Modder packs an entire Nintendo Wii into a box the size of a pack of cards
wii micro —
There’s no disc drive, but there are still ports for GameCube controllers.
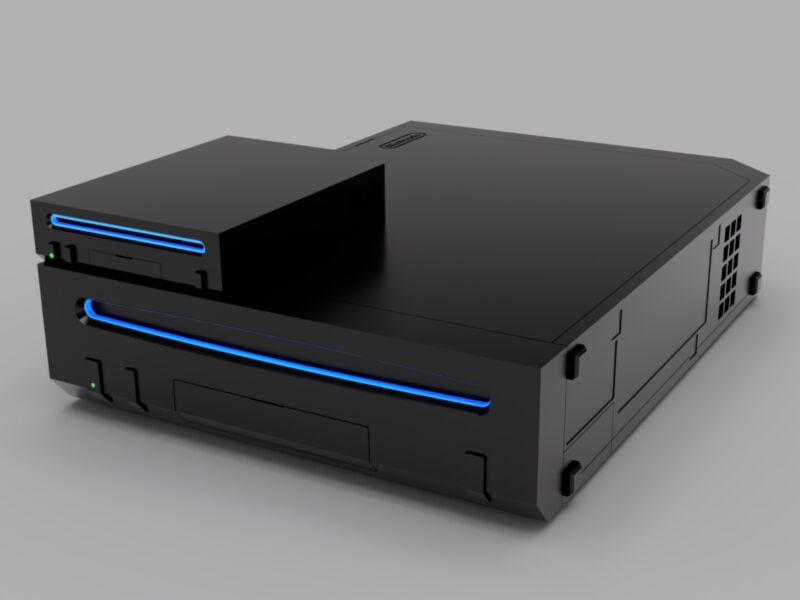

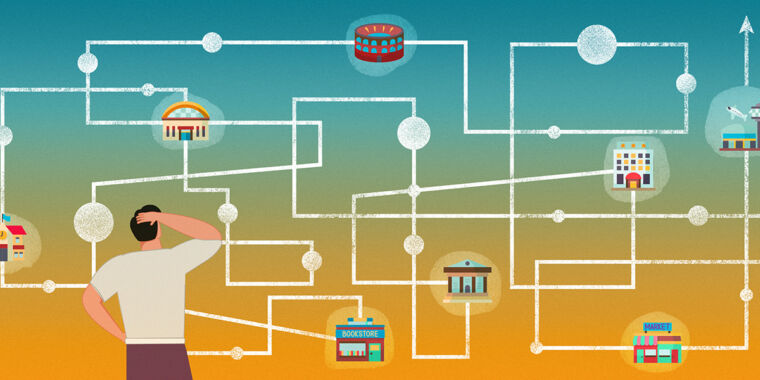
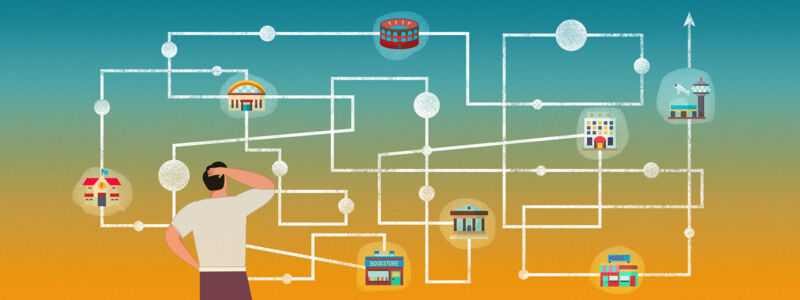
Enlarge / Its creator calls the “Short Stack” the world’s smallest scale model replica of the Nintendo Wii (bottom).
The miniaturization of retro tech has always been a major obsession for modders, from the person who fit an original NES into a Game Boy-sized portable to the person who made a mini-er version of Apple’s Mac mini.
One mod in this storied genre that caught our eye this week is the “Short Stack,” a scale model of the Nintendo Wii that packs the 2006 console’s internal hardware into a 3D-printed enclosure roughly the size of a deck of playing cards.
“You could fit 13.5 of these inside an original Wii,” writes James Smith (aka loopj), the person behind the project. All the design details, custom boards, and other information about recreating the mod are available on GitHub.
Like many space-saving console mods, the Short Stack requires a cut-down version of the original Wii’s PCB, retaining (and occasionally relocating) the original console’s CPU, GPU, RAM, and NAND flash chip. Power delivery, USB, the Wi-Fi and Bluetooth chips, and GameCube controller ports were all relocated to separate custom PCBs, which also allowed Smith to add HDMI output and a microSD card slot (the original Wii used a full-size SD card and didn’t support digital video output).
-
The Short Stack cleverly hides its GameCube controller ports behind a sliding panel on the side.
-
A headphone jack-to-GameCube dongle preserves GameCube controller compatibility while saving space in the console itself.
-
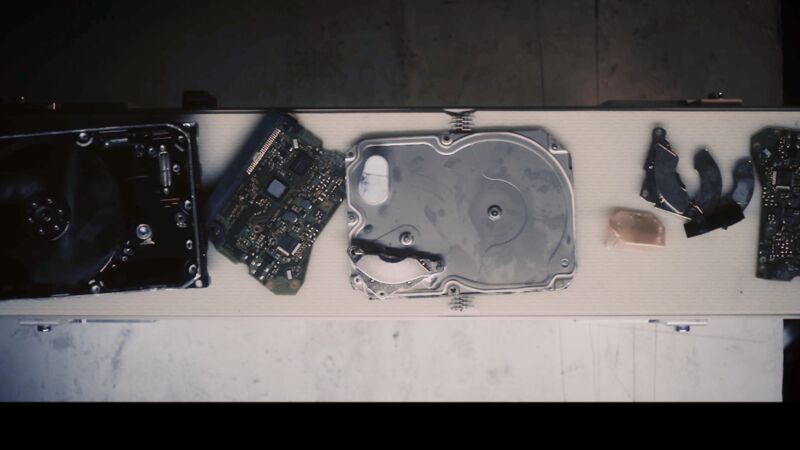
The cut-down Wii PCB, featuring the original console’s CPU, GPU, RAM, and NAND flash.
-
The Short Stack next to a deck of cards.
Some sacrifices were made in the name of miniaturization. The console’s disc drive is gone, so any games will need to be loaded from a microSD card instead. And the four GameCube controller ports are actually headphone jacks that work over a special adapter. Smith made these headphone-to-GameCube dongles pin-compatible with an earlier mod called the GC Nano, a project that did for the GameCube what the Short Stack does for the Wii.
Smith also designed custom front and rear PCBs for the console to handle things like the power button and the glowing blue light around the Short Stack’s (aesthetic, non-functional) DVD slot. A custom heatsink (Smith uses aluminum, though it can also be made with copper to improve heat transfer at the expense of weight) and a tiny fan keep the console cool.
Nintendo released its own Wii Mini toward the end of the Wii’s life in 2012, but it came with significant compromises: no online connectivity, no GameCube controller ports or game compatibility, and no SD card slot. The Short Stack loses the optical drive for space-saving reasons but otherwise retains all of the features of the original Wii.
Smith says that the Short Stack could probably be as much as 20 to 30 percent smaller without giving up features. But one of the goals of the Short Stack project was to make a scale model of the original Wii, and further shrinkage would make the project “tricky to assemble.”
Modder packs an entire Nintendo Wii into a box the size of a pack of cards Read More »