Looking at Framework’s progress on software support for its repairable laptops
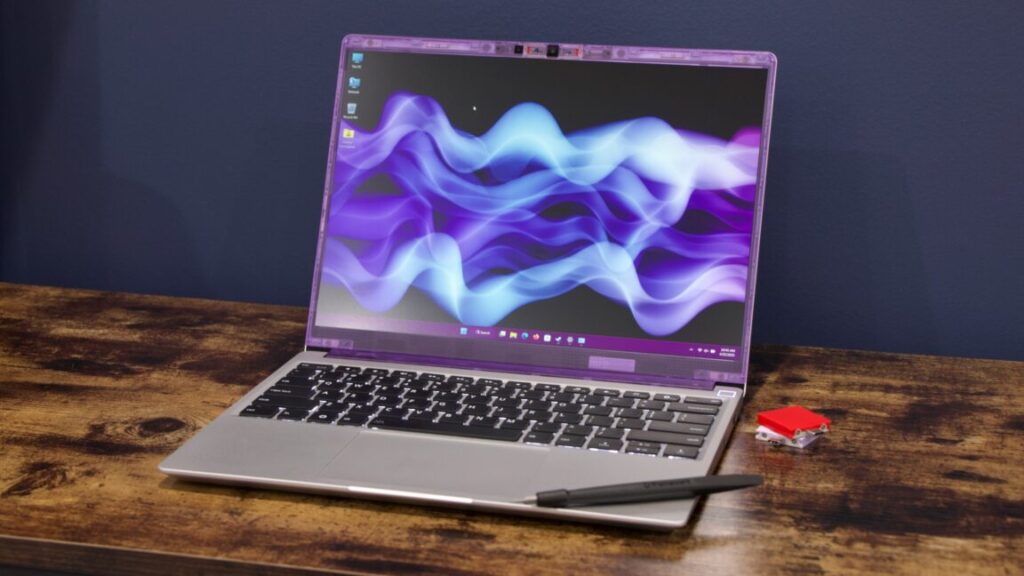
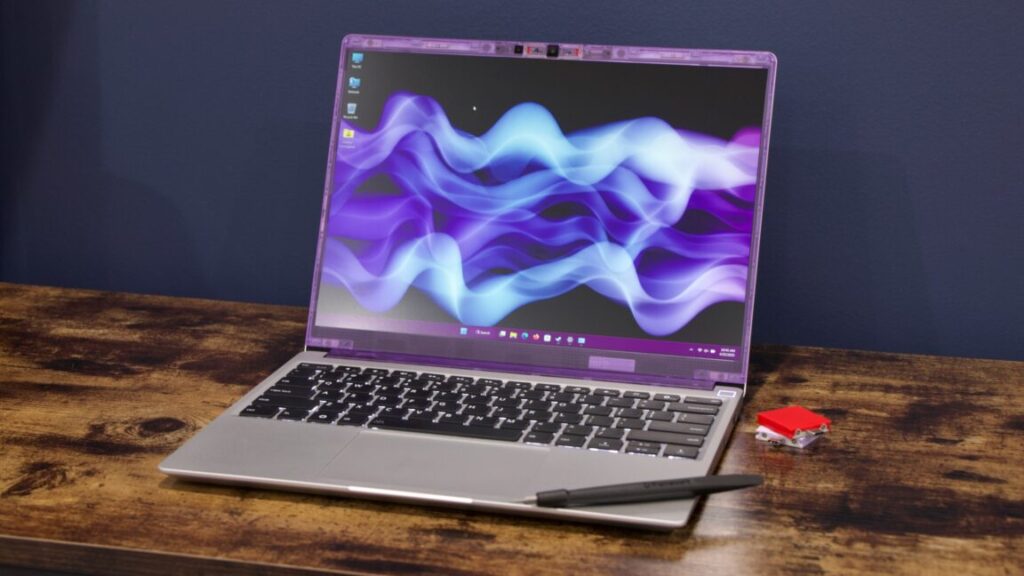
For the past five years, we’ve been paying a lot of attention to Framework, the upstart PC company focused on modular, repairable, upgradeable, and customizable laptop designs.
So far, Framework has done a solid job of offering a steady stream of hardware upgrades for its systems, particularly the original Framework Laptop 13. But the company’s track record on software support—including BIOS updates and driver updates with performance improvements, bug fixes, and important security updates—has been more of a mixed bag.
As of our piece in April 2024, multiple iterations of the Laptop 13 board had gone years without a BIOS update or updated driver package. The first iteration of the laptop still only had “beta” support for Windows 11, which had been out for 2.5 years by then, and the company was also struggling to provide Linux support and promised functional upgrades for other models.
We spoke with Framework CEO Nirav Patel for that article, who acknowledged the issues and provided some explanations—mainly, that Framework is a small company and that it relies on upstream hardware makers like Intel and AMD for some updates. But he also promised that improvements were coming.
Patel said that a dedicated team at Compal, the white-box PC manufacturing company that makes most of Framework’s hardware, had been hired and was being onboarded. And once that team was up to speed, the plan was to continuously cycle through Framework’s entire catalog of old and current products, making sure that no model was neglected for long.
Patel’s “mid-summer [2024]” timeline for making these changes turned out to be a bit optimistic, but it does seem as though the team has made real progress over the past calendar year or so.
Real improvements
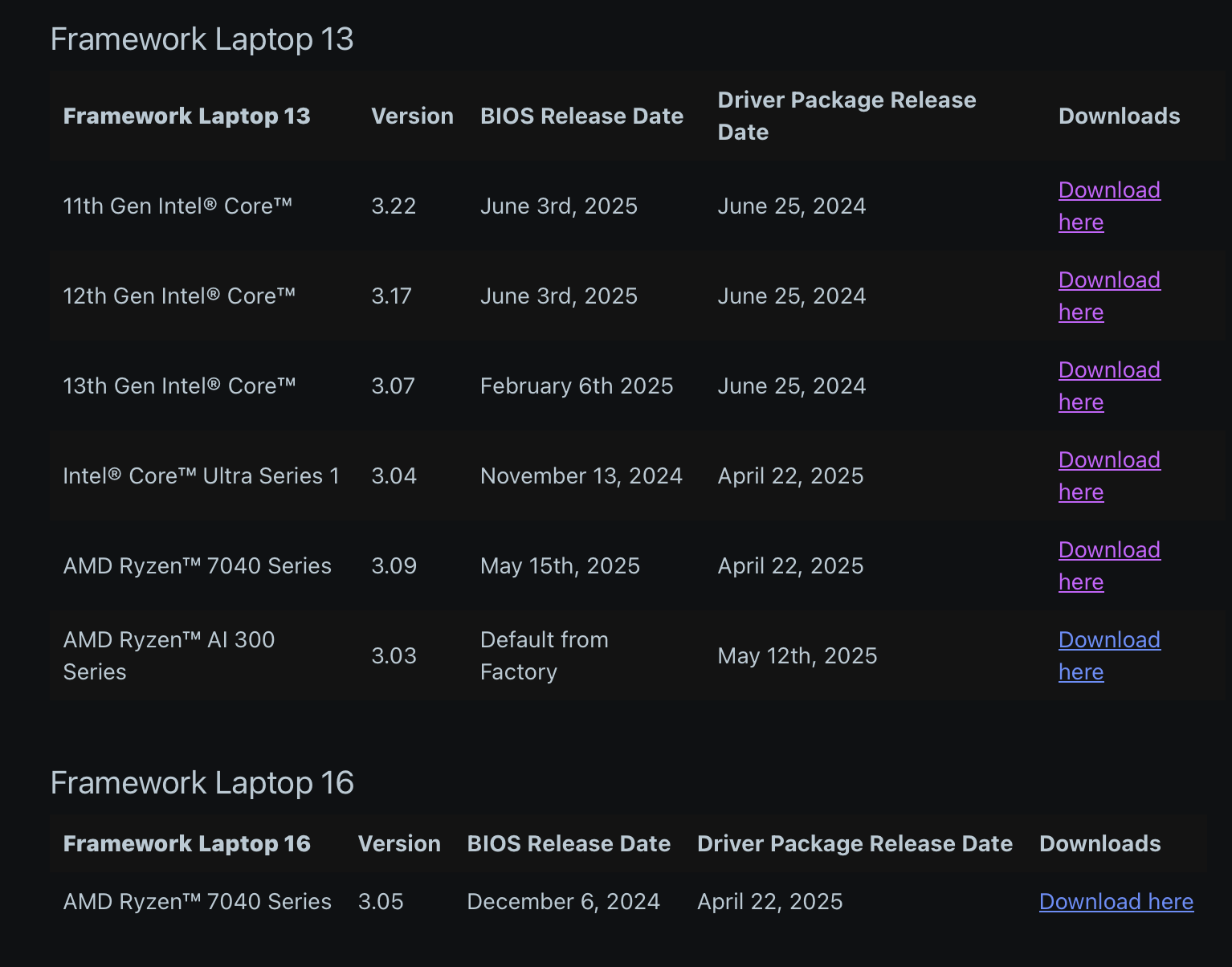
Framework’s BIOS and driver update status page as of June 25, 2025. Every single one of Framework’s laptops has gotten at least one BIOS and driver update in the past calendar year, a big improvement over the state of things in April 2024. Credit: Framework
This thread on Framework’s Reddit gives a high-level overview of the release dates for Framework’s driver packages and BIOS updates, and, for all its products going back to 2021’s 11th-gen Intel Core version of the first Framework Laptop, the company has shipped at least one BIOS update in the past eight months. Most models have seen at least one update in calendar 2025. The driver packages tend to be a bit older, but the oldest ones are from June 2024, and the Core Ultra Framework Laptop and all AMD models have gotten at least one driver package update in 2025.
Looking at Framework’s progress on software support for its repairable laptops Read More »