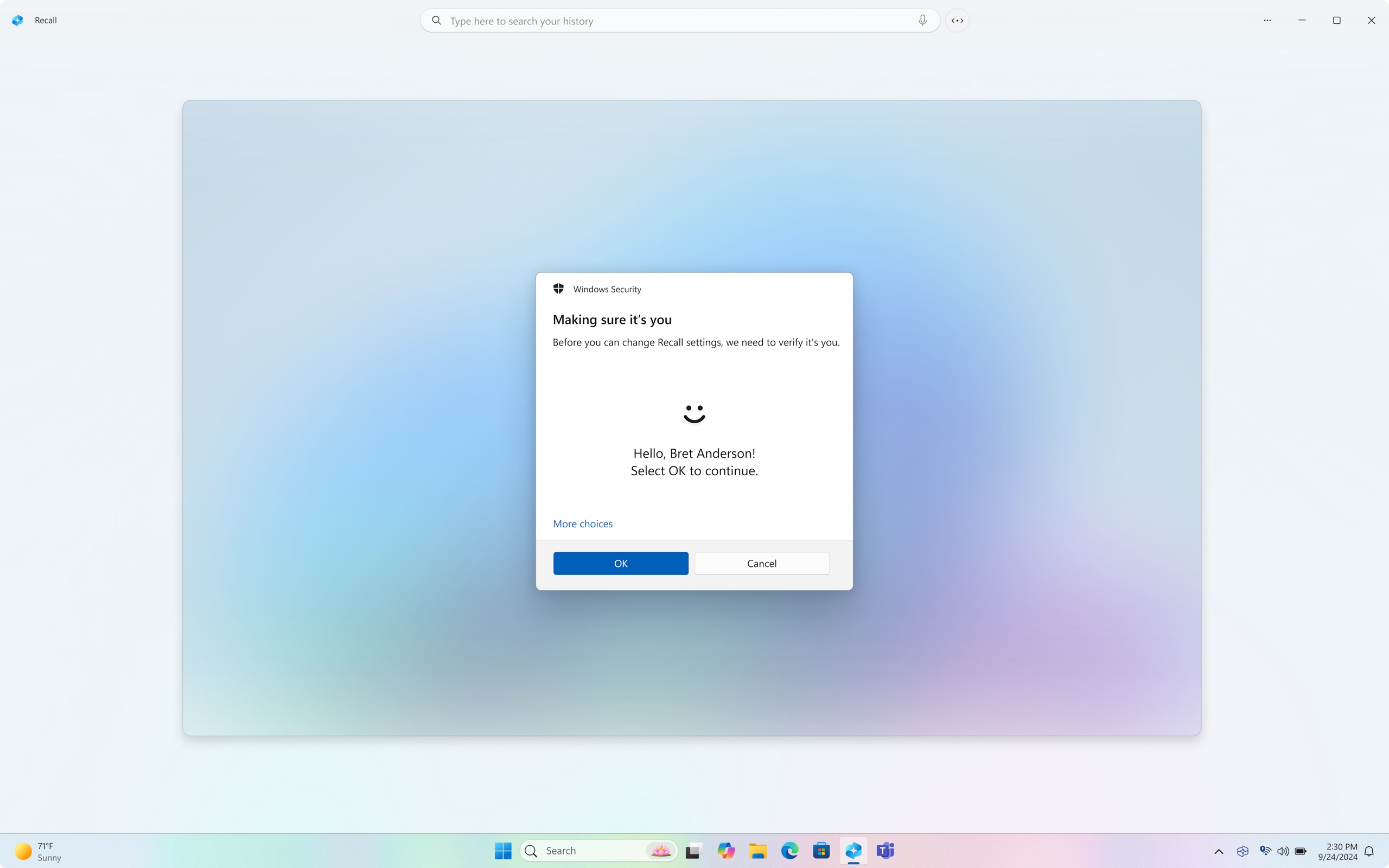
Researcher Kevin Beaumont performed his own deep-dive analysis that also found that some of the new controls were lacking. For instance, Recall continued to screenshot his payment card details. It also decrypted the database with a simple fingerprint scan or PIN. And it’s unclear whether the type of sophisticated malware that routinely infects consumer and enterprise Windows users will be able to decrypt encrypted database contents.
And as Cunningham also noted, Beaumont found that Microsoft still provided no means for developers to prevent content displayed in their apps from being indexed. That left Signal developers at a disadvantage, so they had to get creative.
With no API for blocking Recall in the Windows Desktop version, Signal is instead invoking an API Microsoft provides for protecting copyrighted material. App developers can turn on the DRM setting to prevent Windows from taking screenshots of copyrighted content displayed in the app. Signal is now repurposing the API to add an extra layer of privacy.
“We hope that the AI teams building systems like Recall will think through these implications more carefully in the future,” Signal wrote Wednesday. “Apps like Signal shouldn’t have to implement ‘one weird trick’ in order to maintain the privacy and integrity of their services without proper developer tools. People who care about privacy shouldn’t be forced to sacrifice accessibility upon the altar of AI aspirations either.”
Signal’s move will lessen the chances of Recall permanently indexing private messages, but it also has its limits. The measure only provides protection when all parties to a chat—at least those using the Windows Desktop version—haven’t changed the default settings.
Microsoft officials didn’t immediately respond to an email asking why Windows provides developers with no granular control over Recall and whether the company has plans to add any.
“Microsoft has simply given us no other option,” Signal says as it blocks Windows Recall Read More »