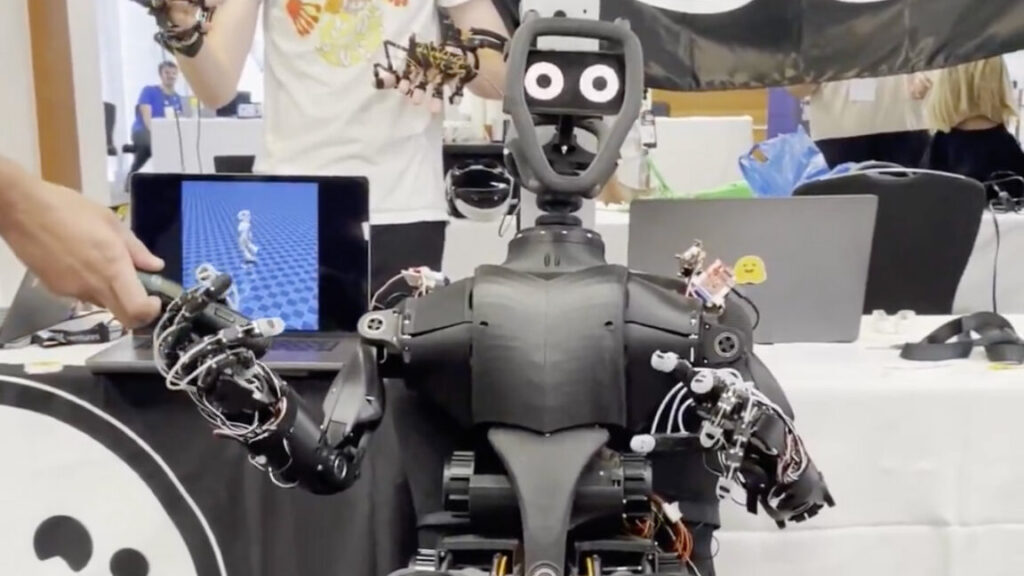
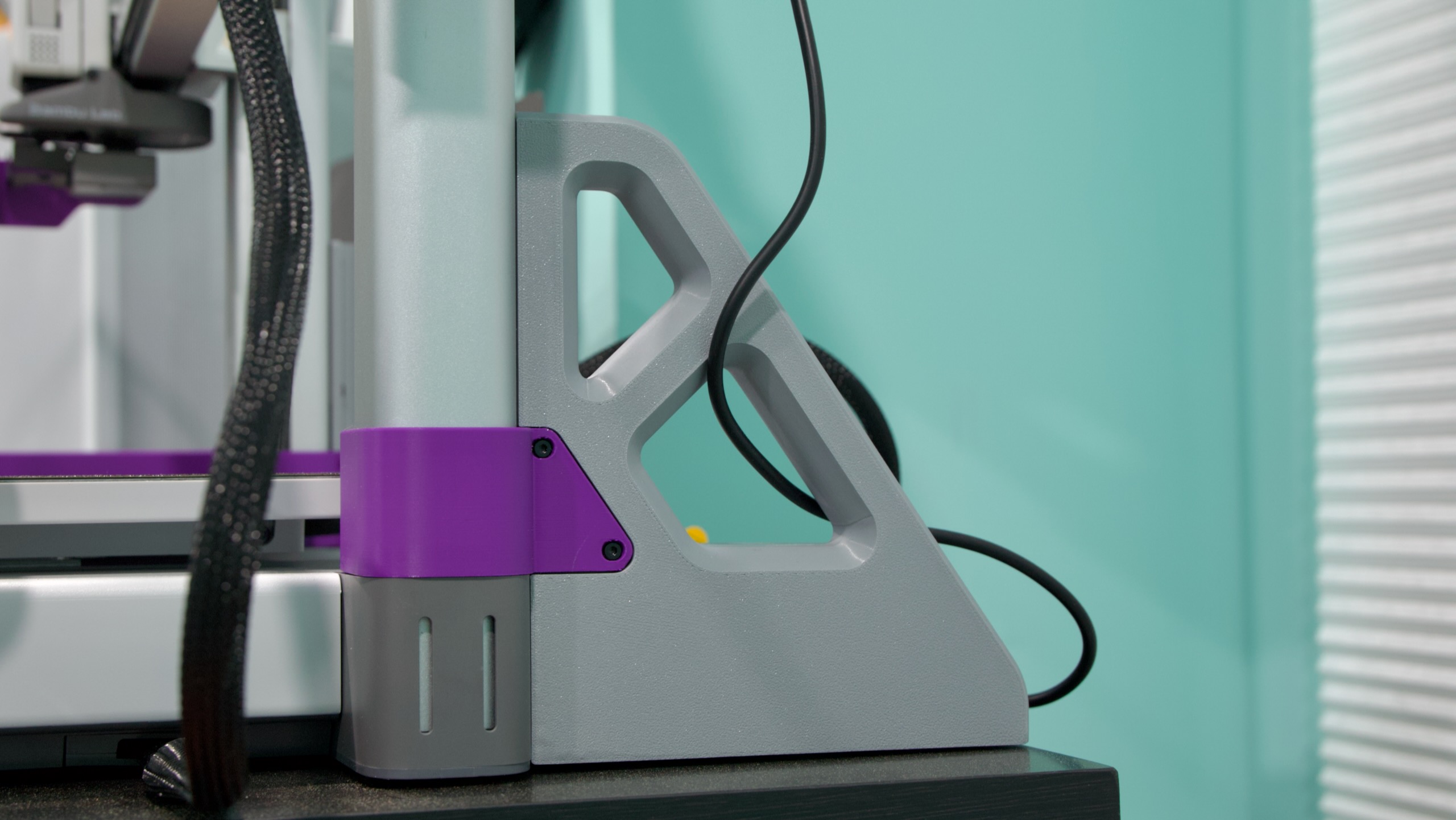
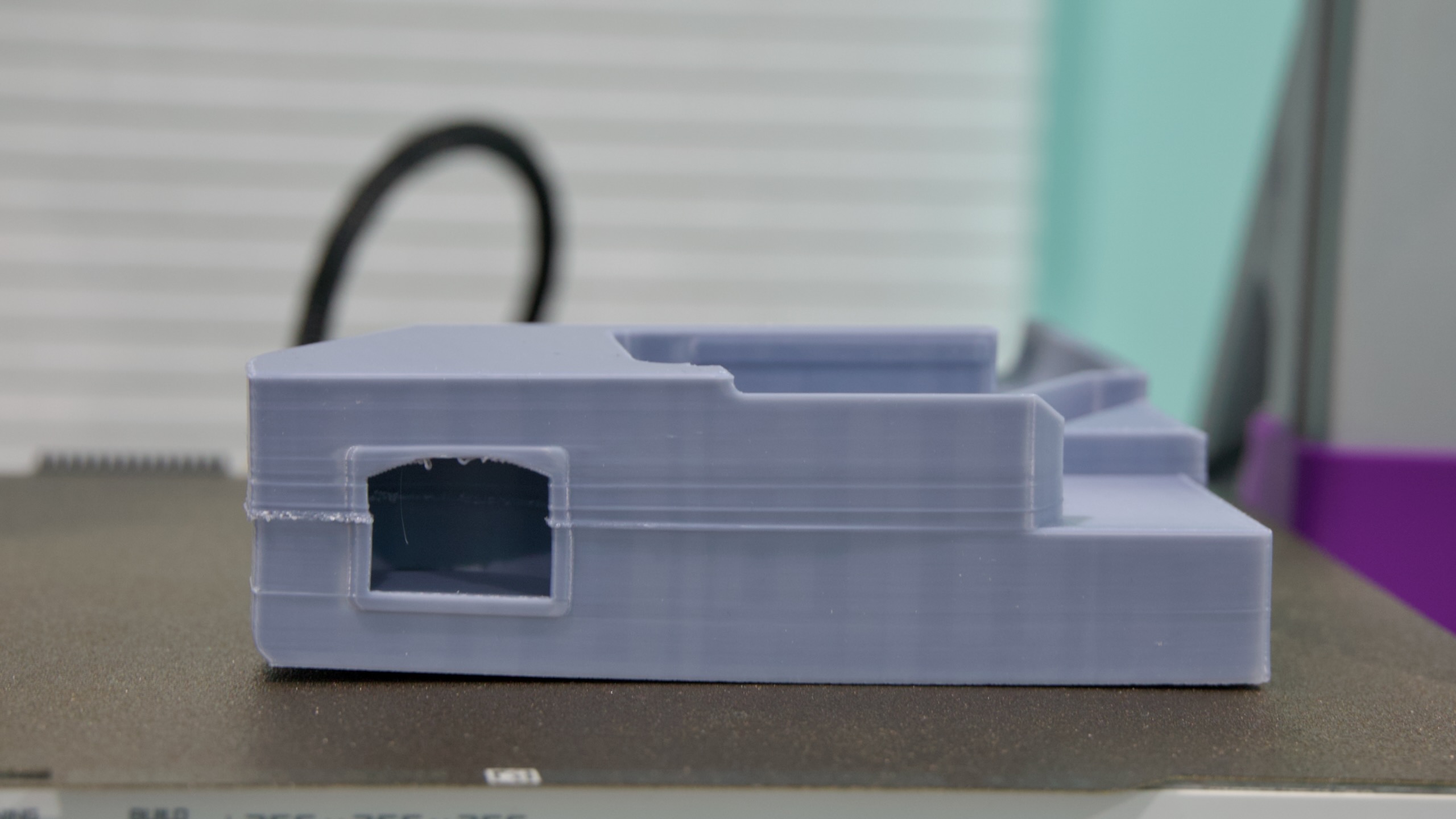
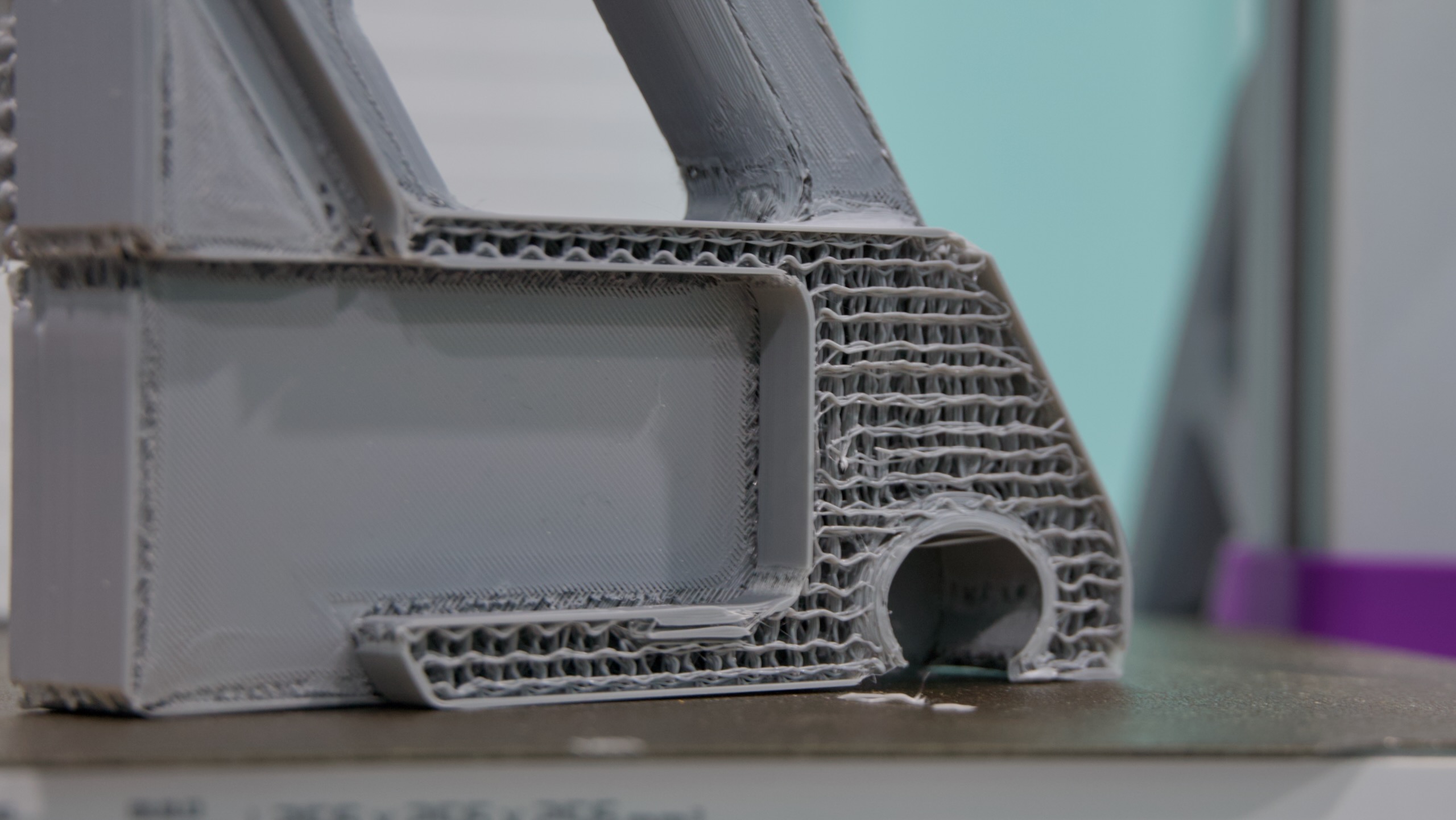
Want a humanoid, open source robot for just $3,000? Hugging Face is on it.
You may have noticed he said “robots” plural—that’s because there’s a second one. It’s called Reachy Mini, and it looks like a cute, Wall-E-esque statue bust that can turn its head and talk to the user. Among other things, it’s meant to be used to test AI applications, and it’ll run between $250 and $300.
You can sort of think of these products as the equivalent to a Raspberry Pi, but in robot form and for AI developers—Hugging Face’s main customer base.
Hugging Face has previously released AI models meant for robots, as well as a 3D-printable robotic arm. This year, it announced an acquisition of Pollen Robotics, a company that was working on humanoid robots. Hugging Face’s Cadene came to the company by way of Tesla.
For context on the pricing, Tesla’s Optimus Gen 2 humanoid robot (while admittedly much more advanced, at least in theory) is expected to cost at least $20,000.
There is a lot of investment in robotics like this, but there are still big barriers—and price isn’t the only one. There’s battery life, for example; Unitree’s G1 only runs for about two hours on a single charge.
Want a humanoid, open source robot for just $3,000? Hugging Face is on it. Read More »