Rocket Report: Starship could fly again in May; Ariane 6 coming together
Eating their lunch —
“I think we’re really going to focus on getting reentry right.”
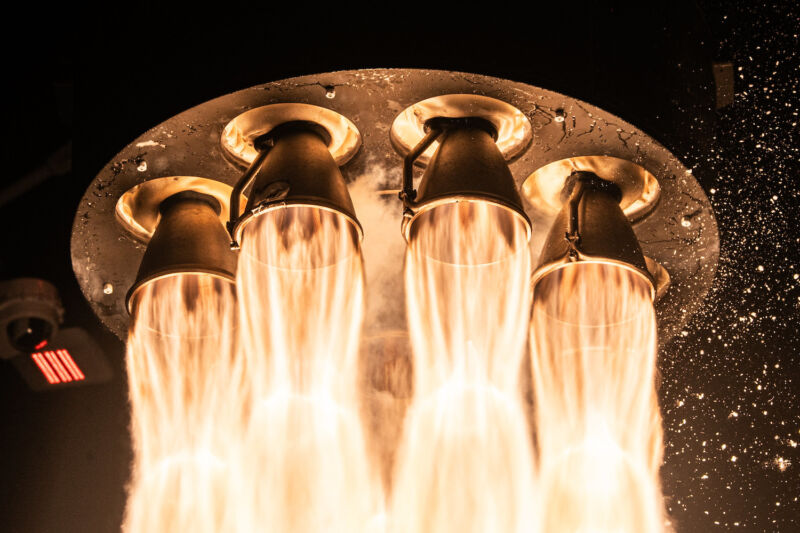

Enlarge / Nine kerosene-fueled Rutherford engines power Rocket Lab’s Electron launch vehicle off the pad at Wallops Island, Virginia, early Thursday.
Welcome to Edition 6.36 of the Rocket Report! SpaceX wants to launch the next Starship test flight as soon as early May, the company’s president and chief operating officer said this week. The third Starship test flight last week went well enough that the Federal Aviation Administration—yes, the FAA, the target of many SpaceX fans’ frustrations—anticipates a simpler investigation and launch licensing process than SpaceX went through before its previous Starship flights. However, it looks like we’ll have to wait a little longer for Starship to start launching real satellites.
As always, we welcome reader submissions, and if you don’t want to miss an issue, please subscribe using the box below (the form will not appear on AMP-enabled versions of the site). Each report will include information on small-, medium-, and heavy-lift rockets, as well as a quick look ahead at the next three launches on the calendar.

Starship could threaten small launch providers. Officials from several companies operating or developing small satellite launch vehicles are worried that SpaceX’s giant Starship rocket could have a big impact on their marketability, Space News reports. Starship’s ability to haul more than 100 metric tons of payload mass into low-Earth orbit will be attractive not just for customers with heavy satellites but also for those with smaller spacecraft. Aggregating numerous smallsats on Starship will mean lower prices than dedicated small satellite launch companies can offer and could encourage customers to build larger satellites with cheaper parts, further eroding business opportunities for small launch providers.
Well, yeah … SpaceX’s dedicated rideshare missions are already reshaping the small satellite launch market. The price per kilogram of payload on a Falcon 9 rocket launching a Transporter mission is less than the price per unit on a smaller rocket, like Rocket Lab’s Electron, Firefly’s Alpha, or Europe’s Vega. Companies operating only in the smallsat launch market tout the benefits of their services, often pointing to their ability to deliver payloads into bespoke orbits, rather than dropping off bunches of satellites into more standardized orbits. But the introduction of Orbital Transfer Vehicles for last-mile delivery services has made SpaceX’s Transporter missions, and potentially Starship rideshares, more attractive. “With Starship, OTVs can become the best option for smallsats,” said Marino Fragnito, senior vice president and head of the Vega business unit at Arianespace. If Starship is able to achieve the very low per-kilogram launch prices proposed for it, “then it will be difficult for small launch vehicles,” Fragnito said.
Rocket Lab launches again from Virginia. Rocket Lab’s fourth launch from Wallops Island, Virginia, and the company’s first there in nine months, took off early Thursday with a classified payload for the National Reconnaissance Office, the US government’s spy satellite agency, Space News reports. A two-stage Electron rocket placed the NRO’s payload into low-Earth orbit, and officials declared it a successful mission. The NRO did not disclose any details about the payload, but in a post-launch statement, the agency suggested the mission was conducting technology demonstrations of some kind. “The knowledge gained from this research will advance innovation and enable the development of critical new technology,” said Chris Scolose, director of the NRO.
A steady customer for Rocket Lab … The National Reconnaissance Office has become a regular customer of Rocket Lab. The NRO has historically launched larger spacecraft, such as massive bus-sized spy satellites, but like the Space Force, is beginning to launch larger numbers of small satellites. This mission, designated NROL-123 by the NRO, was the fifth and last mission under a Rapid Acquisition of a Small Rocket (RASR) contract between NRO and Rocket Lab, dating back to 2020. It was also Rocket Lab’s second launch in nine days, following an Electron flight last week from its primary base in New Zealand. Overall, it was the 46th launch of a light-class Electron rocket since it debuted in 2017. Rocket Lab is building a launch pad for its next-generation Neutron rocket at Wallops. (submitted by EllPeaTea)
The easiest way to keep up with Eric Berger’s space reporting is to sign up for his newsletter, we’ll collect his stories in your inbox.
Night flight for Astrobotic’s Xodiac. The Xodiac rocket, a small terrestrial vertical takeoff and vertical landing technology testbed, made its first night flight, Astrobotic says in a statement. The liquid-fueled Xodiac is designed for vertical hops and can host prototype sensors and other payloads, particularly instruments in development to assist in precision landings on other worlds. This first tethered night flight of Xodiac in Mojave, California, was in preparation for upcoming flight testing with the NASA TechLeap Prize’s Nighttime Precision Landing Challenge. These flights will begin in April, allowing NASA to test the ability of sensors to map a landing field designed to simulate the Moon’s surface in near-total darkness.
Building on the legacy of Masten … Xodiac has completed more than 160 successful flights, dating back to the vehicle’s original owner, Masten Space Systems. Masten filed for bankruptcy in 2022, and the company was acquired by Astrobotic a couple of months later. Astrobotic’s primary business area is in developing and flying robotic Moon landers, so it has a keen interest in mastering automated landing and navigation technologies like those it is testing with NASA on Xodiac. David Masten, founder of Masten Space Systems, is now chief engineer for Astrobotic’s propulsion and test department. “The teams will demonstrate their systems over the LSPG (Lunar Surface Proving Ground) at night to simulate landing on the Moon during the lunar night or in shadowed craters.” (submitted by Ken the Bin)
Rocket Report: Starship could fly again in May; Ariane 6 coming together Read More »