Matrix multiplication breakthrough could lead to faster, more efficient AI models
The Matrix Revolutions —
At the heart of AI, matrix math has just seen its biggest boost “in more than a decade.”

Enlarge / When you do math on a computer, you fly through a numerical tunnel like this—figuratively, of course.
Computer scientists have discovered a new way to multiply large matrices faster than ever before by eliminating a previously unknown inefficiency, reports Quanta Magazine. This could eventually accelerate AI models like ChatGPT, which rely heavily on matrix multiplication to function. The findings, presented in two recent papers, have led to what is reported to be the biggest improvement in matrix multiplication efficiency in over a decade.
Multiplying two rectangular number arrays, known as matrix multiplication, plays a crucial role in today’s AI models, including speech and image recognition, chatbots from every major vendor, AI image generators, and video synthesis models like Sora. Beyond AI, matrix math is so important to modern computing (think image processing and data compression) that even slight gains in efficiency could lead to computational and power savings.
Graphics processing units (GPUs) excel in handling matrix multiplication tasks because of their ability to process many calculations at once. They break down large matrix problems into smaller segments and solve them concurrently using an algorithm.
Perfecting that algorithm has been the key to breakthroughs in matrix multiplication efficiency over the past century—even before computers entered the picture. In October 2022, we covered a new technique discovered by a Google DeepMind AI model called AlphaTensor, focusing on practical algorithmic improvements for specific matrix sizes, such as 4×4 matrices.
By contrast, the new research, conducted by Ran Duan and Renfei Zhou of Tsinghua University, Hongxun Wu of the University of California, Berkeley, and by Virginia Vassilevska Williams, Yinzhan Xu, and Zixuan Xu of the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (in a second paper), seeks theoretical enhancements by aiming to lower the complexity exponent, ω, for a broad efficiency gain across all sizes of matrices. Instead of finding immediate, practical solutions like AlphaTensor, the new technique addresses foundational improvements that could transform the efficiency of matrix multiplication on a more general scale.
Approaching the ideal value
The traditional method for multiplying two n-by-n matrices requires n³ separate multiplications. However, the new technique, which improves upon the “laser method” introduced by Volker Strassen in 1986, has reduced the upper bound of the exponent (denoted as the aforementioned ω), bringing it closer to the ideal value of 2, which represents the theoretical minimum number of operations needed.
The traditional way of multiplying two grids full of numbers could require doing the math up to 27 times for a grid that’s 3×3. But with these advancements, the process is accelerated by significantly reducing the multiplication steps required. The effort minimizes the operations to slightly over twice the size of one side of the grid squared, adjusted by a factor of 2.371552. This is a big deal because it nearly achieves the optimal efficiency of doubling the square’s dimensions, which is the fastest we could ever hope to do it.
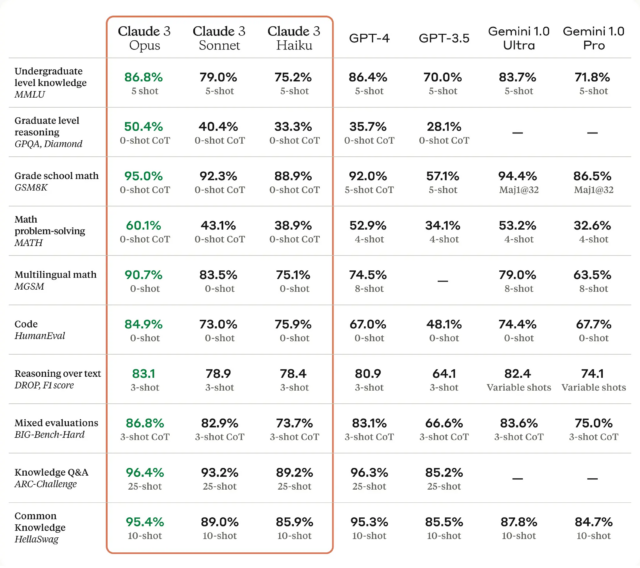
Here’s a brief recap of events. In 2020, Josh Alman and Williams introduced a significant improvement in matrix multiplication efficiency by establishing a new upper bound for ω at approximately 2.3728596. In November 2023, Duan and Zhou revealed a method that addressed an inefficiency within the laser method, setting a new upper bound for ω at approximately 2.371866. The achievement marked the most substantial progress in the field since 2010. But just two months later, Williams and her team published a second paper that detailed optimizations that reduced the upper bound for ω to 2.371552.
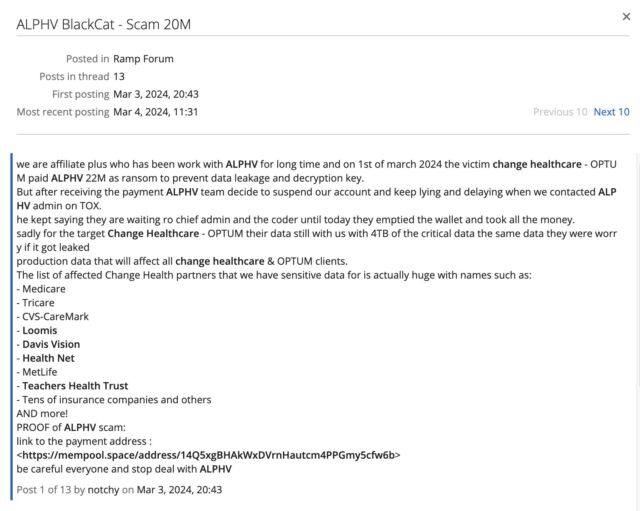
The 2023 breakthrough stemmed from the discovery of a “hidden loss” in the laser method, where useful blocks of data were unintentionally discarded. In the context of matrix multiplication, “blocks” refer to smaller segments that a large matrix is divided into for easier processing, and “block labeling” is the technique of categorizing these segments to identify which ones to keep and which to discard, optimizing the multiplication process for speed and efficiency. By modifying the way the laser method labels blocks, the researchers were able to reduce waste and improve efficiency significantly.
While the reduction of the omega constant might appear minor at first glance—reducing the 2020 record value by 0.0013076—the cumulative work of Duan, Zhou, and Williams represents the most substantial progress in the field observed since 2010.
“This is a major technical breakthrough,” said William Kuszmaul, a theoretical computer scientist at Harvard University, as quoted by Quanta Magazine. “It is the biggest improvement in matrix multiplication we’ve seen in more than a decade.”
While further progress is expected, there are limitations to the current approach. Researchers believe that understanding the problem more deeply will lead to the development of even better algorithms. As Zhou stated in the Quanta report, “People are still in the very early stages of understanding this age-old problem.”
So what are the practical applications? For AI models, a reduction in computational steps for matrix math could translate into faster training times and more efficient execution of tasks. It could enable more complex models to be trained more quickly, potentially leading to advancements in AI capabilities and the development of more sophisticated AI applications. Additionally, efficiency improvement could make AI technologies more accessible by lowering the computational power and energy consumption required for these tasks. That would also reduce AI’s environmental impact.
The exact impact on the speed of AI models depends on the specific architecture of the AI system and how heavily its tasks rely on matrix multiplication. Advancements in algorithmic efficiency often need to be coupled with hardware optimizations to fully realize potential speed gains. But still, as improvements in algorithmic techniques add up over time, AI will get faster.
Matrix multiplication breakthrough could lead to faster, more efficient AI models Read More »