The Air Force’s new ICBM is nearly ready to fly, but there’s nowhere to put it
“There were assumptions that were made in the strategy that obviously didn’t come to fruition.”
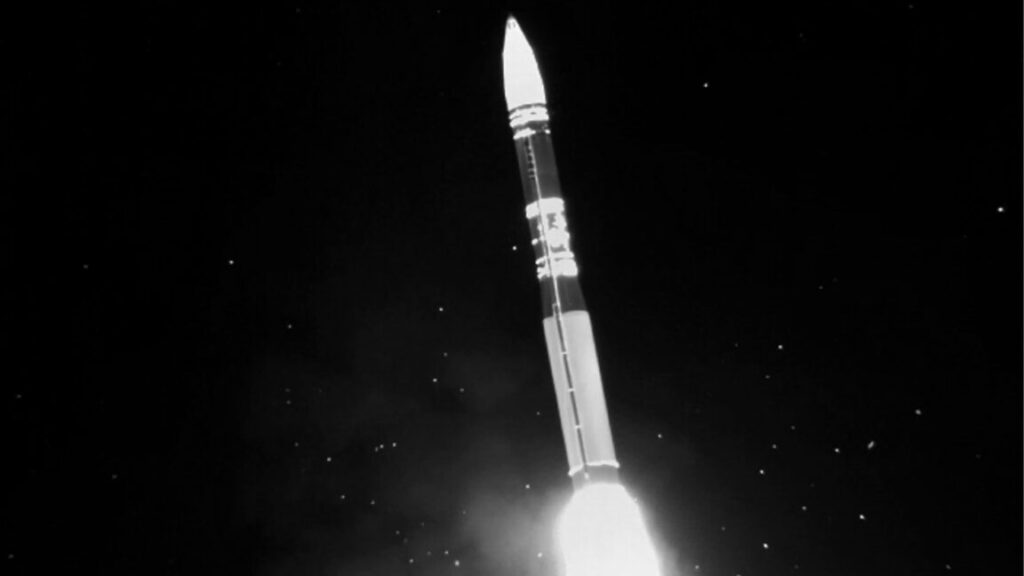
An unarmed Minuteman III missile launches during an operational test at Vandenberg Air Force Base, California, on September 2, 2020. Credit: US Air Force
DENVER—The US Air Force’s new Sentinel intercontinental ballistic missile is on track for its first test flight next year, military officials reaffirmed this week.
But no one is ready to say when hundreds of new missile silos, dug from the windswept Great Plains, will be finished, how much they cost, or, for that matter, how many nuclear warheads each Sentinel missile could actually carry.
The LGM-35A Sentinel will replace the Air Force’s Minuteman III fleet, in service since 1970, with the first of the new missiles due to become operational in the early 2030s. But it will take longer than that to build and activate the full complement of Sentinel missiles and the 450 hardened underground silos to house them.
Amid the massive undertaking of developing a new ICBM, defense officials are keeping their options open for the missile’s payload unit. Until February 5, the Air Force was barred from fitting ballistic missiles with Multiple Independently targetable Reentry Vehicles (MIRVs) under the constraints of the New START nuclear arms control treaty cinched by the US and Russia in 2010. The treaty expired three weeks ago, opening up the possibility of packaging each Sentinel missile with multiple warheads, not just one.
Senior US military officials briefed reporters on the Sentinel program this week at the Air and Space Forces Association’s annual Warfare Symposium near Denver. There was a lot to unpack.
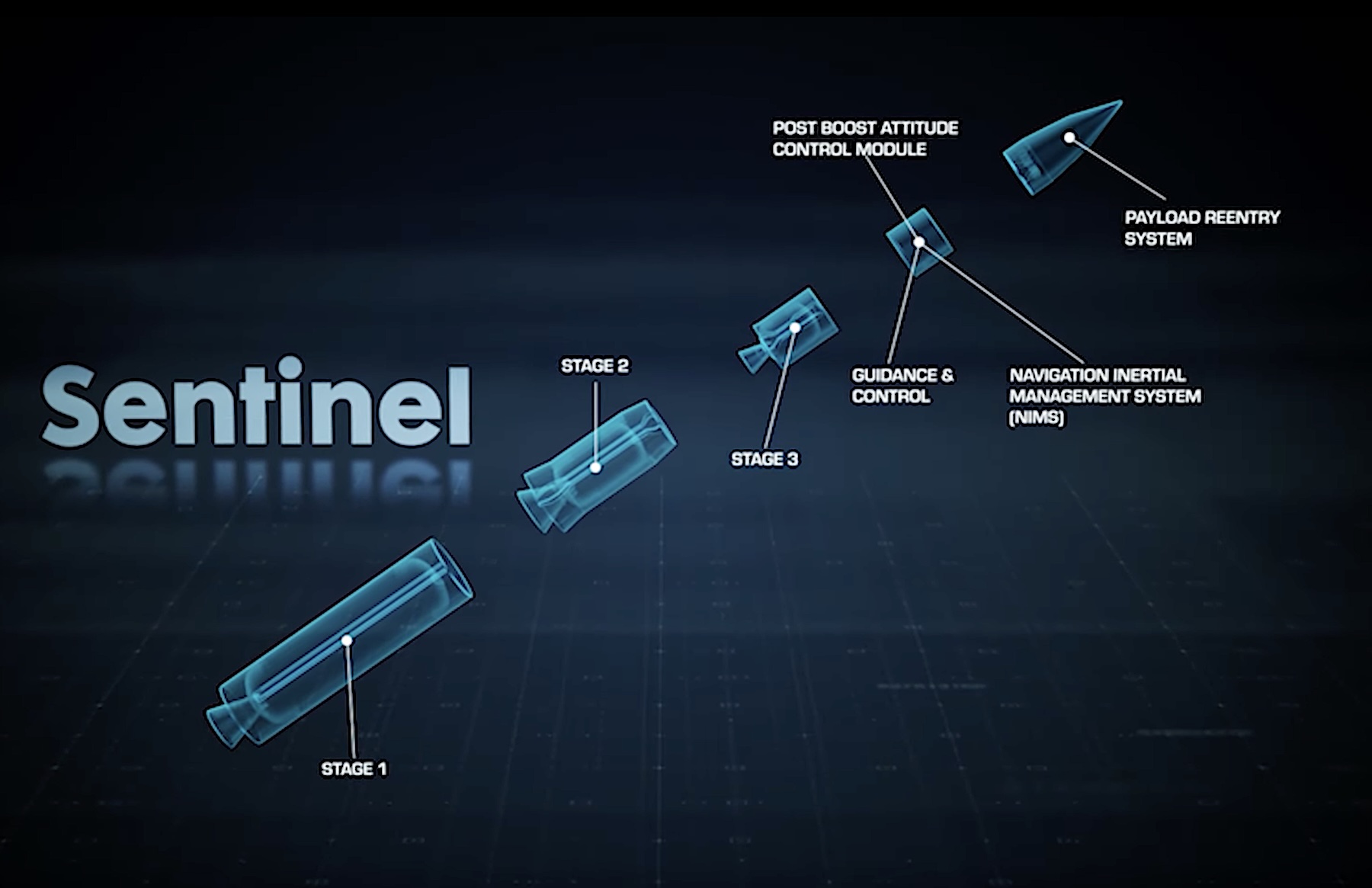
This cutaway graphic shows the major elements of the Sentinel missile. Credit: Northrop Grumman
Into the breach
Two years ago, the Air Force announced the Sentinel program’s budget had grown from $77.7 billion to nearly $141 billion. This was after something known as a “Nunn-McCurdy breach,” referring to the names of two lawmakers behind legislation mandating reviews for woefully overbudget defense programs. In 2024, the Pentagon determined that the Sentinel program was too essential to national security to cancel.
“We’ve gotten all the capability that we can out of the Minuteman,” said Gen. Stephen “S.L.” Davis, commander of Air Force Global Strike Command. Potential enemy threats to the Minuteman ICBM have “evolved significantly” since its initial deployment in the Cold War, Davis said.
The $141 billion figure is already out of date, as the Air Force announced last year that it would need to construct new silos for the Sentinel missile. The original plan was to adapt existing Minuteman III silos for the new weapons, but engineers determined that it would take too long and cost too much to modify the aging Minuteman facilities.
Instead, the Air Force, in partnership with contractors and the US Army Corps of Engineers, will dig hundreds of new holes across Colorado, Montana, Nebraska, North Dakota, and Wyoming. The new silos will include 24 new forward launch centers, three centralized wing command centers, and more than 5,000 miles of fiber connections to wire it all together, military and industry officials said.
Sentinel, which had its official start in 2016, will be the largest US government civil works project since the completion of the interstate highway system, and is the most complex acquisition program the Air Force has ever undertaken, wrote Sen. Roger Wicker (R-Mississippi) and Sen. Deb Fischer (R-Nebraska) in a 2024 op-ed published in the Wall Street Journal.
Gen. Dale White, the Pentagon’s director of critical major weapons systems, said Wednesday the Defense Department plans to complete a “restructuring” of the Sentinel program by the end of the year. Only then will an updated budget be made public.
The military stopped constructing new missile silos in the late 1960s and hasn’t developed a new ICBM since the 1980s. It shows.
“It’s been a very, very long time since we’ve done this,” White said. “At the very core, there were assumptions that were made in the strategy that obviously didn’t come to fruition.”
Military planners also determined it would not be as easy as they hoped to maintain the existing Minuteman III missiles on alert while converting their silos for Sentinel. Building new silos will keep the Minuteman III online—perhaps until as late as 2050, according to a government watchdog—as the Air Force activates Sentinel emplacements. The Minuteman III was previously supposed to retire around 2036.
“We’re not reusing the Minuteman III silos, but at the same time that obviously gives much greater operational flexibility to the combatant commander,” White said. “So, we had to take a step back and have a more enduring look at what we were trying to do, what capability is needed, making sure we do not have a gap in capability.”
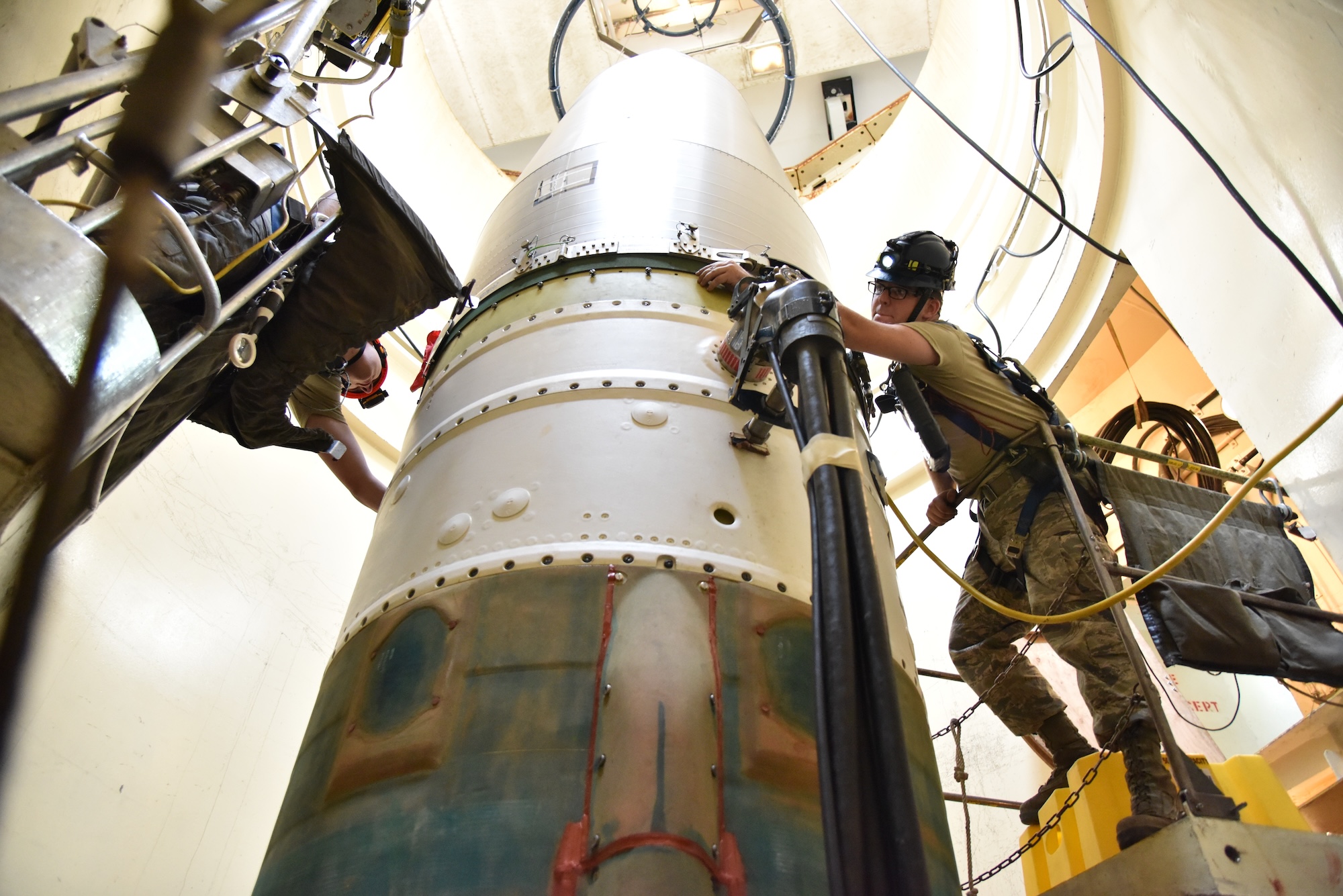
341st Missile Maintenance Squadron technicians connect a reentry system to a spacer on an intercontinental ballistic missile during a Simulated Electronic Launch-Minuteman test September 22, 2020, at a launch facility near Great Falls, Montana.
Credit: US Air Force photo by Senior Airman Daniel Brosam
341st Missile Maintenance Squadron technicians connect a reentry system to a spacer on an intercontinental ballistic missile during a Simulated Electronic Launch-Minuteman test September 22, 2020, at a launch facility near Great Falls, Montana. Credit: US Air Force photo by Senior Airman Daniel Brosam
Decommissioning the Minuteman III silos will come with its own difficulties. An Air Force official said on background that commanders recently took one Minuteman silo off alert to better gauge how long it will take to decommission each location. Meanwhile, Northrop Grumman, Sentinel’s prime contractor, broke ground on the first “prototype” Sentinel silo in Promontory, Utah, earlier this month.
The Air Force has ordered 659 Sentinel missiles from Northrop Grumman, including more than 400 to go on alert, plus spares and developmental missiles for flight testing. The first Sentinel test launch from a surface pad at Vandenberg Space Force Base, California, is scheduled for 2027.
To ReMIRV or not to ReMIRV
For the first time in more than 50 years, the world’s two largest nuclear forces have been unshackled from any arms control agreements. New START was the latest in a series of accords between the United States and Russia, and with it came the ban on MIRVs aboard land-based ICBMs. The Air Force removed the final MIRV units from Minuteman III missiles in 2014.
The Trump administration wants a new agreement that includes Russia as well as China, which was not part of New START. US officials were expected to meet with Russian and Chinese diplomats this week to discuss the topic. There’s no guarantee of any agreement between the three powers, and even if there is one, it may take the form of an informal personal accord among leaders, rather than a ratified treaty.
“The strategic environment hasn’t changed overnight, from before New START was in effect, until it has lapsed, and within our nation’s nuclear deterrent,” said Adm. Rich Correll, head of US Strategic Command. “We have the flexibility to address any adjustments to the security environment as a result of that treaty lapsing.”
This flexibility includes the option to “reMIRV” missiles to accommodate more than one nuclear warhead, Correll said. “We have the ability to do that. That’s obviously a national-level decision that would go up to the president, and those policy levers, if needed, provide additional resiliency within the capabilities that we have.”
MIRVs are more difficult for missile defense systems to counter, and allow offensive missile forces to package more ordnance in a single shot. With New START gone, there’s no longer any mechanism for international arms inspections. Russia may now also stack more nukes on its ICBMs. Gone, too, is the limitation for the United States and Russia to deploy no more than 1,550 nuclear warheads at one time.
“The expiration of this treaty is going to lead us into a world for the first time since 1972 where there are no limits on the sizes of those arsenals,” said Ankit Panda of the Carnegie Endowment for International Peace.
“I think this opens up the question of whether we’re going to be heading into a world that’s just going to be a lot more unpredictable and dangerous when you have countries like the United States and Russia that have a lot less transparency into each other’s nuclear arsenals, and fundamentally, as a result, a lot less predictability about the world that they’re operating in,” Panda continued.
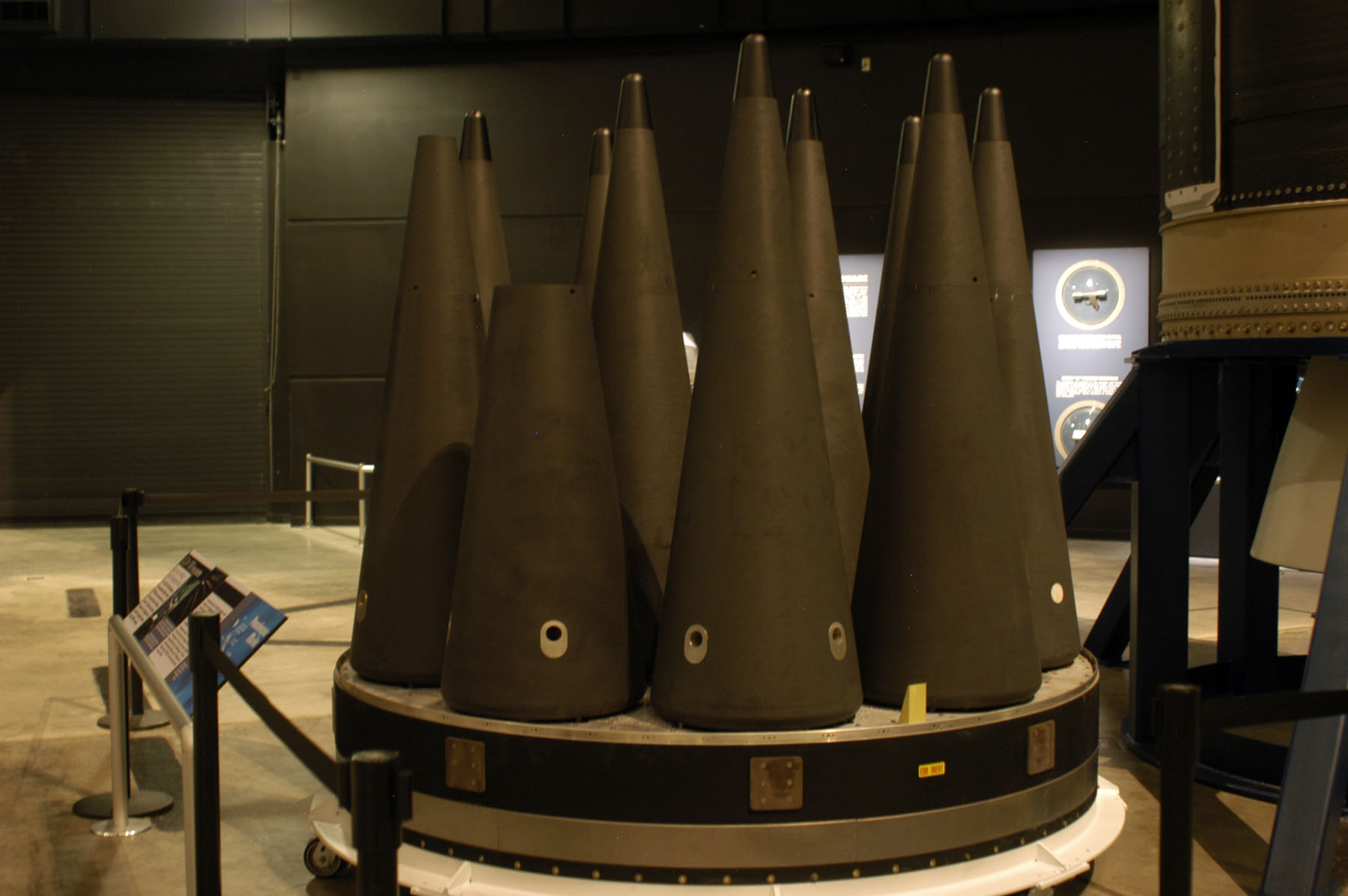
Mk21 reentry vehicles on display in the Missile and Space Gallery at the National Museum of the US Air Force in Dayton, Ohio. Credit: US Air Force
Some strategists have questioned the need for land-based ICBMs in the modern era. The locations of the Air Force’s missile fields are well known, making them juicy targets for an adversary seeking to take out a leg of the military’s nuclear triad. The stationary nature of the land-based missile component contrasts with the mobility and stealth of the nation’s bomber and submarine fleets. Also, bombers and subs can already deliver multiple nukes, something land-based missiles couldn’t do under New START.
Proponents of maintaining the triad say the ICBM missile fields serve an important, if not macabre, function in the event of the unimaginable. They would soak up the brunt of any large-scale nuclear attack. Hundreds of miles of the Great Plains would be incinerated.
“The main rationale for maintaining silo-based ICBMs is to complicate an adversary’s nuclear strategy by forcing them to target 400 missile silos dispersed throughout the United States to limit a retaliatory nuclear strike, which is why ICBMs are often referred to as the ‘nuclear sponge,’” the Center for Arms Control and Non-Proliferation wrote in 2021. “However, with the development of sea-based nuclear weapons, which are essentially undetectable, and air-based nuclear weapons, which provide greater flexibility, ground-based ICBMs have become increasingly technologically redundant.”
Policymakers in power do not agree. The ICBM program has powerful backers in Congress, and Sentinel has enjoyed support from the Obama, Biden, and both Trump administrations. The Pentagon is also developing the B-21 Raider strategic bomber and a new generation of “Columbia-class” nuclear-armed subs.
The Air Force’s new ICBM is nearly ready to fly, but there’s nowhere to put it Read More »