Reentry of NASA satellite will exceed the agency’s own risk guidelines
No one on the ground has ever been injured by falling space junk, but there are examples of space debris causing property damage.
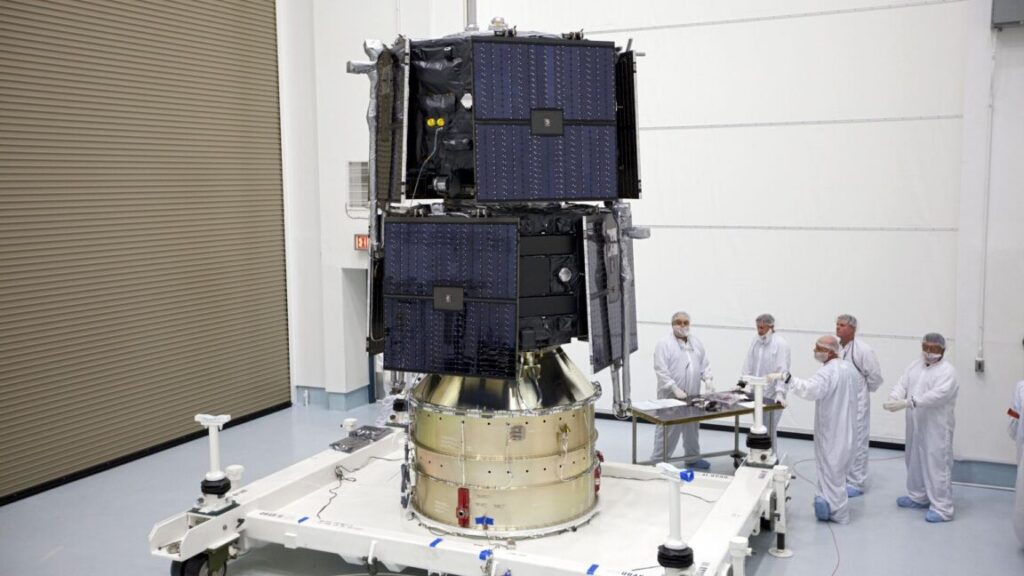
NASA’s two Van Allen Probes launched into elliptical orbits ranging from a few hundred miles above Earth up to an apogee, or high point, of nearly 20,000 miles. The orbits are inclined 10 degrees to the equator, limiting the risk of injury or damage to a swath of the tropics. NASA ended the mission in 2019 when the satellites ran out of fuel.
At that time, NASA engineers expected the spacecraft to reenter the atmosphere in 2034. But higher-than-anticipated solar activity caused the atmosphere to swell outward, increasing atmospheric drag on the satellites beyond initial estimates, according to NASA. Van Allen Probe B is expected to reenter no earlier than 2030, with a similar risk to the public.
The two spacecraft were built by the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Lab. NASA said the mission made several major discoveries, including “the first data showing the existence of a transient third radiation belt, which can form during times of intense solar activity.”
Several NASA satellites have reentered the atmosphere without complying with the government’s risk standard. One of the satellites, the Rossi X-ray Timing Explorer, fell out of orbit in 2018 with a 1-in-1,000 chance of harming someone on the ground. No one was hurt. RXTE was launched in 1995, just four months before NASA issued its first standard on orbital debris mitigation and reentry risk management.
While NASA has exceeded its standards before, the US government is not a top offender when it comes to unmitigated reentry risks. China launched four heavy-lift Long March 5B rockets between 2020 and 2022, and left its massive core stages in orbit to fall back to Earth. The four abandoned rocket cores, each nearly 24 tons in mass, reentered the atmosphere uncontrolled. Two of them dropped wreckage on land—in the Ivory Coast and Borneo—but no injuries were reported.
Reentry of NASA satellite will exceed the agency’s own risk guidelines Read More »