AI companies want you to stop chatting with bots and start managing them
Claude Opus 4.6 and OpenAI Frontier pitch a future of supervising AI agents.
On Thursday, Anthropic and OpenAI shipped products built around the same idea: instead of chatting with a single AI assistant, users should be managing teams of AI agents that divide up work and run in parallel. The simultaneous releases are part of a gradual shift across the industry, from AI as a conversation partner to AI as a delegated workforce, and they arrive during a week when that very concept reportedly helped wipe $285 billion off software stocks.
Whether that supervisory model works in practice remains an open question. Current AI agents still require heavy human intervention to catch errors, and no independent evaluation has confirmed that these multi-agent tools reliably outperform a single developer working alone.
Even so, the companies are going all-in on agents. Anthropic’s contribution is Claude Opus 4.6, a new version of its most capable AI model, paired with a feature called “agent teams” in Claude Code. Agent teams let developers spin up multiple AI agents that split a task into independent pieces, coordinate autonomously, and run concurrently.
In practice, agent teams look like a split-screen terminal environment: A developer can jump between subagents using Shift+Up/Down, take over any one directly, and watch the others keep working. Anthropic describes the feature as best suited for “tasks that split into independent, read-heavy work like codebase reviews.” It is available as a research preview.
OpenAI, meanwhile, released Frontier, an enterprise platform it describes as a way to “hire AI co-workers who take on many of the tasks people already do on a computer.” Frontier assigns each AI agent its own identity, permissions, and memory, and it connects to existing business systems such as CRMs, ticketing tools, and data warehouses. “What we’re fundamentally doing is basically transitioning agents into true AI co-workers,” Barret Zoph, OpenAI’s general manager of business-to-business, told CNBC.
Despite the hype about these agents being co-workers, from our experience, these agents tend to work best if you think of them as tools that amplify existing skills, not as the autonomous co-workers the marketing language implies. They can produce impressive drafts fast but still require constant human course-correction.
The Frontier launch came just three days after OpenAI released a new macOS desktop app for Codex, its AI coding tool, which OpenAI executives described as a “command center for agents.” The Codex app lets developers run multiple agent threads in parallel, each working on an isolated copy of a codebase via Git worktrees.
OpenAI also released GPT-5.3-Codex on Thursday, a new AI model that powers the Codex app. OpenAI claims that the Codex team used early versions of GPT-5.3-Codex to debug the model’s own training run, manage its deployment, and diagnose test results, similar to what OpenAI told Ars Technica in a December interview.
“Our team was blown away by how much Codex was able to accelerate its own development,” the company wrote. On Terminal-Bench 2.0, the agentic coding benchmark, GPT-5.3-Codex scored 77.3%, which exceeds Anthropic’s just-released Opus 4.6 by about 12 percentage points.
The common thread across all of these products is a shift in the user’s role. Rather than merely typing a prompt and waiting for a single response, the developer or knowledge worker becomes more like a supervisor, dispatching tasks, monitoring progress, and stepping in when an agent needs direction.
In this vision, developers and knowledge workers effectively become middle managers of AI. That is, not writing the code or doing the analysis themselves, but delegating tasks, reviewing output, and hoping the agents underneath them don’t quietly break things. Whether that will come to pass (or if it’s actually a good idea) is still widely debated.
A new model under the Claude hood
Opus 4.6 is a substantial update to Anthropic’s flagship model. It succeeds Claude Opus 4.5, which Anthropic released in November. In a first for the Opus model family, it supports a context window of up to 1 million tokens (in beta), which means it can process much larger bodies of text or code in a single session.
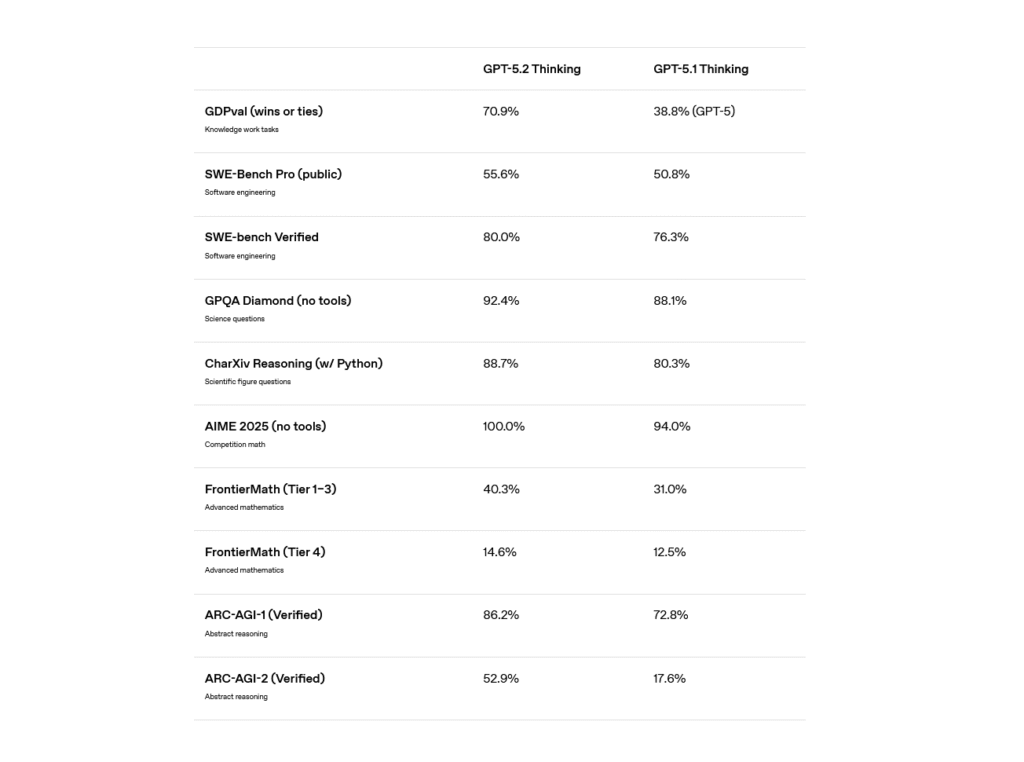
On benchmarks, Anthropic says Opus 4.6 tops OpenAI’s GPT-5.2 (an earlier model than the one released today) and Google’s Gemini 3 Pro across several evaluations, including Terminal-Bench 2.0 (an agentic coding test), Humanity’s Last Exam (a multidisciplinary reasoning test), and BrowseComp (a test of finding hard-to-locate information online)
Although it should be noted that OpenAI’s GPT-5.3-Codex, released the same day, seemingly reclaimed the lead on Terminal-Bench. On ARC AGI 2, which attempts to test the ability to solve problems that are easy for humans but hard for AI models, Opus 4.6 scored 68.8 percent, compared to 37.6 percent for Opus 4.5, 54.2 percent for GPT-5.2, and 45.1 percent for Gemini 3 Pro.
As always, take AI benchmarks with a grain of salt, since objectively measuring AI model capabilities is a relatively new and unsettled science.
Anthropic also said that on a long-context retrieval benchmark called MRCR v2, Opus 4.6 scored 76 percent on the 1 million-token variant, compared to 18.5 percent for its Sonnet 4.5 model. That gap matters for the agent teams use case, since agents working across large codebases need to track information across hundreds of thousands of tokens without losing the thread.
Pricing for the API stays the same as Opus 4.5 at $5 per million input tokens and $25 per million output tokens, with a premium rate of $10/$37.50 for prompts that exceed 200,000 tokens. Opus 4.6 is available on claude.ai, the Claude API, and all major cloud platforms.
The market fallout outside
These releases occurred during a week of exceptional volatility for software stocks. On January 30, Anthropic released 11 open source plugins for Cowork, its agentic productivity tool that launched on January 12. Cowork itself is a general-purpose tool that gives Claude access to local folders for work tasks, but the plugins extended it into specific professional domains: legal contract review, non-disclosure agreement triage, compliance workflows, financial analysis, sales, and marketing.
By Tuesday, investors reportedly reacted to the release by erasing roughly $285 billion in market value across software, financial services, and asset management stocks. A Goldman Sachs basket of US software stocks fell 6 percent that day, its steepest single-session decline since April’s tariff-driven sell-off. Thomson Reuters led the rout with an 18 percent drop, and the pain spread to European and Asian markets.
The purported fear among investors centers on AI model companies packaging complete workflows that compete with established software-as-a-service (SaaS) vendors, even if the verdict is still out on whether these tools can achieve those tasks.
OpenAI’s Frontier might deepen that concern: its stated design lets AI agents log in to applications, execute tasks, and manage work with minimal human involvement, which Fortune described as a bid to become “the operating system of the enterprise.” OpenAI CEO of Applications Fidji Simo pushed back on the idea that Frontier replaces existing software, telling reporters, “Frontier is really a recognition that we’re not going to build everything ourselves.”
Whether these co-working apps actually live up to their billing or not, the convergence is hard to miss. Anthropic’s Scott White, the company’s head of product for enterprise, gave the practice a name that is likely to roll a few eyes. “Everybody has seen this transformation happen with software engineering in the last year and a half, where vibe coding started to exist as a concept, and people could now do things with their ideas,” White told CNBC. “I think that we are now transitioning almost into vibe working.”
AI companies want you to stop chatting with bots and start managing them Read More »