US blocks all offshore wind construction, says reason is classified
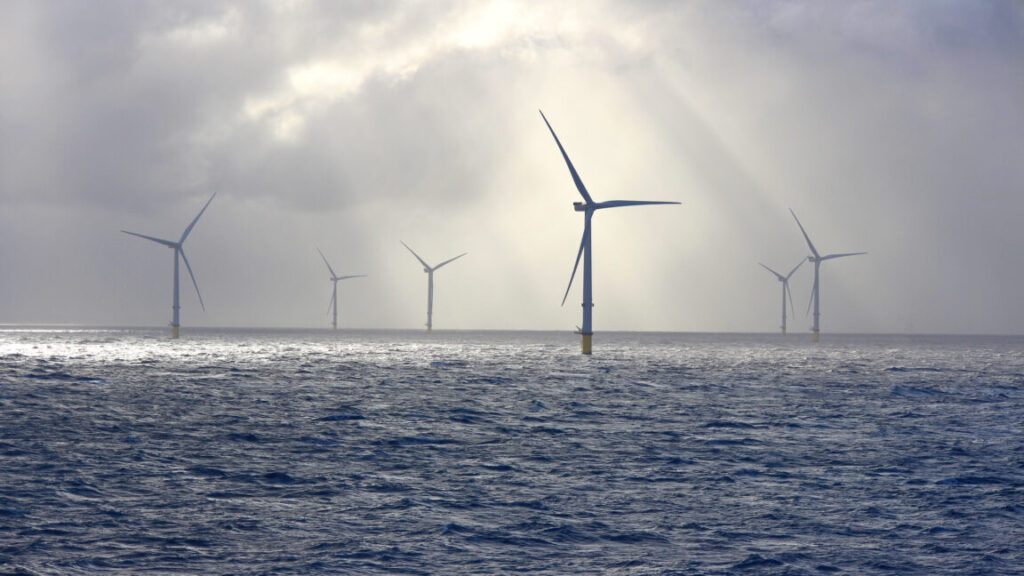
On Monday, the US Department of the Interior announced that it was pausing the leases on all five offshore wind sites currently under construction in the US. The move comes despite the fact that these projects already have installed significant hardware in the water and on land; one of them is nearly complete. In what appears to be an attempt to avoid legal scrutiny, the Interior is blaming the decisions on a classified report from the Department of Defense.
The second Trump administration announced its animosity toward offshore wind power literally on day one, issuing an executive order on inauguration day that called for a temporary halt to issuing permits for new projects pending a re-evaluation. Earlier this month, however, a judge vacated that executive order, noting that the government has shown no indication that it was even attempting to start the re-evaluation it said was needed.
But a number of projects have gone through the entire permitting process, and construction has started. Before today, the administration had attempted to stop these in an erratic, halting manner. Empire Wind, an 800 MW farm being built off New York, was stopped by the Department of the Interior, which alleged that it had been rushed through permitting. That hold was lifted following lobbying and negotiations by New York and the project developer Orsted, and the Department of the Interior never revealed why it changed its mind. When the Interior Department blocked a second Orsted project, Revolution Wind offshore of southern New England, the company took the government to court and won a ruling that let it continue construction.
US blocks all offshore wind construction, says reason is classified Read More »