She’ll mess with Texas: Nurse keeps mailing abortion pills, despite Paxton lawsuit
Texas sues Delaware nurse practitioner shipping out hundreds of abortion pills each month.
A Texas fight with a nurse practitioner may eventually push the Supreme Court to settle an intensifying battle between states with strict abortion-ban laws and those with shield laws to protect abortion providers supporting out-of-state patients.
In a lawsuit filed Tuesday, Texas Attorney General Ken Paxton accused Debra Lynch, a Delaware-based nurse practitioner, of breaking Texas laws by shipping abortion pills that Lynch once estimated last January facilitated “up to 162 abortions per week” in the state.
“No one, regardless of where they live, will be freely allowed to aid in the murder of unborn children in Texas,” Paxton’s press release said.
In August, Paxton sent a cease-and-desist letter to shut down Lynch’s website, Her Safe Harbor, which she runs with her husband, Jay, a former communications director for Delaware’s health and social services department, alongside other volunteer licensed prescribers.
Fretting that Her Safe Harbor continues to advertise that Texas patients can get access to abortion pills “within days,” Paxton characterized Her Safe Harbor as an “extremist group” supposedly endangering women and unborn children in the state. To support that claim, Paxton cited two unrelated lawsuits where men allegedly ordered pills from other providers to poison pregnant partners and force miscarriages.
But Lynch told The New York Times that her lawyers advised her to ignore the demand letter, because Delaware’s shield law is one of the strongest in the country. Just before Paxton sent the letter, Delaware’s law was updated to clarify that it specifically “provides protection from civil and criminal actions that arise in another state that are based on the provision of health care services that are legal in Delaware,” the Times noted. And “even before that,” she said her lawyers “advised her that Delaware’s shield law protects her work.”
Paxton seems to expect the court will agree that shield laws cannot overrule state abortion ban laws or laws prohibiting out-of-state health practitioners from operating on Texans without a state license. His lawsuit demands a temporary and permanent injunction shutting down Her Safe Harbor, as well as the highest possible fines.
In a loss, Lynch could owe millions, as each mail order would be considered a violation of the state’s Human Life Protection Act, Paxton alleged, triggering a minimum $100,000 fine per violation. She could also face substantial jail time, the Austin American-Statesman reported, since Texas abortion “providers risk up to 99 years in prison.”
However, Lynch told the Times on Wednesday that the lawsuit will not stop her from shipping pills into Texas. She’s been anticipating this fight since at least the beginning of last year and remains committed to helping pregnant people in states with strict abortion laws get support from a qualified health provider. She fears that otherwise, they’ll feel driven to take riskier steps that could endanger their lives.
“I don’t fear Ken Paxton,” Lynch told the Statesman last January. “I don’t fear getting arrested or anything like that.”
Nurse plans to defend shield laws
This is the third lawsuit Paxton has filed against an out-of-state abortion pill provider, his press release noted. Legal experts who support abortion ban laws, as well as those supporting abortion shield laws, told the NYT they expect the Supreme Court to eventually weigh the arguments on both sides. If that happened, it could impact law enforcement in about a third of states with “near-total” abortion bans, as well as more than 20 states that enacted abortion shield laws.
To Lynch, abortion ban laws have already proven disastrous, doing more harm than good.
The Statesman cited data from the Society of Family Planning (SFP), showing that after the Supreme Court overturned Roe v. Wade in 2022, medication abortion by telehealth became much more popular in the US. In 2022, this type of service accounted for approximately 1 in 25 abortions; by 2024, the numbers had shot to 1 in 5.
“Nearly half of those prescriptions went to patients in states with abortion bans or restrictions on telehealth abortion,” the Statesman reported, and SFP’s data showed that Texas residents, particularly, were turning more to telehealth. In the first half of 2024, 2,800 Texans per month received abortion medication by mail, which was “more than any other abortion-restricted state,” the data showed.
SFP also found that, overall, abortions had increased following tighter restrictions, totaling more than 1 million in 2023, which SFP noted was “the highest number in more than a decade.”
Lynch told the Statesman that abortion-ban laws “hadn’t stopped her from mailing the medications. They hadn’t stopped patients from receiving them. They just created hundreds of miles between patients and providers,” leaving women “feeling isolated and afraid to access a procedure that’s legal in half the country, and which had been legal everywhere in the US for half a century.”
“They’re truly alone,” Lynch said. “That frightens the hell out of me.”
Lynch’s case, or one of the other Texas lawsuits, could put shield laws to the test and one day clarify for all US residents if medication abortion by telehealth is legal in states with more restrictive laws.
A win could back up shield laws and block Texas from prosecuting providers like Lynch, as well as from enforcing proposed laws like Texas’ House Bill 991. If passed, that law would let Texas residents sue Internet service providers for failing to block abortion pill providers’ websites.
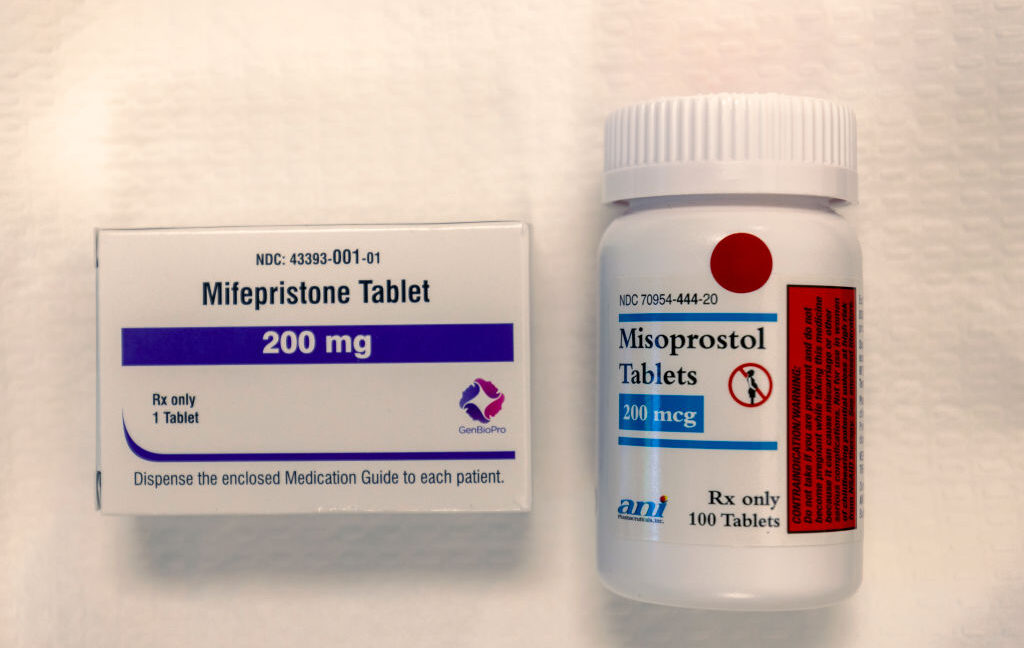
On the Her Safe Harbor website, Lynch and her partners say that patient safety is their priority and that they go beyond what typical providers offer to ensure that people seeking abortions are well cared for. The website details which abortion pills patients will receive (Mifepristone and Misoprostol), while, unlike other abortion providers, also sends pain and nausea medication at no cost. Both the NYT and the Statesman’s reporters confirmed that Her Safe Harbor is also available for patients to check in with any questions or concerns throughout the process.
Paxton seems fixated on Her Safe Harbor’s claims that orders can be shipped to all states, regardless of state laws, which he alleged makes women not seeking abortions vulnerable to attacks by male partners.
However, Her Safe Harbor takes steps to speak directly with patients in states with the most restrictive abortion laws. An Ars test showed that patients seeking consultations from such states are encouraged to call health care providers directly, rather than submit a form that their state could try to subpoena, a step that could prevent the kinds of attacks that Paxton fears. Of course, anyone can still choose to initiate the process using the consultation form, with Her Safe Harbor providing reassurances that the group “has never and will never disclose any private health data to any authority. We will not comply if we are ever subpoenaed.”
“This lawsuit is not about patient safety”
In email comments, Jay Lynch, who helps run Her Safe Harbor with his wife, told Ars that Paxton’s lawsuit is not trying to “protect life” but seeking to “silence medicine.”
“Every day, we provide evidence-based medical care to women who are scared, vulnerable, and often out of options,” Jay said. “We assess medical history. We evaluate risk. We follow clinical guidelines. We act to prevent complications, hospitalizations, infertility, and death. That is what medicine is supposed to do: save lives and reduce harm.”
Jay accused Paxton of “trying to expand state control across borders” and “intimidate providers everywhere.”
“This lawsuit is not about patient safety,” Jay said. “It is about who gets to decide what care is allowed: trained medical professionals—or politicians with no clinical expertise.”
To Jay, a win for Paxton would put patients in a risky place, forcing doctors and nurses to choose between “doing what is medically right, or doing what is politically ‘safe.’”
“That is a dangerous place for any healthcare system to be,” Jay said, noting that “when politicians override clinicians, patients pay the price” through delayed treatment, worsening injuries, preventable emergencies, lost fertility, or their lives.
Working with her husband and other providers, Lynch told the NYT that Her Safe Harbor is currently shipping out hundreds of packages a month. She vowed that as long as threats to abortion access continued to risk women’s lives, the shipments would never stop.
“Women are losing their lives and children are winding up orphans, and babies are being born with non-life-sustaining medical conditions” due to abortion bans and restrictive laws, Lynch told the NYT. “As long as that is happening, there’s absolutely nothing or nobody that will deter us from our mission to bring health care to women.”
She’ll mess with Texas: Nurse keeps mailing abortion pills, despite Paxton lawsuit Read More »