Mother of one of Elon Musk’s offspring sues xAI over sexualized deepfakes
The news comes as xAI and Musk have come under fire over fake sexualized images of women and children, which proliferated on the platform this year, particularly after Musk jokingly shared an AI-altered post of himself in a bikini.
Over the past week, the issue has prompted threats of fines and bans in the EU, UK, and France, as well as investigations by the California attorney-general and Britain’s Ofcom regulator. Grok has also been banned in Indonesia and Malaysia.
On Wednesday, xAI took action to restrict the image-generation function on its Grok AI model to block the chatbot from undressing users, insisting that it removed Child Sexual Abuse Material (CSAM) and non-consensual nudity material.
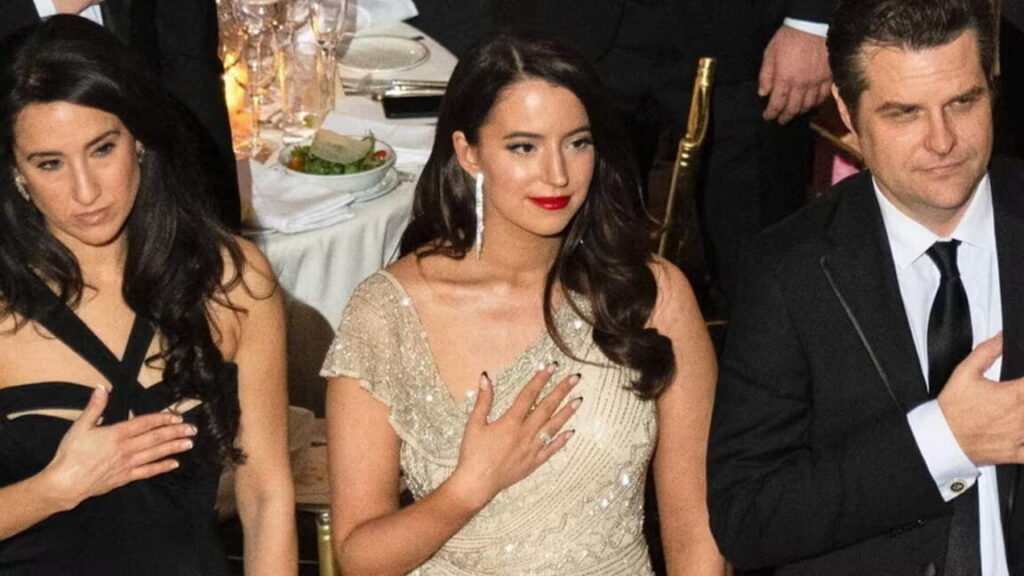
St Clair, who has in recent months been increasingly critical of Musk, is also seeking a temporary restraining order to prevent xAI from generating images that undress her.
“Ms St Clair is humiliated, depressed, fearful for her life, angry and desperately in need of action from this court to protect her against xAI’s facilitation of this unfathomable nightmare,” lawyers wrote in a filing seeking the restraining order.
xAI filed a lawsuit against St Clair in Texas on Thursday, claiming she had breached the company’s terms of service by bringing her lawsuit against the company in a New York court instead of in Texas.
Earlier this week, Musk also said on X that he would be filing for “full custody” of their 1-year-old son Romulus, after St Clair apologized for sharing posts critical of transgender people in the past. Musk, who has a transgender child, has repeatedly been critical of transgender people and the rights of trans individuals.
Additional reporting by Kaye Wiggins in New York.
© 2026 The Financial Times Ltd. All rights reserved Not to be redistributed, copied, or modified in any way.
Mother of one of Elon Musk’s offspring sues xAI over sexualized deepfakes Read More »