Amazon Alexa+ released to the general public via an early access website
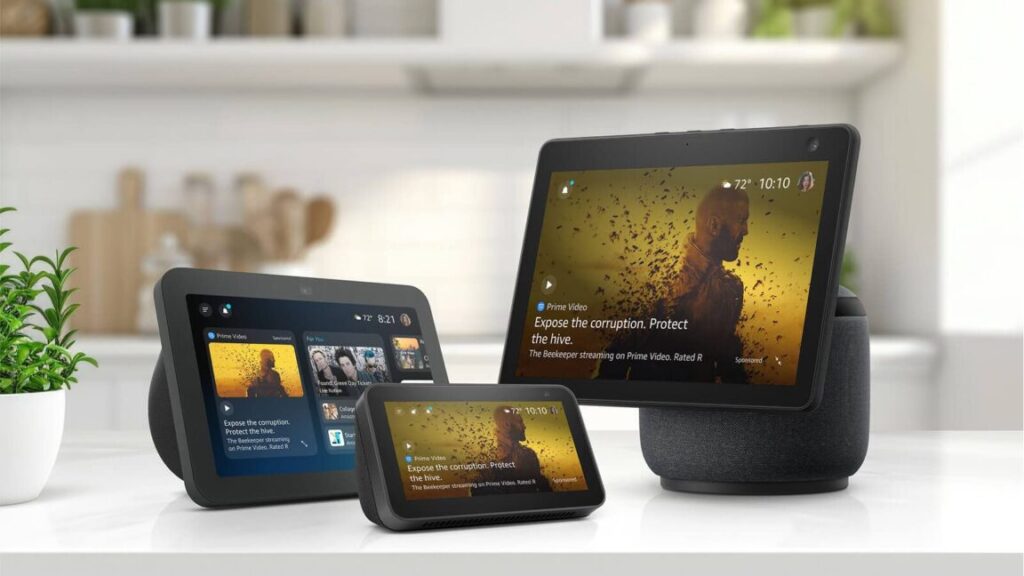
Anyone can now try Alexa+, Amazon’s generative AI assistant, through a free early access program at Alexa.com. The website frees the AI, which Amazon released via early access in February, from hardware and makes it as easily accessible as more established chatbots, like OpenAI’s ChatGPT and Google’s Gemini.
Until today, you needed a supporting device to access Alexa+. Amazon hasn’t said when the early access period will end, but when it does, Alexa+ will be included with Amazon Prime memberships, which start at $15 per month, or cost $20 per month on its own.
The above pricing suggests that Amazon wants Alexa+ to drive people toward Prime subscriptions. By being interwoven with Amazon’s shopping ecosystem, including Amazon’s e-commerce platform, grocery delivery business, and Whole Foods, Alexa+ can make more money for Amazon.
Just like it has with Alexa+ on devices, Amazon is pushing Alexa.com as a tool for people to organize and manage their household. Amazon’s announcement of Alexa.com today emphasizes Alexa+’s features for planning trips and meals, to-do lists, calendars, and smart homes. Alexa.com “also provides persistent context and continuity, allowing you to access Alexa on whichever device or interface best serves the task at hand, with all previous chats, preferences, and personalization” carrying over, Amazon said.
Amazon already knew a browser-based version of Alexa would be helpful. Alexa was available via Alexa.Amazon.com until around the time Amazon started publicly discussing a generative AI version of Alexa in 2023. Alexa+ is now accessible through Alexa.Amazon.com (in addition to Alexa.com).
“This is a new interaction model and adds a powerful way to use and collaborate with Alexa+,” Amazon said today. “Combined with the redesigned Alexa mobile app, which will feature an agent-forward design, Alexa+ will be accessible across every surface—whether you’re at your desk, on the go, or at home.”
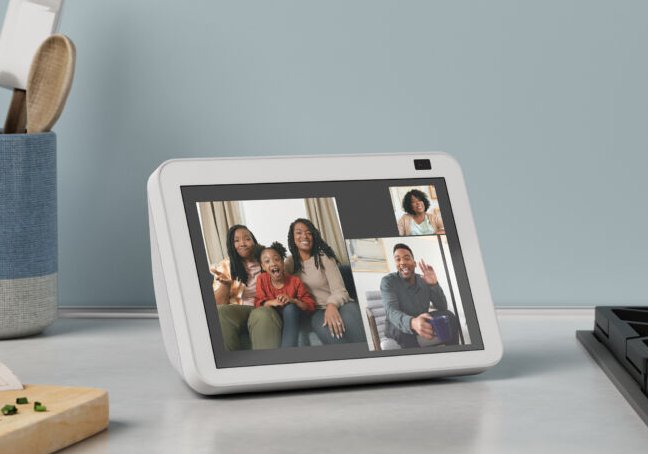
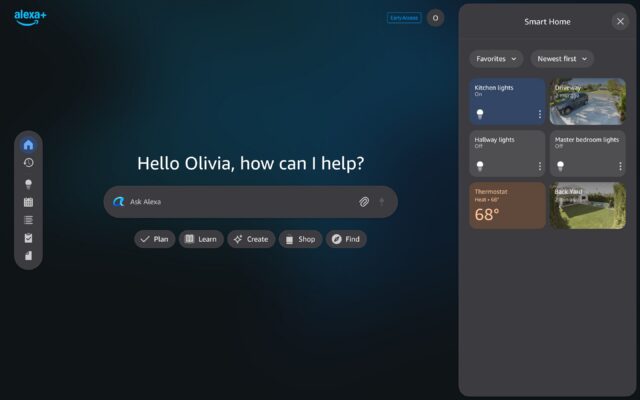
Amazon provided this example of someone using the Alexa+ website to manage smart home devices. Credit: Amazon
Alexa has largely been reported to cost Amazon billions of dollars, despite Amazon’s claim that 600 million Alexa-powered devices have been sold. By incorporating more powerful and generative AI-based features and a subscription fee, Amazon hopes people will use Alexa+ more frequently and for more advanced and essential tasks, resulting in the financial success that has eluded the original Alexa. Amazon is also considering injecting ads into Alexa+ conversations.
Notably, ahead of its final release and while still in early access, Alexa+ has been reported to be slower than expected and struggle with inaccuracies at times. It also lacks some features that Amazon executives have previously touted, like the ability to order takeout.
Amazon Alexa+ released to the general public via an early access website Read More »