Workers report watching Ray-Ban Meta-shot footage of people using the bathroom
Meta accused of “concealing the facts” about smart glass users’ privacy.
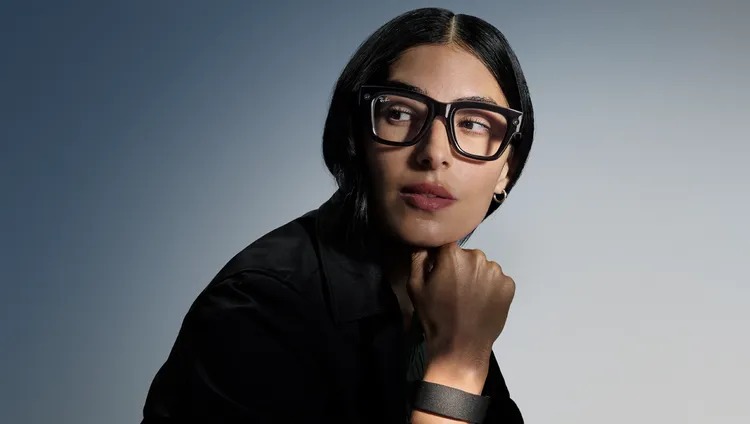
A marketing image for Ray-Ban Meta smart glasses. Credit: Meta
Meta’s approach to user privacy is under renewed scrutiny following a Swedish report that employees of a Meta subcontractor have watched footage captured by Ray-Ban Meta smart glasses showing sensitive user content.
The workers reportedly work for Kenya-headquartered Sama and provide data annotation for Ray-Ban Metas.
The February report, a collaboration from Swedish newspapers Svenska Dagbladet, Göteborgs-Posten, and Kenya-based freelance journalist Naipanoi Lepapa, is, per a machine translation, based on interviews with over 30 employees at various levels of Sama, including several people who work with video, image, and speech annotation for Meta’s AI systems. Some of the people interviewed have worked on projects other than Meta’s smart glasses. The report’s authors said they did not gain access to the materials that Sama workers handle or the area where workers perform data annotation. The report is also based on interviews with former US Meta employees who have reportedly witnessed live data annotation for several Meta projects.
The report pointed to, per the translation, a “stream of privacy-sensitive data that is fed straight into the tech giant’s systems,” and that makes Sama workers uncomfortable. The authors said that several people interviewed for the report said they have seen footage shot with Ray-Ban Meta smart glasses that shows people having sex and using the bathroom.
“I saw a video where a man puts the glasses on the bedside table and leaves the room. Shortly afterwards, his wife comes in and changes her clothes,” an anonymous Sama employee reportedly said, per the machine translation.
Another anonymous employee said that they have seen users’ partners come out of the bathroom naked.
“You understand that it is someone’s private life you are looking at, but at the same time you are just expected to carry out the work,” an anonymous Sama employee reportedly said.
Meta confirms use of data annotators
In statements shared with the BBC on Wednesday, Meta confirmed that it “sometimes” shares content that users share with the Meta AI generative AI chatbot with contractors to review with “the purpose of improving people’s experience, as many other companies do.”
“This data is first filtered to protect people’s privacy,” the statement said, pointing to, as an example, blurring out faces in images.
Meta’s privacy policy for wearables says that photos and videos taken with its smart glasses are sent to Meta “when you turn on cloud processing on your AI Glasses, interact with the Meta AI service on your AI Glasses, or upload your media to certain services provided by Meta (i.e., Facebook or Instagram). You can change your choices about cloud processing of your Media at any time in Settings.”
The policy also says that video and audio from livestreams recorded with Ray-Ban Metas are sent to Meta, as are text transcripts and voice recordings created by Meta’s chatbot.
“We use machine learning and trained reviewers to process this data to improve, troubleshoot, and train our products. We share that information with third-party vendors and service providers to improve our products. You can access and delete recordings and related transcripts in the Meta AI App,” the policy says.
Meta’s broader privacy policy for the Meta AI chatbot adds: “In some cases, Meta will review your interactions with AIs, including the content of your conversations with or messages to AIs, and this review may be automated or manual (human).”
That policy also warns users against sharing “information that you don’t want the AIs to use and retain, such as information about sensitive topics.”
“When information is shared with AIs, the AIs will sometimes retain and use that information,” the Meta AI privacy policy says.
Notably, in August, Meta made “Meta AI with camera” on by default until a user turns off support for the “Hey Meta” voice command, per an email sent to users at the time. Meta spokesperson Albert Aydin told The Verge at the time that “photos and videos captured on Ray-Ban Meta are on your phone’s camera roll and not used by Meta for training.”
However, some Ray-Ban Meta users may not have read or understood the numerous privacy policies associated with Meta’s smart glasses.
Sama employees suggested that Ray-Ban Meta owners may be unaware that the devices are sometimes recording. Employees reportedly pointed to users recording their bank card or porn that they’re watching, seemingly inadvertently.
Meta’s smart glasses flash a red light when they are recording video or taking a photo, but there has been criticism that people may not notice the light or misinterpret its meaning.
“We see everything, from living rooms to naked bodies. Meta has that type of content in its databases. People can record themselves in the wrong way and not even know what they are recording,” an anonymous employee was quoted as saying.
When reached for comment by Ars Technica, a Sama representative shared a statement saying that Sama doesn’t “comment on specific client relationships or projects” but is GDPR and CCPA-compliant and uses “rigorously audited policies and procedures designed to protect all customer information, including personally identifiable information.”
Saama’s statement added:
This work is conducted in secure, access-controlled facilities. Personal devices are not permitted on production floors, and all team members undergo background checks and receive ongoing training in data protection, confidentiality, and responsible AI practices. Our teams receive living wages and full benefits, and have access to comprehensive wellness resources and on-site support.
Meta sued
The Swedish report has reignited concerns about the privacy of Meta’s smart glasses, including from the Information Commissioner’s Office, a UK data watchdog that has written to Meta about the report. The debate also comes as Meta is reportedly planning to add facial recognition to its Ray-Ban and Oakley-branded smart glasses “as soon as this year,” per a February report from The New York Times citing anonymous people “involved with the plans.”
The claims have also led to a proposed class-action lawsuit [PDF] filed yesterday against Meta and Luxottica of America, a subsidiary of Ray-Ban parent company EssilorLuxottica. The lawsuit challenges Meta’s slogan for the glasses, “designed for privacy, controlled by you,” saying:
No reasonable consumer would understand “designed for privacy, controlled by you” and similar promises like “built for your privacy” to mean that deeply personal footage from inside their homes would be viewed and catalogued by human workers overseas. Meta chose to make privacy the centerpiece of its pervasive marketing campaign while concealing the facts that reveal those promises to be false.
The lawsuit alleges that Meta has broken state consumer protection laws and seeks damages, punitive penalties, and an injunction requiring Meta to change business practices “to prevent or mitigate the risk of the consumer deception and violations of law.”
Ars Technica reached out to Meta for comment but didn’t hear back before publication. Meta has declined to comment on the lawsuit to other outlets.
Workers report watching Ray-Ban Meta-shot footage of people using the bathroom Read More »