Lawmakers ask what it would take to “store” the International Space Station
NASA shall evaluate the “viability of transferring the ISS to a safe orbital harbor” after retirement.
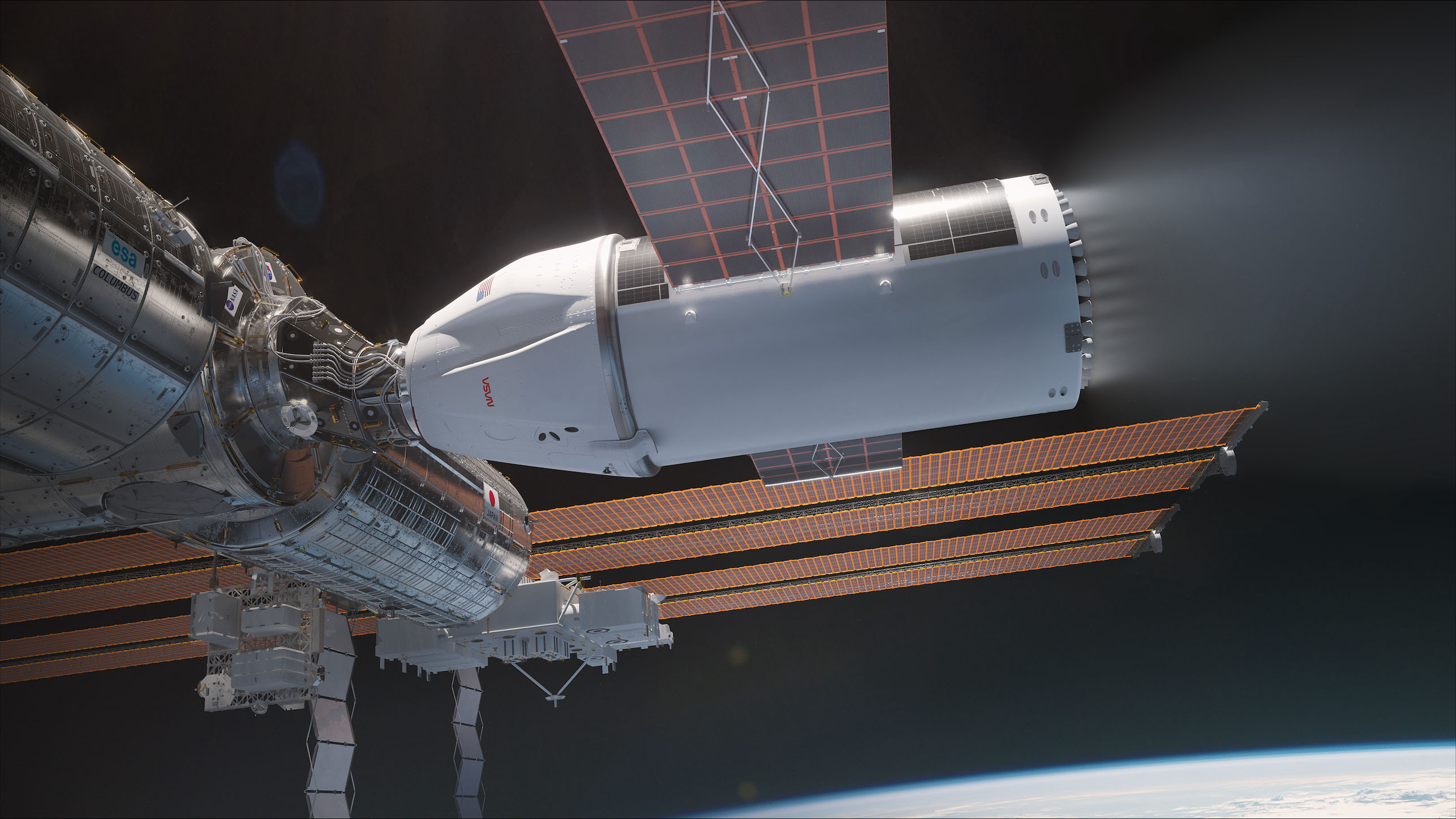
The International Space Station, with a crew of six onboard, is seen in silhouette as it transits the Moon at roughly five miles per second on Saturday, December 2, 2017, in Manchester Township, York County, Pennsylvania. Credit: NASA/Joel Kowsky
Members of the House Science, Space, and Technology Committee voted to approve a NASA authorization bill this week, advancing legislation chock full of policy guidelines meant to give lawmakers a voice in the space agency’s strategic direction.
The committee met to “mark up” the NASA Reauthorization Act of 2026, adding more than 40 amendments to the bill before a unanimous vote to refer the legislation to the full House of Representatives. Wednesday’s committee vote was just one of several steps needed for the bill to become law. It must pass a vote on the House floor, win approval from the Senate, and then go to the White House for President Donald Trump’s signature.
Ars has reported on one of the amendments, which would authorize NASA to take steps toward a “commercial” deep space program using privately owned rockets and spacecraft rather than vehicles owned by the government.
Another add-on to the authorization bill would require NASA to reassess whether to guide the International Space Station (ISS) toward a destructive atmospheric reentry after it is decommissioned in 2030. The space agency’s current plan is to deorbit the space station in 2031 over the Pacific Ocean, where debris that survives the scorching reentry will fall into a remote, unpopulated part of the sea.
No policy change—yet
The most recent NASA authorization act, passed in 2022, extended the US government’s support for the ISS program until 2030. The amendment tacked onto this year’s bill would not change the timeline for ending operations on the ISS, but it asks NASA to reconsider its decision about what to do with the complex after retirement.
The amendment would direct NASA to “carry out an engineering analysis to evaluate the technical, operational, and logistical viability of transferring the ISS to a safe orbital harbor and storing the ISS in such harbor after the end of the operational low-Earth orbit lifetime of the ISS to preserve the ISS for potential reuse and satisfy the objectives of NASA.”
Rep. George Whitesides (D-Calif.) submitted the amendment with cosponsorship from Rep. Nick Begich (R-Alaska). The proposal passed the committee through a voice vote with bipartisan support. Whitesides was a NASA chief of staff and longtime executive in the space industry before his election to the House last year.
“The International Space Station is one of the most complex engineering achievements in human history,” Whitesides said. “It represents more than three decades of international collaboration and investment by US taxpayers estimated at well over $100 billion. Current plans call for the station to be deorbited at the end of its service life in 2030. This amendment does not seek to change that policy. Instead, it asks a straightforward question: Before we permanently dispose of an asset of this magnitude, should we fully understand whether it’s viable to preserve it in orbit for potential use by future generations?”
In 2024, NASA awarded SpaceX a nearly $1 billion contract to develop a souped-up version of its Dragon spacecraft, which would be equipped with additional thrusters and propellant tanks to provide the impulse required to steer the space station toward a targeted reentry. The deorbit maneuvers will slow the station’s velocity enough for Earth’s gravity to pull it back into the atmosphere.
Artist’s illustration of SpaceX’s deorbit vehicle, based on the design of the company’s Dragon spacecraft. The modified spacecraft will have 46 Draco thrusters—30 for the deorbit maneuvers and 16 for attitude control. Credit: SpaceX
The deorbit vehicle needs to slow the station’s speed by about 127 mph (57 meters per second), a tiny fraction of the spacecraft’s orbital velocity of more than 17,000 mph (7.7 kilometers per second). But the station mass is around 450 tons (400 metric tons), equivalent to two freight train locomotives, and measures about the length of a football field. Changing its speed by just 127 mph will consume about 10 tons (9 metric tons) of propellant, according to a NASA analysis released in 2024.
The analysis document shows that NASA considered alternatives to discarding the space station through reentry. One option NASA studied involved moving the station into a higher orbit. At its current altitude, roughly 260 miles (420 kilometers) above the Earth, the ISS would take one to two years to reenter the atmosphere due to aerodynamic drag if reboosts weren’t performed. NASA does not want the space station to make an uncontrolled reentry because of the risk of fatalities, injuries, and property damage from debris reaching the ground.
Boosting the space station’s orbit to somewhere between 400 and 420 miles (640 to 680 kilometers) would require a little more than twice the propellant (18.9 to 22.3 metric tons) needed for deorbit maneuvers, according to NASA’s analysis. At that altitude, without any additional boosts, NASA says the space station would likely remain in orbit for 100 years before succumbing to atmospheric drag and burning up. Going higher still, the space station could be placed in a 1,200-mile-high (2,000-kilometer) orbit, stable for more than 10,000 years, with about 146 tons (133 metric tons) of propellant.
There are two problems with sending the ISS to higher altitudes. One is that it would require the development of new propulsive and tanker vehicles that do not currently exist, according to NASA.
“While still currently in development, vehicles such as the SpaceX Starship are being designed to deliver significant amounts of cargo to these orbits,” NASA officials wrote in their analysis. “However, there are prohibitive engineering challenges with docking such a large vehicle to the space station and being able to use its thrusters while remaining within space station structural margins. Other vehicles would require both new certifications to fly at higher altitudes and multiple flights to deliver propellant.”
Going higher would also expose the space station to an increased risk of collision with space junk. The hazards from space debris are most severe at about 500 miles (800 kilometers), according to the engineers who conducted the analysis. “This means that the likelihood of an impact leaving station unable to maneuver or react to future threats, or even a significant impact resulting in complete fragmentation, is unacceptably high.”
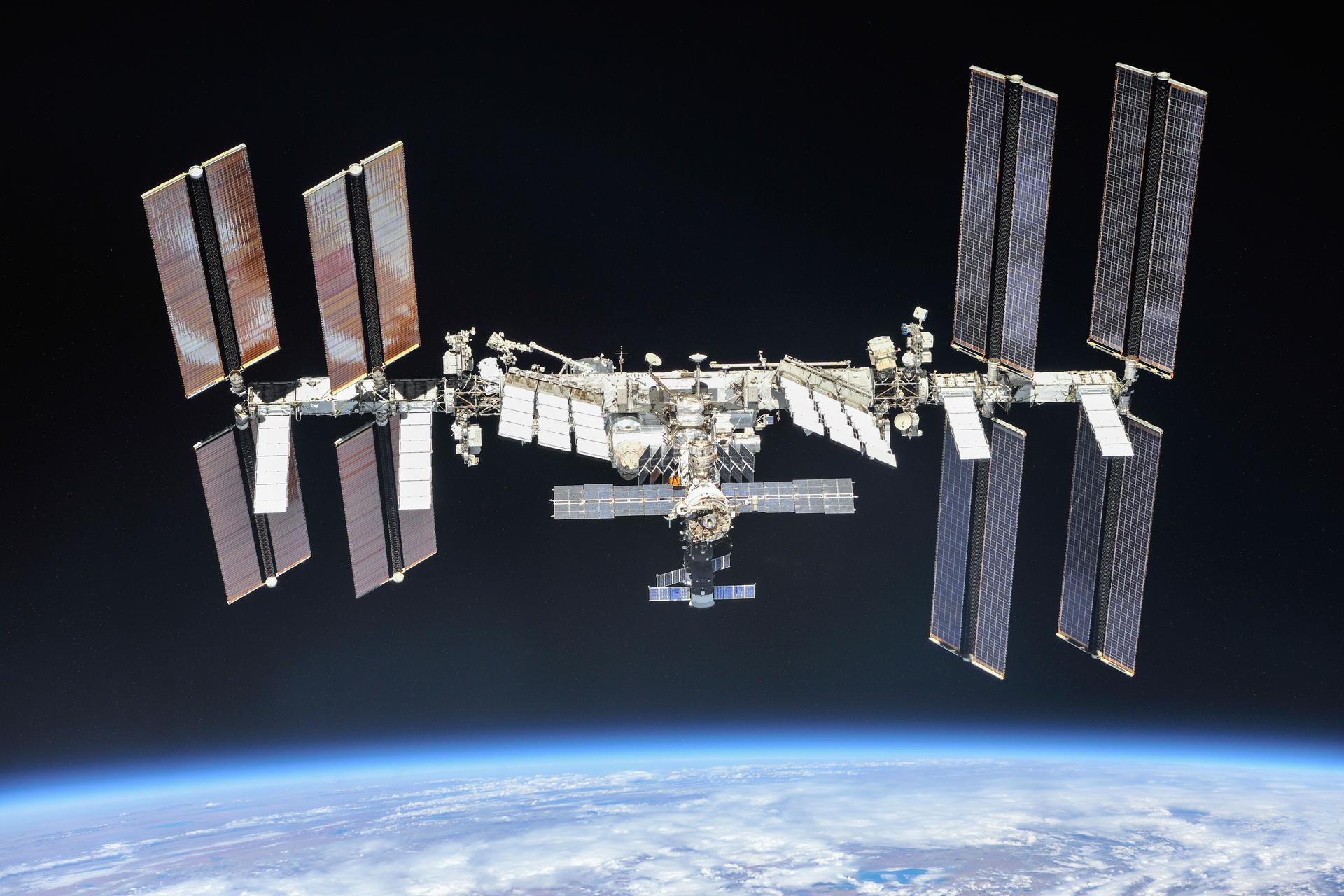
This photo of the International Space Station was captured by a crew member on a Soyuz spacecraft. Credit: NASA/Roscosmos
Whitesides’ office did not respond to Ars’ questions, but he said in Wednesday’s hearing that his amendment would direct NASA to further examine the costs and risks of putting the ISS in a higher orbit. The legislation “simply ensures that Congress receives a rigorous fact-based analysis so that future decisions involving the ISS are informed by scientific reality,” he said.
“At a time when we’re thinking seriously about sustainability in space, this amendment protects taxpayer investments and ensures that we fully understand our options before an irreplaceable asset is permanently retired.”
Rep. Brian Babin (R-Texas) said he “wholeheartedly” supports Whitesides’ amendment. Rep. Don Beyer (D-Va.) also endorsed it in brief remarks during Wednesday’s markup hearing.
“I just hate the thought that we would take something not just that we spent all the money on, but such an important part of human history, and dump it in the Pacific Ocean, never to be seen again, rather than preserving it,” Beyer said. “We don’t know whether we can do it in orbit, but if we can, we should really explore that hard.”
It’s not too late
Although NASA’s official policy is still to decommission the ISS in 2030, the door hasn’t closed on extending the lab’s operations into the next decade. There are some concerns about aging hardware, but NASA said in 2024 that engineers have “high confidence” that the primary structure of the station could support operations beyond 2030.
The oldest segments of the station have been in orbit since 1998, undergoing day-night thermal cycles every 45 minutes as they orbit the planet. The structural stability of the Russian section of the outpost is also in question. Russian engineers traced a small but persistent air leak to microscopic structural cracks in one Russian module, but cosmonauts were able to seal the cracks, and air pressure in the area is “holding steady,” a NASA spokesperson said last month.
One of the lab’s most critical elements, its power-generation system, is in good shape after NASA recently installed upgraded solar arrays outside the station. Another set of upgraded solar panels is scheduled to arrive at the station later this year, just a few years before the complex is to be retired.
NASA’s strategy is to decommission the ISS and turn to the commercial sector for new, cheaper, smaller space stations to continue conducting research in low-Earth orbit. This would allow NASA to buy time on a commercial space station for its astronauts and experiments, while the agency’s human spaceflight program focuses on missions to the Moon.
That’s a fine plan, but NASA’s program to support commercial space stations, known as Commercial LEO Destinations (CLDs), is going nowhere fast. Supporters of the CLD program say it has been underfunded from the start, and the strategy became more muddled last year when Sean Duffy, then NASA’s acting administrator, changed the agency’s rules for private space stations. NASA Administrator Jared Isaacman is reviewing the changes, and the requirements for stations may shift again.
NASA spends more than $3 billion per year for ISS operations, including crew and cargo transportation services to staff and support the outpost. NASA’s budget for deep space exploration in fiscal year 2026 is nearly $7.8 billion. NASA is receiving $273 million for the Commercial LEO Destinations program this year, with the money to be divided among multiple companies.
Any private space station will need to sustain itself, at least partially, on commercial business to be profitable. Developers have raised concerns that they will be unable to attract sufficient commercial business—in areas like pharmaceutical research, tech demos, or space tourism—as long as the government-funded ISS is still operating.
One of the companies vying for NASA funding is Vast, which plans to launch its first single-module private outpost to orbit in early 2027. This first station, named Haven-1, will accommodate crews for short-duration temporary stays. Vast plans to follow Haven-1 with a much larger multi-module station capable of supporting a permanent crew.
Max Haot, Vast’s CEO, does not seem bothered by lawmakers’ efforts to revisit the question of deorbiting the International Space Station.
“The amendment directs NASA to study the feasibility of something other than deorbit and disposal after ISS end of life, which is separate from the issue of retiring the space station and transitioning to commercial partners,” Haot said in a statement to Ars. “We support President Trump’s directive in national space policy to replace the ISS by 2030, with commercial partners who can ensure there is no gap in America’s continuous human presence in space.”
The other top contenders in the commercial space station arena are Starlab, a joint venture between Voyager Space and Airbus, the Blue Origin-led Orbital Reef project, and Axiom Space. Voyager and Blue Origin did not respond to requests for comment from Ars, and an Axiom spokesperson was unable to provide a statement by publication time.
Lawmakers ask what it would take to “store” the International Space Station Read More »