Vision Pro M5 review: It’s time for Apple to make some tough choices
A state of the union from someone who actually sort of uses the thing.
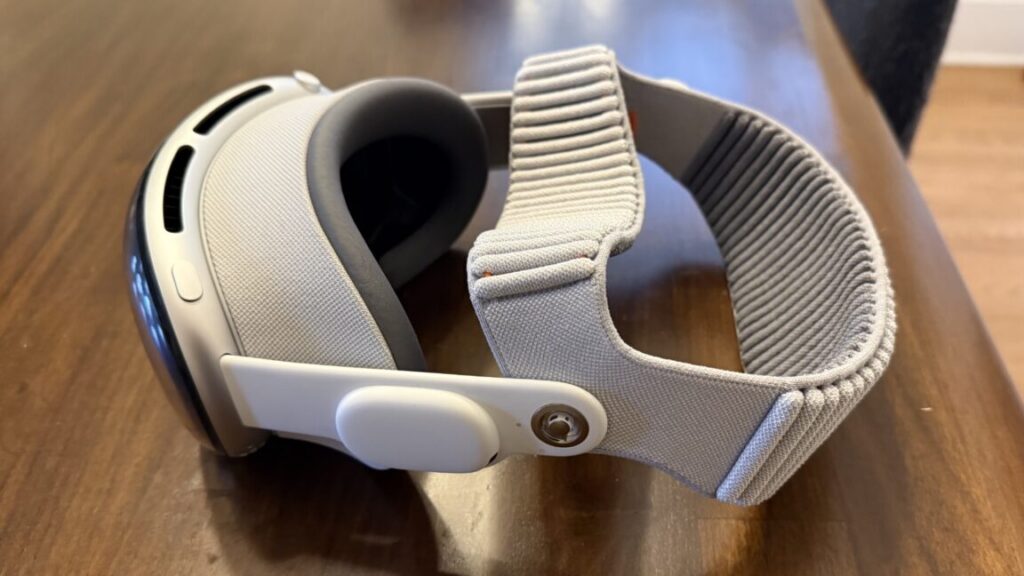
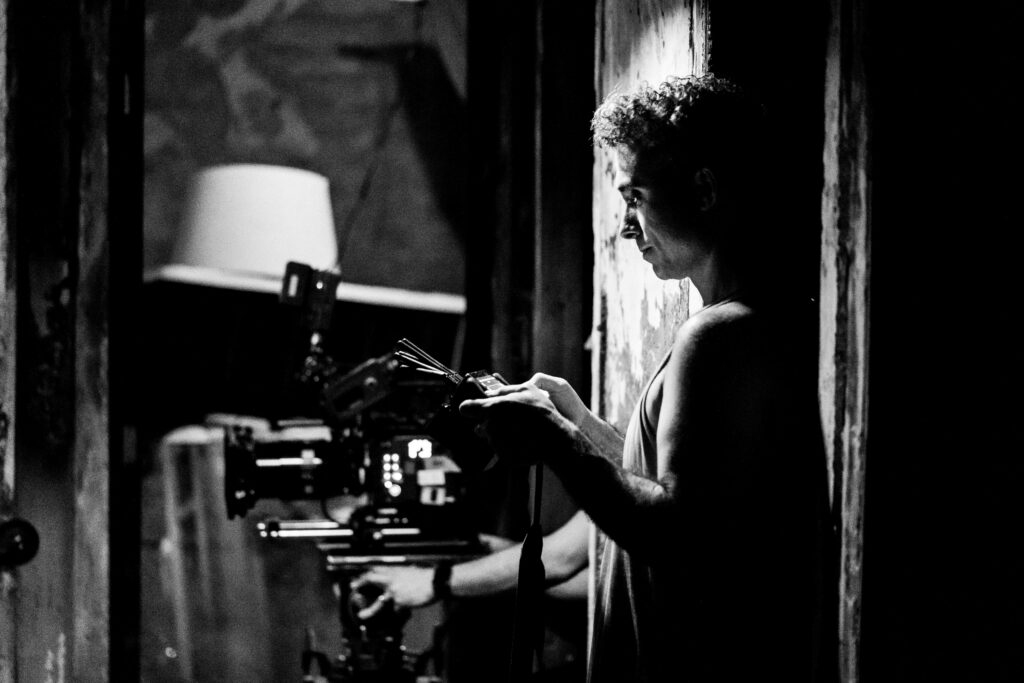
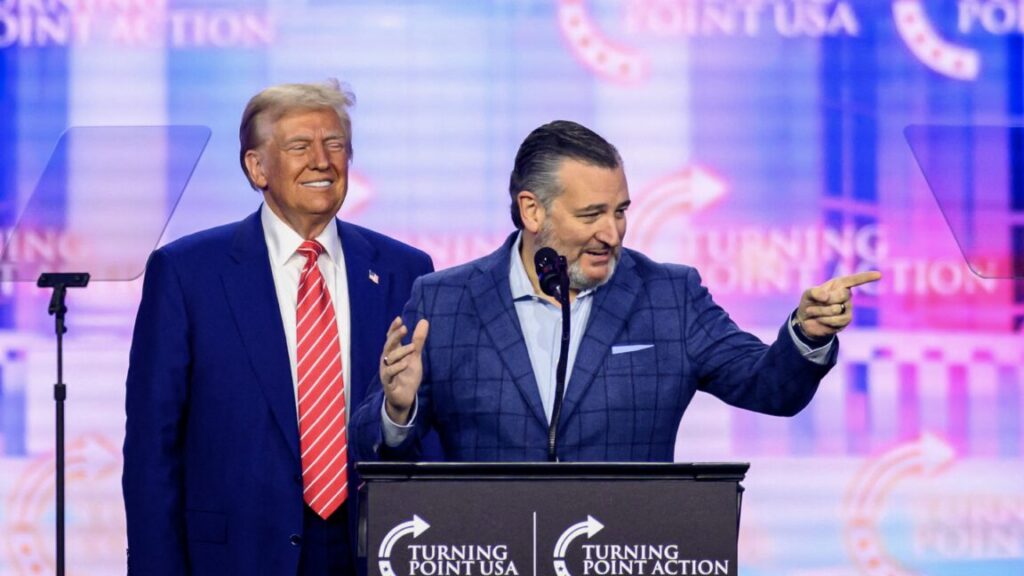
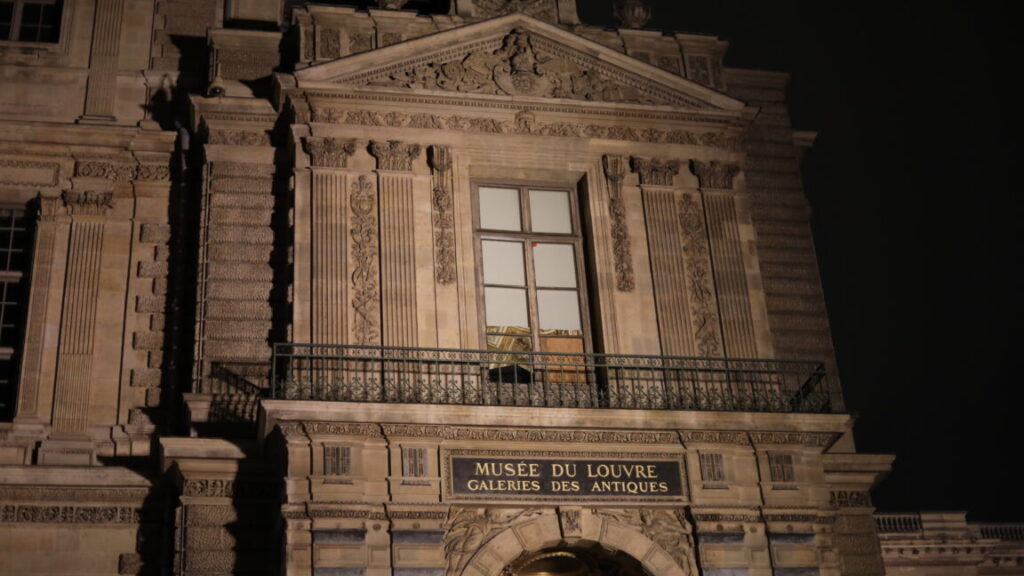
The M5 Vision Pro with the Dual Knit Band. Credit: Samuel Axon
With the recent releases of visionOS 26 and newly refreshed Vision Pro hardware, it’s an ideal time to check in on Apple’s Vision Pro headset—a device I was simultaneously amazed and disappointed by when it launched in early 2024.
I still like the Vision Pro, but I can tell it’s hanging on by a thread. Content is light, developer support is tepid, and while Apple has taken action to improve both, it’s not enough, and I’m concerned it might be too late.
When I got a Vision Pro, I used it a lot: I watched movies on planes and in hotel rooms, I walked around my house placing application windows and testing out weird new ways of working. I tried all the neat games and educational apps, and I watched all the immersive videos I could get ahold of. I even tried my hand at developing my own applications for it.
As the months went on, though, I used it less and less. The novelty wore off, and as cool as it remained, practicality beat coolness. By the time Apple sent me the newer model a couple of weeks ago, I had only put the original one on a few times in the prior couple of months. I had mostly stopped using it at home, but I still took it on trips as an entertainment device for hotel rooms now and then.
That’s not an uncommon story. You even see it in the subreddit for Vision Pro owners, which ought to be the home of the device’s most dedicated fans. Even there, people say, “This is really cool, but I have to go out of my way to keep using it.”
Perhaps it would have been easier to bake it into my day-to-day habits if developer and content creator support had been more robust, a classic chicken-and-egg problem.
After a few weeks of using the new Vision Pro hardware refresh daily, it’s clear to me that the platform needs a bigger rethink. As a fan of the device, I’m concerned it won’t get that, because all the rumors point to Apple pouring its future resources into smart glasses, which, to me, are a completely different product category.
What changed in the new model?
For many users, the most notable change here will be something you can buy separately (albeit at great expense) for the old model: A new headband that balances the device’s weight on your head better, making it more comfortable to wear for long sessions.
Dubbed the Dual Knit Band, it comes with an ingeniously simple adjustment knob that can be used to tighten or loosen either the band that goes across the back of your head (similar to the old band) or the one that wraps around the top.
It’s well-designed, and it will probably make the Vision Pro easier to use for many people who found the old model to be too uncomfortable—even though this model is slightly heavier than its predecessor.
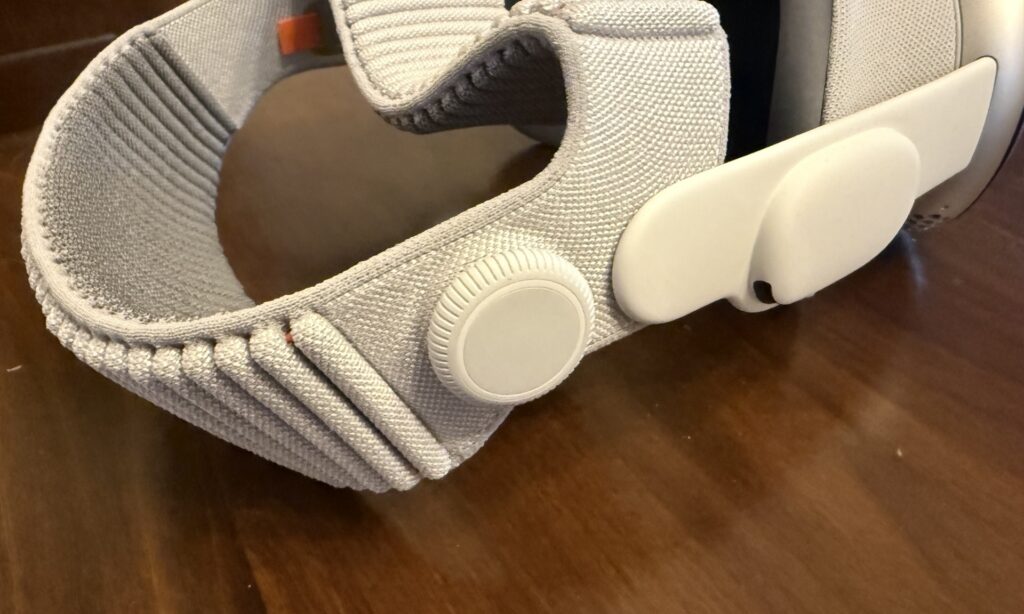

The band fit is adjusted with this knob. You can turn it to loosen or tighten one strap, then pull it out and turn it again to adjust the other. Credit: Samuel Axon
I’m one of the lucky few who never had any discomfort problems with the Vision Pro, but I know a bunch of folks who said the pressure the device put on their foreheads was unbearable. That’s exactly what this new band remedies, so it’s nice to see.
The M5 chip offers more than just speed
Whereas the first Vision Pro had Apple’s M2 chip—which was already a little behind the times when it launched—the new one adds the M5. It’s much faster, especially for graphics-processing and machine-learning tasks. We’ve written a lot about the M5 in our articles on other Apple products if you’re interested to learn more about it.
Functionally, this means a lot of little things are a bit faster, like launching certain applications or generating a Persona avatar. I’ll be frank: I didn’t notice any difference that significantly impacted the user experience. I’m not saying I couldn’t tell it was faster sometimes. I’m just saying it wasn’t faster in a way that’s meaningful enough to change any attitudes about the device.
It’s most noticeable with games—both native mixed-reality Vision Pro titles and the iPad versions of demanding games that you can run on a virtual display on the device. Demanding 3D games look and run nicer, in many cases. The M5 also supports more recent graphics advancements like ray tracing and mesh shading, though very few games support them, even in terms of iPad versions.
All this is to say that while I always welcome performance improvements, they are definitely not enough to convince an M2 Vision Pro owner to upgrade, and they won’t tip things over for anyone who has been on the fence about buying one of these things.
The main perk of the new chip is improved efficiency, which is the driving force behind modestly increased battery life. When I first took the M2 Vision Pro on a plane, I tried watching 2021’s Dune. I made it through the movie, but just barely; the battery ran out during the closing credits. It’s not a short movie, but there are longer ones.
Now, the new headset can easily get another 30 or 60 minutes, depending on what you’re doing, which finally puts it in “watch any movie you want” territory.
Given how short battery life was in the original version, even a modest bump like that makes a big difference. That, alongside a marginally increased field of view (about 10 percent) and a new 120 Hz maximum refresh rate for passthrough are the best things about the new hardware. These are nice-to-haves, but they’re not transformational by any means.
We already knew the Vision Pro offered excellent hardware (even if it’s overkill for most users), but the platform’s appeal is really driven by software. Unfortunately, this is where things are running behind expectations.
For content, it’s quality over quantity
When the first Vision Pro launched, I was bullish about the promise of the platform—but a lot of that was contingent on a strong content cadence and third-party developer support.
And as I’ve written since, the content cadence for the first year was a disappointment. Whereas I expected weekly episodes of Apple’s Immersive Videos in the TV app, those short videos arrived with gaps of several months. There’s an enormous wealth of great immersive content outside of Apple’s walled garden, but Apple didn’t seem interested in making that easily accessible to Vision Pro owners. Third-party apps did some of that work, but they lagged behind those on other platforms.
The first-party content cadence picked up after the first year, though. Plus, Apple introduced the Spatial Gallery, a built-in app that aggregates immersive 3D photos and the like. It’s almost TikTok-like in that it lets you scroll through short-form content that leverages what makes the device unique, and it’s exactly the sort of thing that the platform so badly needed at launch.
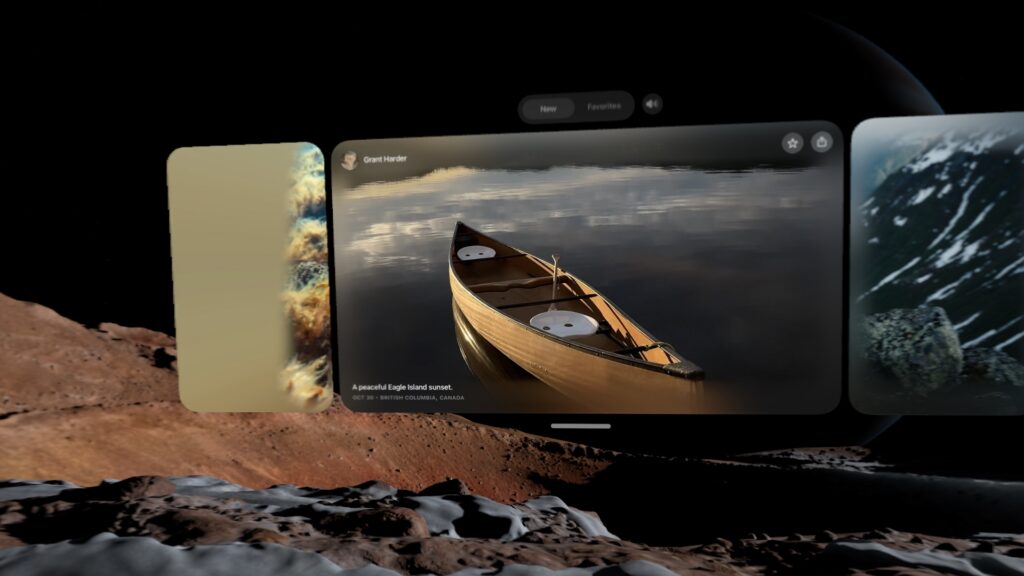
The Spatial Gallery is sort of like a horizontally-scrolling TikTok for 3D photos and video. Credit: Samuel Axon
The content that is there—whether in the TV app or the Spatial Gallery—is fantastic. It’s beautifully, professionally produced stuff that really leans on the hardware. For example, there is an autobiographical film focused on U2’s Bono that does some inventive things with the format that I had never seen or even imagined before.
Bono, of course, isn’t everybody’s favorite, but if you can stomach the film’s bloviating, it’s worth watching just with an eye to what a spatial video production can or should be.
I still think there’s significant room to grow, but the content situation is better than ever. It’s not enough to keep you entertained for hours a day, but it’s enough to make putting on the headset for a bit once a week or so worth it. That wasn’t there a year ago.
The software support situation is in a similar state.
App support is mostly frozen in the year 2024
Many of us have a suite of go-to apps that are foundational to our individual approaches to daily productivity. For me, primarily a macOS user, they are:
- Firefox
- Spark
- Todoist
- Obsidian
- Raycast
- Slack
- Visual Studio Code
- Claude
- 1Password
As you can see, I don’t use most of Apple’s built-in apps—no Safari, no Mail, no Reminders, no Passwords, no Notes… no Spotlight, even. All that may be atypical, but it has never been a problem on macOS, nor has it been on iOS for a few years now.
Impressively, almost all of these are available on visionOS—but only because it can run iPad apps as flat, virtual windows. Firefox, Spark, Todoist, Obsidian, Slack, 1Password, and even Raycast are all available as supported iPad apps, but surprisingly, Claude isn’t, even though there is a Claude app for iPads. (ChatGPT’s iPad app works, though.) VS Code isn’t available, of course, but I wasn’t expecting it to be.
Not a single one of these applications has a true visionOS app. That’s too bad, because I can think of lots of neat things spatial computing versions could do. Imagine browsing your Obsidian graph in augmented reality! Alas, I can only dream.

You can tell the native apps from the iPad ones: The iPad ones have rectangular icons nested within circles, whereas the native apps fill the whole circle. Credit: Samuel Axon
If you’re not such a huge productivity software geek like me and you use Apple’s built-in apps, things look a little better, but surprisingly, there are still a few apps that you would imagine would have really cool spatial computing features—like Apple Maps—that don’t. Maps, too, is just an iPad app.
Even if you set productivity aside and focus on entertainment, there are still frustrating gaps. Almost two years later, there is still no Netflix or YouTube app. There are decent-enough third-party options for YouTube, but you have to watch Netflix in a browser, which is lower-quality than in a native app and looks horrible on one of the Vision Pro’s big virtual screens.
To be clear, there is a modest trickle of interesting spatial app experiences coming in—most of them games, educational apps, or cool one-off ideas that are fun to check out for a few minutes.
All this is to say that nothing has really changed since February 2024. There was an influx of apps at launch that included a small number of show-stoppers (mostly educational apps), but the rest ranged from “basically the iPad app but with one or two throwaway tech-demo-style spatial features you won’t try more than once” to “basically the iPad app but a little more native-feeling” to “literally just the iPad app.” As far as support from popular, cross-platform apps, it’s mostly the same list today as it was then.
Its killer app is that it’s a killer monitor
Even though Apple hasn’t made a big leap forward in developer support, it has made big strides in making the Vision Pro a nifty companion to the Mac.
From the start, it has had a feature that lets you simply look at a Mac’s built-in display, tap your fingers, and launch a large, resizable virtual monitor. I have my own big, multi-monitor setup at home, but I have used the Vision Pro this way sometimes when traveling.
I had some complaints at the start, though. It could only do one monitor, and that monitor was limited to 60 Hz and a standard widescreen resolution. That’s better than just using a 14-inch MacBook Pro screen, but it’s a far cry from the sort of high-end setup a $3,500 price tag suggests. Furthermore, it didn’t allow you to switch audio between the two devices.
Thanks to both software and hardware updates, that has all changed. visionOS now supports three different monitor sizes: the standard widescreen aspect ratio, a wider one that resembles a standard ultra-wide monitor, and a gigantic, ultra-ultra-wide wrap-around display that I can assure you will leave no one wanting for desktop space. It looks great. Problem solved! Likewise, it will now transfer your Mac audio to the Vision Pro or its Bluetooth headphones automatically.
All of that works not just on the new Vision Pro, but also on the M2 model. The new M5 model exclusively addresses the last of my complaints: You can now achieve higher refresh rates for that virtual monitor than 60 Hz. Apple says it goes “up to 120 Hz,” but there’s no available tool for measuring exactly where it’s landing. Still, I’m happy to see any improvement here.
This is the standard width for the Mac monitor feature… Samuel Axon
Through a series of updates, Apple has turned a neat proof-of-concept feature into something that is genuinely valuable—especially for folks who like ultra-wide or multi-monitor setups but have to travel a lot (like myself) or who just don’t want to invest in the display hardware at home.
You can also play your Mac games on this monitor. I tried playing No Man’s Sky and Cyberpunk 2077 on it with a controller, and it was a fantastic experience.
This, alongside spatial video and watching movies, is the Vision Pro’s current killer app and one of the main areas where Apple has clearly put a lot of effort into improving the platform.
Stop trying to make Personas happen
Strangely, another area where Apple has invested quite a bit to make things better is in the Vision Pro’s usefulness as a communications and meetings device. Personas—the 3D avatars of yourself that you create for Zoom calls and the like—were absolutely terrible when the M2 Vision Pro came out.
There is also EyeSight, which uses your Persona to show a simulacrum of your eyes to people around you in the real world, letting them know you are aware of your surroundings and even allowing them to follow your gaze. I understand the thought behind this feature—Apple doesn’t want mixed reality to be socially isolating—but it sometimes puts your eyes in the wrong place, it’s kind of hard to see, and it honestly seems like a waste of expensive hardware.
Primarily via software updates, I’m pleased to report that Personas are drastically improved. Mine now actually looks like me, and it moves more naturally, too.
I joined a FaceTime call with Apple reps where they showed me how Personas float and emote around each other, and how we could look at the same files and assets together. It was indisputably cool and way better than before, thanks to the improved Personas.
I can’t say as much for EyeSight, which looks the same. It’s hard for me to fathom that Apple has put multiple sensors and screens on this thing to support this feature.
In my view, dropping EyeSight would be the single best thing Apple could do for this headset. Most people don’t like it, and most people don’t want it, yet there is no question that its inclusion adds a not-insignificant amount to both the price and the weight, the product’s two biggest barriers to adoption.
Likewise, Personas are theoretically cool, and it is a novel and fun experience to join a FaceTime call with people and see how it works and what you could do. But it’s just that: a novel experience. Once you’ve done it, you’ll never feel the need to do it again. I can barely imagine anyone who would rather show up to a call as a Persona than take the headset off for 30 minutes to dial in on their computer.
Much of this headset is dedicated to this idea that it can be a device that connects you with others, but maintaining that priority is simply the wrong decision. Mixed reality is isolating, and Apple is treating that like a problem to be solved, but I consider that part of its appeal.
If this headset were capable of out-in-the-world AR applications, I would not feel that way, but the Vision Pro doesn’t support any application that would involve taking it outside the home into public spaces. A lot of the cool, theoretical AR uses I can think of would involve that, but still no dice here.
The metaverse (it’s telling that this is the first time I’ve typed that word in at least a year) already exists: It’s on our phones, in Instagram and TikTok and WeChat and Fortnite. It doesn’t need to be invented, and it doesn’t need a new, clever approach to finally make it take off. It has already been invented. It’s already in orbit.
Like the iPad and the Apple Watch before it, the Vision Pro needs to stop trying to be a general-purpose device and instead needs to lean into what makes it special.
In doing so, it will become a better user experience, and it will get lighter and cheaper, too. There’s real potential there. Unfortunately, Apple may not go that route if leaks and insider reports are to be believed.
There’s still a ways to go, so hopefully this isn’t a dead end
The M5 Vision Pro was the first of four planned new releases in the product line, according to generally reliable industry analyst Ming-Chi Kuo. Next up, he predicted, would be a full Vision Pro 2 release with a redesign, and a Vision Air, a cheaper, lighter alternative. Those would all precede true smart glasses many years down the road.
I liked that plan: keep the full-featured Vision Pro for folks who want the most premium mixed reality experience possible (but maybe drop EyeSight), and launch a cheaper version to compete more directly with headsets like Meta’s Quest line of products, or the newly announced Steam Frame VR headset from Valve, along with planned competitors by Google, Samsung, and others.
True augmented reality glasses are an amazing dream, but there are serious problems of optics and user experience that we’re still a ways off from solving before those can truly replace the smartphone as Tim Cook once predicted.
All that said, it looks like that plan has been called into question. A Bloomberg report in October claimed that Apple CEO Tim Cook had told employees that the company was redirecting resources from future passthrough HMD products to accelerate work on smart glasses.
Let’s be real: It’s always going to be a once-in-a-while device, not a daily driver. For many people, that would be fine if it cost $1,000. At $3,500, it’s still a nonstarter for most consumers.
I believe there is room for this product in the marketplace. I still think it’s amazing. It’s not going to be as big as the iPhone, or probably even the iPad, but it has already found a small audience that could grow significantly if the price and weight could come down. Removing all the hardware related to Personas and EyeSight would help with that.
I hope Apple keeps working on it. When Apple released the Apple Watch, it wasn’t entirely clear what its niche would be in users’ lives. The answer (health and fitness) became crystal clear over time, and the other ambitions of the device faded away while the company began building on top of what was working best.
You see Apple doing that a little bit with the expanded Mac spatial display functionality. That can be the start of an intriguing journey. But writers have a somewhat crass phrase: “kill your darlings.” It means that you need to be clear-eyed about your work and unsentimentally cut anything that’s not working, even if you personally love it—even if it was the main thing that got you excited about starting the project in the first place.
It’s past time for Apple to start killing some darlings with the Vision Pro, but I truly hope it doesn’t go too far and kill the whole platform.
Samuel Axon is the editorial lead for tech and gaming coverage at Ars Technica. He covers AI, software development, gaming, entertainment, and mixed reality. He has been writing about gaming and technology for nearly two decades at Engadget, PC World, Mashable, Vice, Polygon, Wired, and others. He previously ran a marketing and PR agency in the gaming industry, led editorial for the TV network CBS, and worked on social media marketing strategy for Samsung Mobile at the creative agency SPCSHP. He also is an independent software and game developer for iOS, Windows, and other platforms, and he is a graduate of DePaul University, where he studied interactive media and software development.
Vision Pro M5 review: It’s time for Apple to make some tough choices Read More »