5 things in Trump’s budget that won’t make NASA great again
If signed into law as written, the White House’s proposal to slash nearly 25 percent from NASA’s budget would have some dire consequences.
It would cut the agency’s budget from $24.8 billion to $18.8 billion. Adjusted for inflation, this would be the smallest NASA budget since 1961, when the first American launched into space.
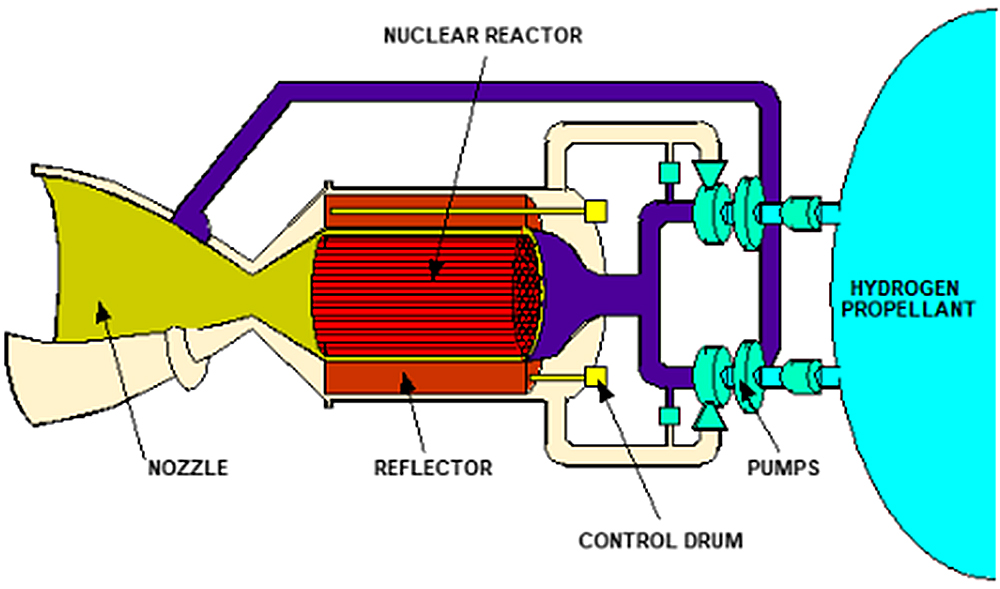
The proposed funding plan would halve NASA’s funding for robotic science missions and technology development next year, scale back research on the International Space Station, turn off spacecraft already exploring the Solar System, and cancel NASA’s Space Launch System rocket and Orion spacecraft after two more missions in favor of procuring lower-cost commercial transportation to the Moon and Mars.
The SLS rocket and Orion spacecraft have been targets for proponents of commercial spaceflight for several years. They are single-use, and their costs are exorbitant, with Moon missions on SLS and Orion projected to cost more than $4 billion per flight. That price raises questions about whether these vehicles will ever be able to support a lunar space station or Moon base where astronauts can routinely rotate in and out on long-term expeditions, like researchers do in Antarctica today.
Reusable rockets and spaceships offer a better long-term solution, but they won’t be ready to ferry people to the Moon for a while longer. The Trump administration proposes flying SLS and Orion two more times on NASA’s Artemis II and Artemis III missions, then retiring the vehicles. Artemis II’s rocket is currently being assembled at Kennedy Space Center in Florida for liftoff next year, carrying a crew of four around the far side of the Moon. Artemis III would follow with the first attempt to land humans on the Moon since 1972.
The cuts are far from law
Every part of Trump’s budget proposal for fiscal year 2026 remains tentative. Lawmakers in each house of Congress will write their own budget bills, which must go to the White House for Trump’s signature. A Senate bill released last week includes language that would claw back funding for SLS and Orion to support the Artemis IV and Artemis V missions.
5 things in Trump’s budget that won’t make NASA great again Read More »