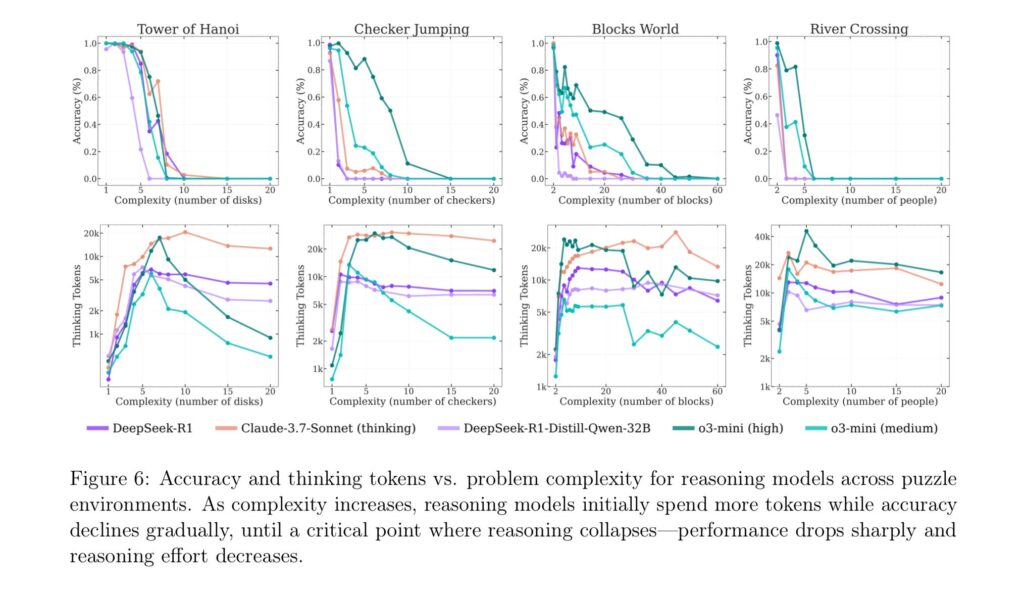
Analyst: M5 Vision Pro, Vision Air, and smart glasses coming in 2026–2028
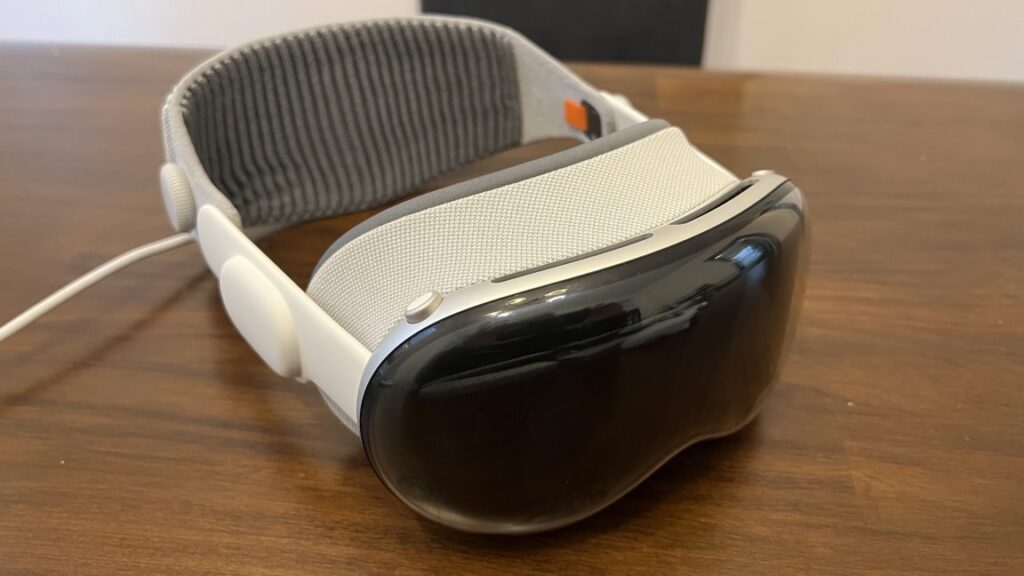
Apple is also reportedly planning a “Vision Air” product, with production expected to start in Q3 2027. Kuo says it will be more than 40 percent lighter than the first-generation Vision Pro, and that it will include Apple’s flagship iPhone processor instead the more robust Mac processor found in the Vision Pro—all at a “significantly lower price than Vision Pro.” The big weight reduction is “achieved through glass-to-plastic replacement, extensive magnesium alloy use (titanium alloy deemed too expensive), and reduced sensor count.”
True smart glasses in 2027
The Vision Pro (along with the planned Vision Air) is a fully immersive VR headset that supports augmented reality by displaying the wearer’s surroundings on the internal screens based on what’s captured by 3D cameras on the outside of the device. That allows for some neat applications, but it also means the device is bulky and impractical to wear in public.
The real dream for many is smart glasses that are almost indistinguishable from normal glasses, but which display some of the same AR content as the Vision Pro on transparent lenses instead of via a camera-to-screen pipeline.
Apple is also planning to roll that out, Kuo says. But first, mass production of display-free “Ray-Ban-like” glasses is scheduled for Q2 2027, and Kuo claims Apple plans to ship between 3 million and 5 million units through 2027, suggesting the company expects this form factor to make a much bigger impact than the Vision Pro’s VR-like HMD approach.
The glasses would have a “voice control and gesture recognition user interface” but no display functionality at all. Instead, “core features include: audio playback, camera, video recording, and AI environmental sensing.”
The actual AR glasses would come later, in 2028.
Analyst: M5 Vision Pro, Vision Air, and smart glasses coming in 2026–2028 Read More »