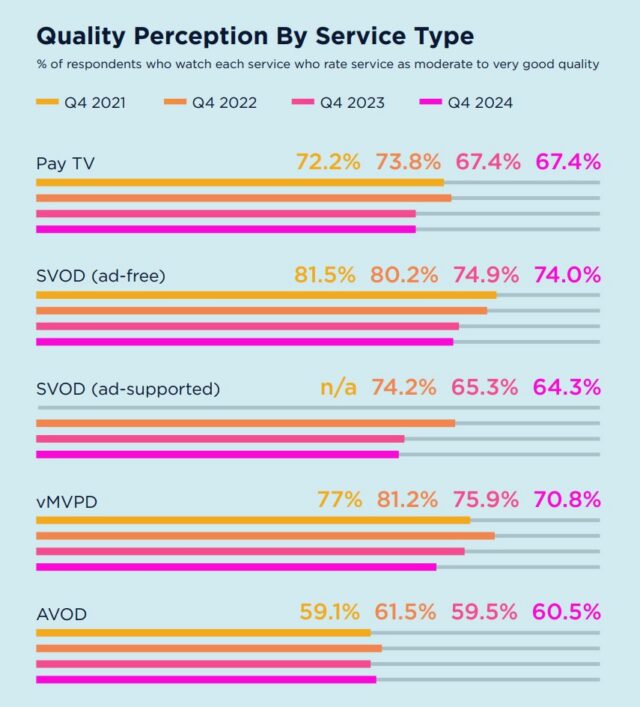
Disney+ gets HDR10+ via “over 1,000” Hulu titles
Disney+ has started streaming movies and shows in the HDR10+ format.
Support is somewhat limited for now. Only certain content from Hulu, which The Walt Disney Company acquired in June, is available in HDR10+. In an announcement today, Samsung said that “over 1,000” Hulu titles are available in HDR10+ and that “additional Disney+” content will support HDR10+ “in the future.” Previously, Disney+ only supported the HDR10 and Dolby Vision HDR formats.
Samsung TVs are the first devices to gain the ability to stream HDR10+ content from Disney+, according to an announcement from Samsung today. The electronics company said that its Samsung Crystal UHD TVs and above from 2018 onward, including its OLED TVs, The Frame TVs, QLED TVs, and Micro RGB TV, support HDR10+.
The Disney+ app on Apple’s tvOS also lists HDR10+, site FlatpanelsHD pointed out.
Hulu started offering some content in HDR10, HDR10+, and Dolby Vision in 2021. Now that Disney owns Hulu and has created a unified app with both Disney+ and Hulu content, Disney+ is also able to offer a restricted number of titles in HDR10+.
Today’s announcement also caters to Samsung TV users, since Samsung TVs don’t support Dolby Vision. By offering HDR10+, Disney+ can make itself more appealing to the many home theater enthusiasts who own a TV from Samsung, which is the world’s top-selling TV brand.
Disney+ gets HDR10+ via “over 1,000” Hulu titles Read More »