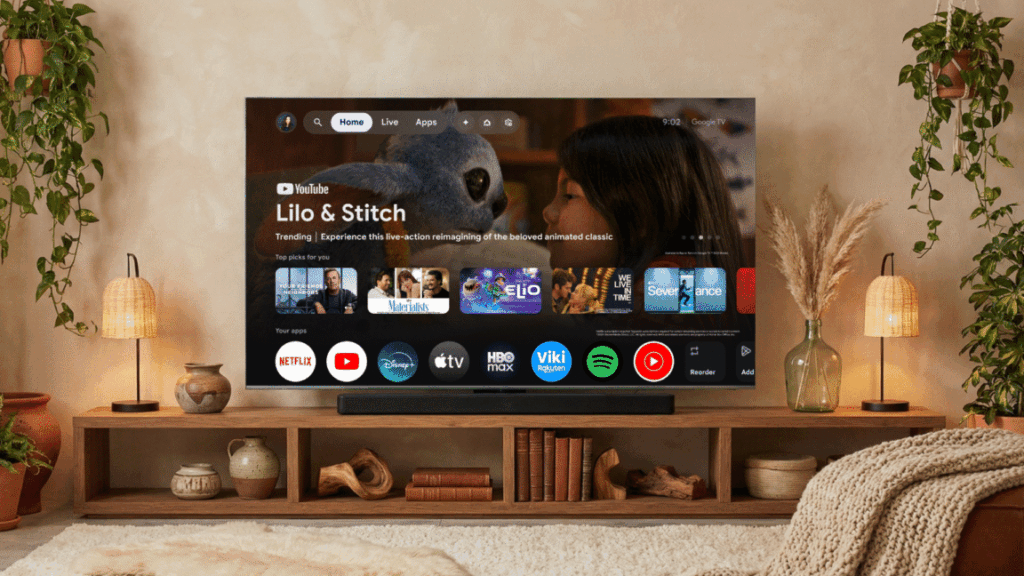
Google TV’s big Gemini update adds image and video generation, voice control for settings
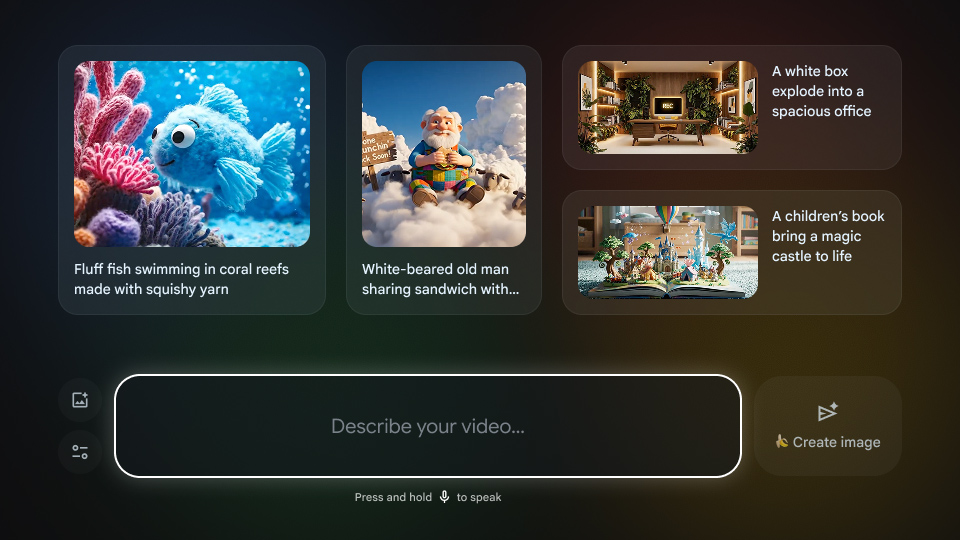
That might be a fun distraction, but it’s not a core TV experience. Google’s image and video models are good enough that you might gain some benefit from monkeying around with them on a larger screen, but Gemini is also available for more general tasks.
Google TV will support generating new images and videos with Google’s AI models. Credit: Google
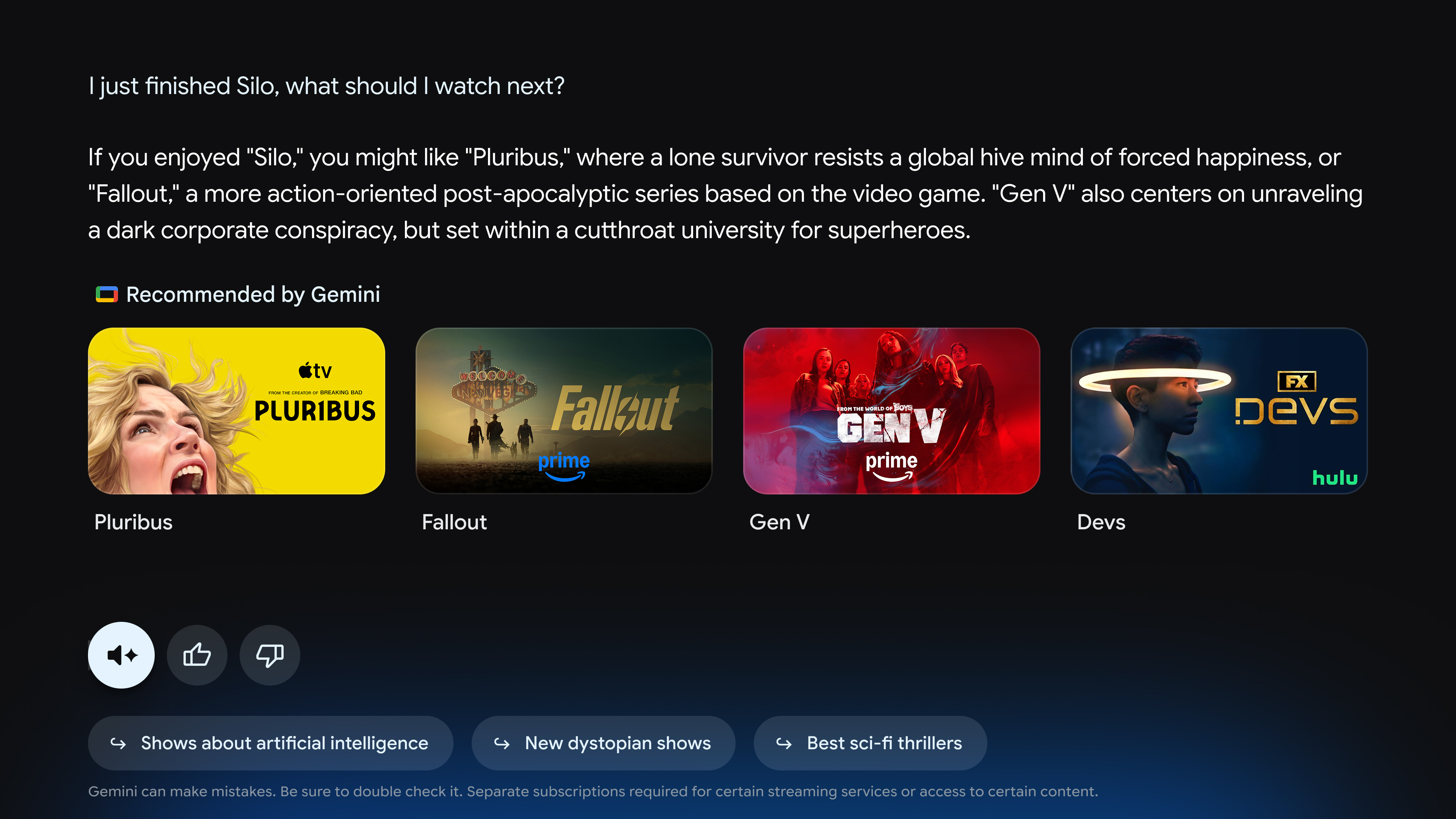
This update brings a full chatbot-like experience to TVs. If you want to catch up on sports scores or get recommendations for what to watch, you can ask the robot. The outputs might be a little different from what you would expect from using Gemini on the web or in an app. Google says it has devised a “visually rich framework” that will make the AI more usable on a TV. There will also be a “Dive Deeper” option in each response to generate an interactive overview of the topic.
Gemini can also take action to tweak system settings based on your complaints. For example, pull up Gemini and say “the dialog is too quiet” and watch as the AI makes adjustments to address that.
Gemini’s replies on Google TV will be more visual. Credit: Google
The new Gemini features will debut on TCL TVs that run Google TV, but most other devices, even Google’s own TV Streamer, will have to wait a few months. Even then, you won’t see Gemini taking over every TV or streaming box with Google’s software. The new Gemini features require the full Google TV experience with Android OS version 14 or higher.