SpaceX may have solved one problem only to find more on latest Starship flight
SpaceX’s ninth Starship survived launch, but engineers now have more problems to overcome.
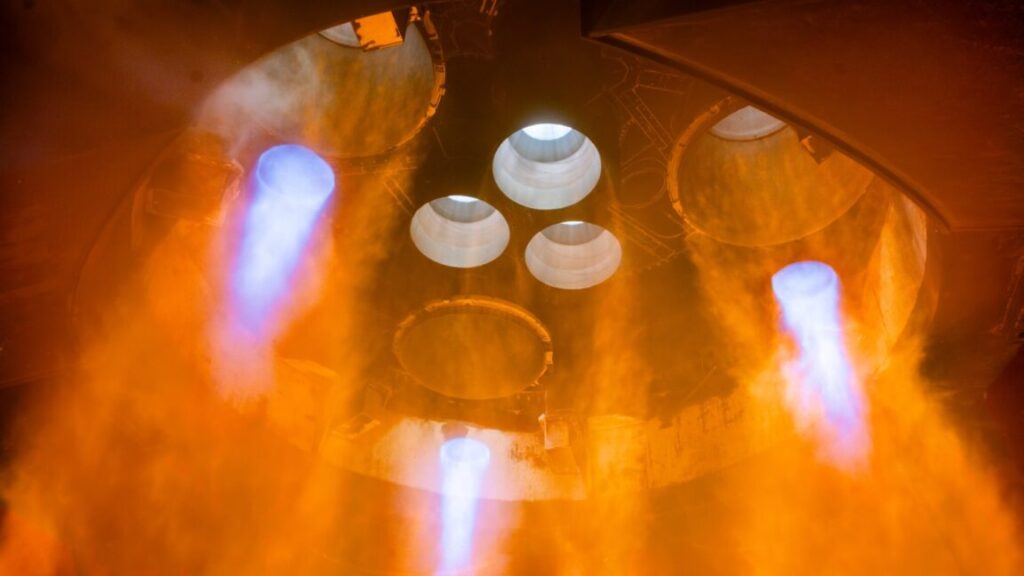
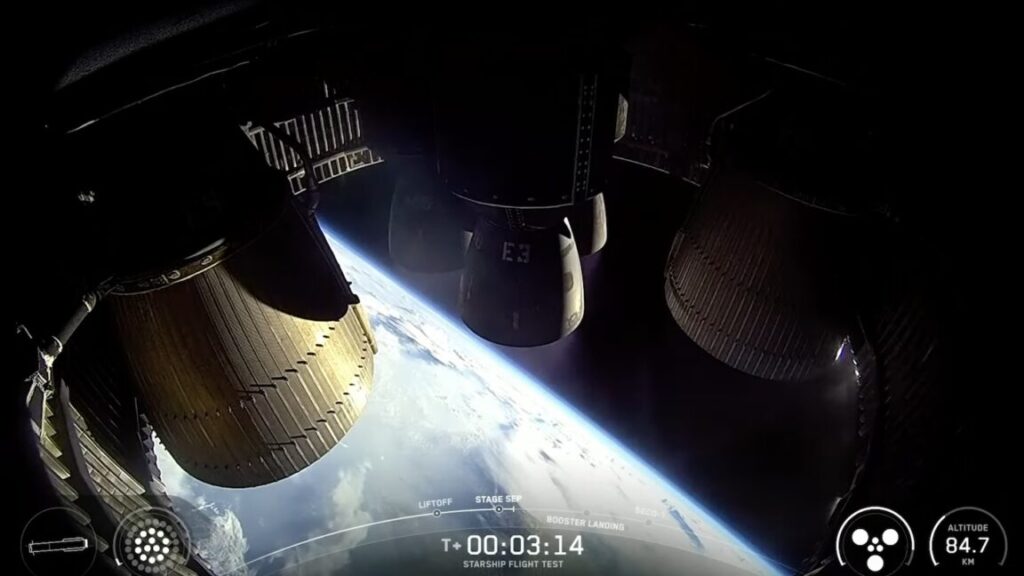
An onboard camera shows the six Raptor engines on SpaceX’s Starship upper stage, roughly three minutes after launching from South Texas on Tuesday. Credit: SpaceX
SpaceX made some progress on another test flight of the world’s most powerful rocket Tuesday, finally overcoming technical problems that plagued the program’s two previous launches.
But minutes into the mission, SpaceX’s Starship lost control as it cruised through space, then tumbled back into the atmosphere somewhere over the Indian Ocean nearly an hour after taking off from Starbase, Texas, the company’s privately owned spaceport near the US-Mexico border.
SpaceX’s next-generation rocket is designed to eventually ferry cargo and private and government crews between the Earth, the Moon, and Mars. The rocket is complex and gargantuan, wider and longer than a Boeing 747 jumbo jet, and after nearly two years of steady progress since its first test flight in 2023, this has been a year of setbacks for Starship.
During the rocket’s two previous test flights—each using an upgraded “Block 2” Starship design—problems in the ship’s propulsion system led to leaks during launch, eventually triggering an early shutdown of the rocket’s main engines. On both flights, the vehicle spun out of control and broke apart, spreading debris over an area near the Bahamas and the Turks and Caicos Islands.
The good news is that that didn’t happen Tuesday. The ship’s main engines fired for their full duration, putting the vehicle on its expected trajectory toward a splashdown in the Indian Ocean. For a short time, it appeared the ship was on track for a successful flight.
“Starship made it to the scheduled ship engine cutoff, so big improvement over last flight! Also, no significant loss of heat shield tiles during ascent,” wrote Elon Musk, SpaceX’s founder and CEO, on X.
The bad news is that Tuesday’s test flight revealed more problems, preventing SpaceX from achieving the most important goals Musk outlined going into the launch.
“Leaks caused loss of main tank pressure during the coast and reentry phase,” Musk posted on X. “Lot of good data to review.”
With the loss of tank pressure, the rocket started slowly spinning as it coasted through the blackness of space more than 100 miles above the Earth. This loss of control spelled another premature end to a Starship test flight. Most notable among the flight’s unmet objectives was SpaceX’s desire to study the performance of the ship’s heat shield, which includes improved heat-absorbing tiles to better withstand the scorching temperatures of reentry back into the atmosphere.
“The most important thing is data on how to improve the tile design, so it’s basically data during the high heating, reentry phase in order to improve the tiles for the next iteration,” Musk told Ars Technica before Tuesday’s flight. “So we’ve got like a dozen or more tile experiments. We’re trying different coatings on tiles. We’re trying different fabrication techniques, different attachment techniques. We’re varying the gap filler for the tiles.”
Engineers are hungry for data on the changes to the heat shield, which can’t be fully tested on the ground. SpaceX officials hope the new tiles will be more robust than the ones flown on the first-generation, or Block 1, version of Starship, allowing future ships to land and quickly launch again, without the need for time-consuming inspections, refurbishment, and in some cases, tile replacements. This is a core tenet of SpaceX’s plans for Starship, which include delivering astronauts to the surface of the Moon, proliferating low-Earth orbit with refueling tankers, and eventually helping establish a settlement on Mars, all of which are predicated on rapid reusability of Starship and its Super Heavy booster.
Last year, SpaceX successfully landed three Starships in the Indian Ocean after they survived hellish reentries, but they came down with damaged heat shields. After an early end to Tuesday’s test flight, SpaceX’s heat shield engineers will have to wait a while longer to satiate their appetites. And the longer they have to wait, the longer the wait for other important Starship developmental tests, such as a full orbital flight, in-space refueling, and recovery and reuse of the ship itself, replicating what SpaceX has now accomplished with the Super Heavy booster.
Failing forward or falling short?
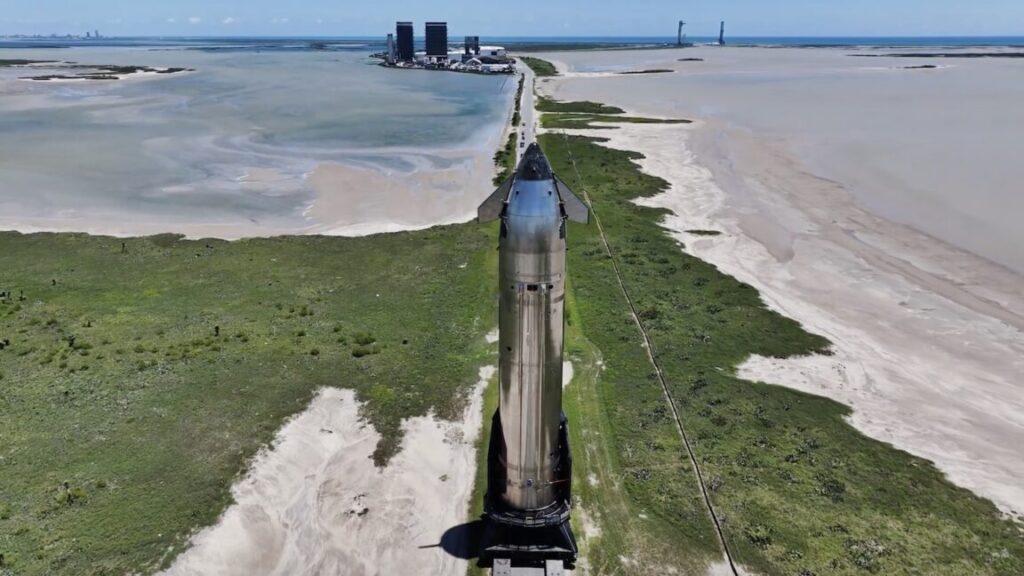
The ninth flight of Starship began with a booming departure from SpaceX’s Starbase launch site at 6: 35 pm CDT (7: 35 pm EDT; 23: 35 UTC) Tuesday.
After a brief hold to resolve last-minute technical glitches, SpaceX resumed the countdown clock to tick away the final seconds before liftoff. A gush of water poured over the deck of the launch pad just before 33 methane-fueled Raptor engines ignited on the rocket’s massive Super Heavy first stage booster. Once all 33 engines lit, the enormous stainless steel rocket—towering more than 400 feet (123 meters)—began to climb away from Starbase.
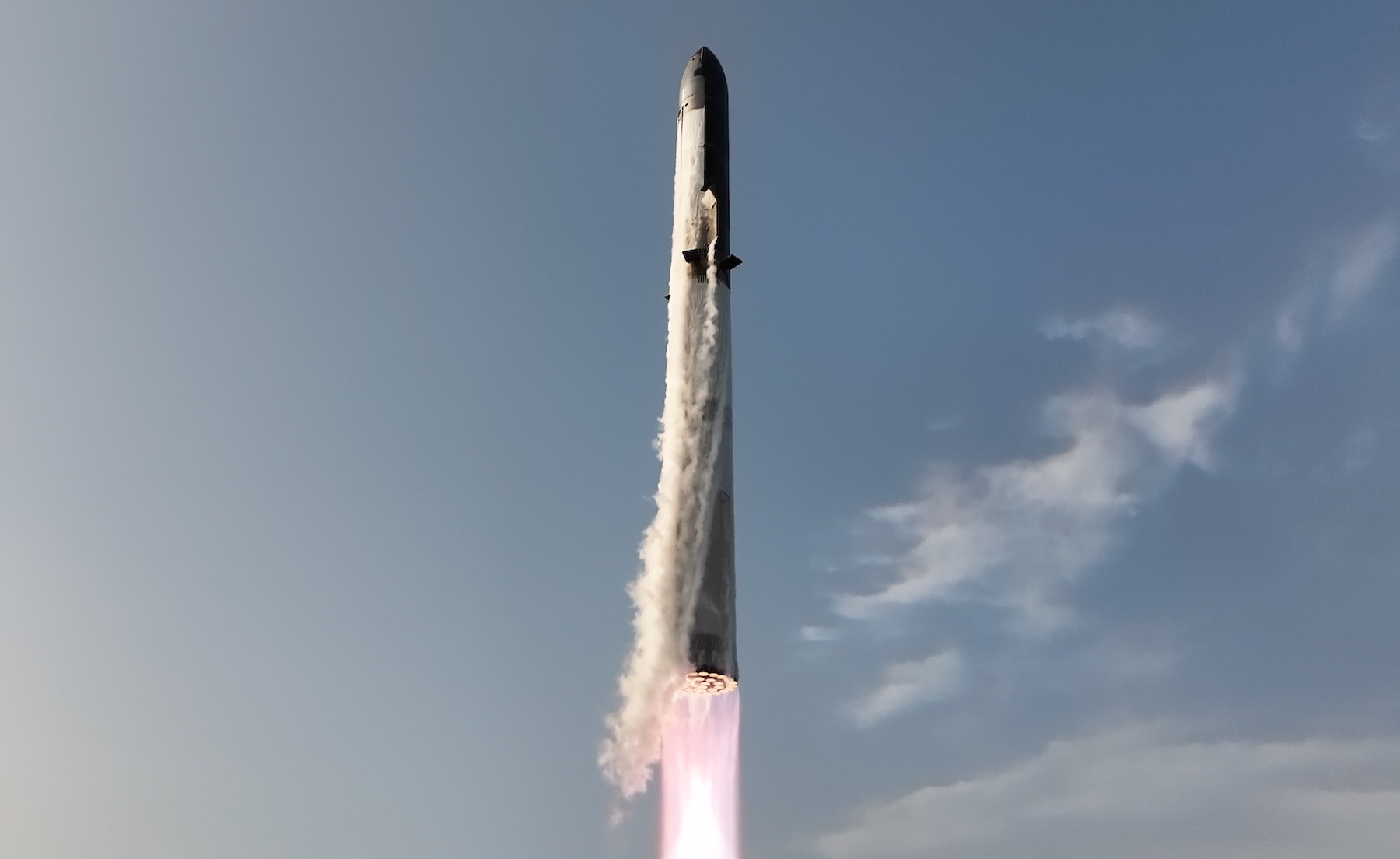

SpaceX’s Starship rocket, flying with a reused first-stage booster for the first time, climbs away from Starbase, Texas. Credit: SpaceX
Heading east, the Super Heavy booster produced more than twice the power of NASA’s Saturn V rocket, an icon of the Apollo Moon program, as it soared over the Gulf of Mexico. After two-and-a-half minutes, the Raptor engines switched off and the Super Heavy booster separated from Starship’s upper stage.
Six Raptor engines fired on the ship to continue pushing it into space. As the booster started maneuvering for an attempt to target an intact splashdown in the sea, the ship burned its engines more than six minutes, reaching a top speed of 16,462 mph (26,493 kilometers per hour), right in line with preflight predictions.
A member of SpaceX’s launch team declared “nominal orbit insertion” a little more than nine minutes into the flight, indicating the rocket reached its planned trajectory, just shy of the velocity required to enter a stable orbit around the Earth.
The flight profile was supposed to take Starship halfway around the world, with the mission culminating in a controlled splashdown in the Indian Ocean northwest of Australia. But a few minutes after engine shutdown, the ship started to diverge from SpaceX’s flight plan.
First, SpaceX aborted an attempt to release eight simulated Starlink Internet satellites in the first test of the Starship’s payload deployer. The cargo bay door would not fully open, and engineers called off the demonstration, according to Dan Huot, a member of SpaceX’s communications team who hosted the company’s live launch broadcast Tuesday.
That, alone, would not have been a big deal. However, a few minutes later, Huot made a more troubling announcement.
“We are in a little bit of a spin,” he said. “We did spring a leak in some of the fuel tank systems inside of Starship, which a lot of those are used for attitude control. So, at this point, we’ve essentially lost our attitude control with Starship.”
This eliminated any chance for a controlled reentry and an opportunity to thoroughly scrutinize the performance of Starship’s heat shield. The spin also prevented a brief restart of one of the ship’s Raptor engines in space.
“Not looking great for a lot of our on-orbit objectives for today,” Huot said.
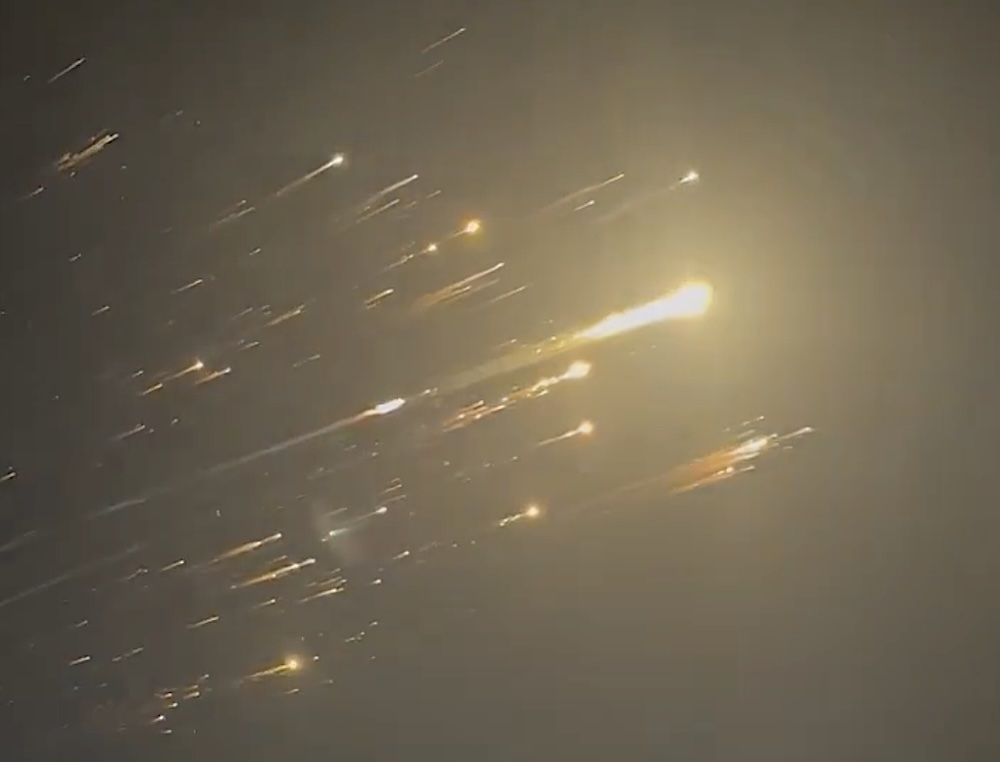
SpaceX continued streaming live video from Starship as it soared over the Atlantic Ocean and Africa. Then, a blanket of super-heated plasma enveloped the vehicle as it plunged into the atmosphere. Still in a slow tumble, the ship started shedding scorched chunks of its skin before the screen went black. SpaceX lost contact with the vehicle around 46 minutes into the flight. The ship likely broke apart over the Indian Ocean, dropping debris into a remote swath of sea within its expected flight corridor.
Victories where you find them
Although the flight did not end as well as SpaceX officials hoped, the company made some tangible progress Tuesday. Most importantly, it broke the streak of back-to-back launch failures on Starship’s two most recent test flights in January and March.
SpaceX’s investigation earlier this year into a January 16 launch failure concluded vibrations likely triggered fuel leaks and fires in the ship’s engine compartment, causing an early shutdown of the rocket’s engines. Engineers said the vibrations were likely in resonance with the vehicle’s natural frequency, intensifying the shaking beyond the levels SpaceX predicted.
Engineers made fixes and launched the next Starship test flight March 6, but it again encountered trouble midway through the ship’s main engine burn. SpaceX said earlier this month that the inquiry into the March 6 failure found its most probable root cause was a hardware failure in one of the upper stage’s center engines, resulting in “inadvertent propellant mixing and ignition.”
In its official statement, the company was silent on the nature of the hardware failure but said engines for future test flights will receive additional preload on key joints, a new nitrogen purge system, and improvements to the propellant drain system. A new generation of Raptor engines, known as Raptor 3, should begin flying around the end of this year with additional improvements to address the failure mechanism, SpaceX said.
Another bright spot in Tuesday’s test flight was that it marked the first time SpaceX reused a Super Heavy booster from a prior launch. The booster used Tuesday previously launched on Starship’s seventh test flight in January before it was caught back at the launch pad and refurbished for another space shot.
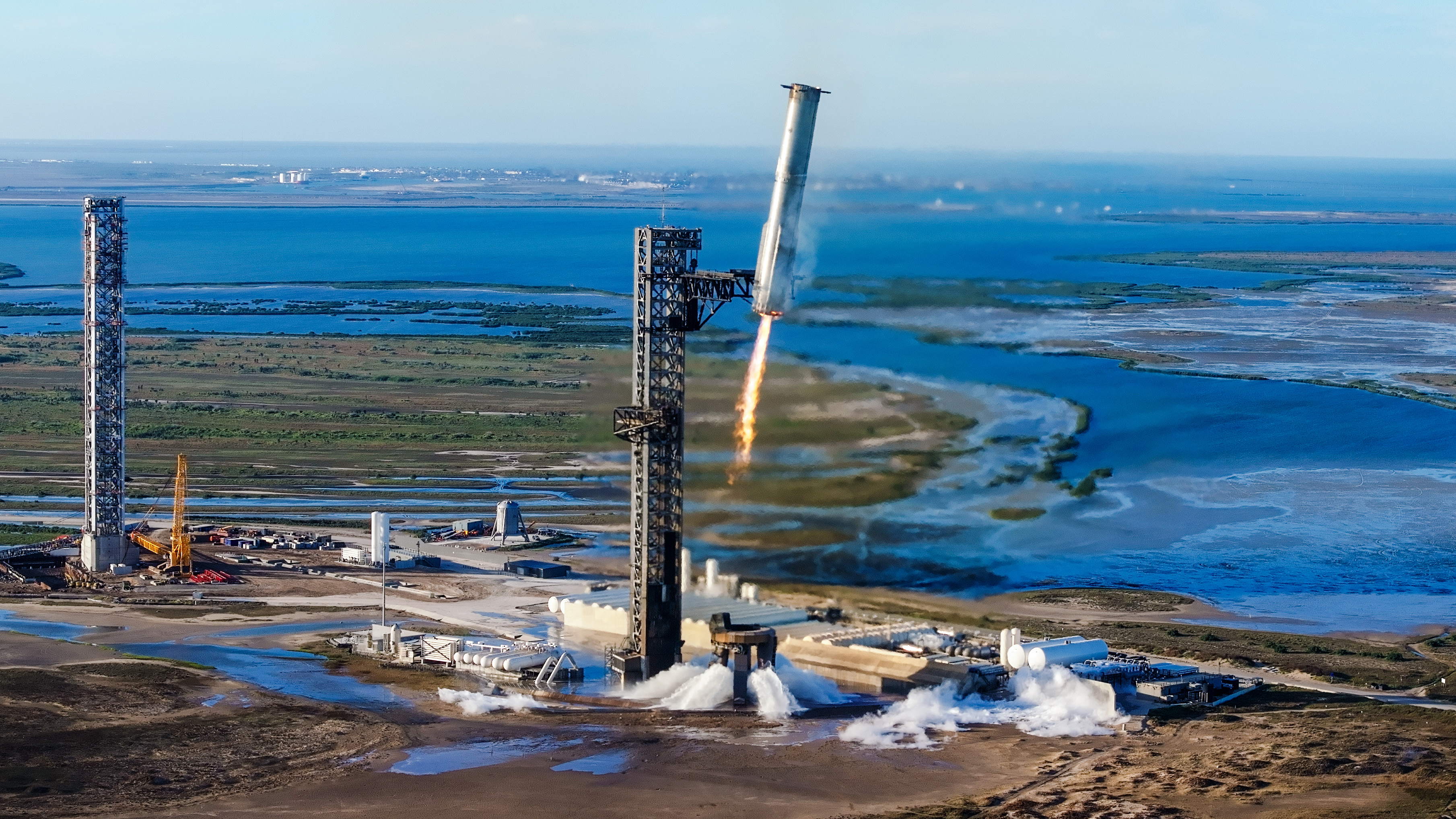

Booster 14 comes in for the catch after flying to the edge of space on January 16. SpaceX flew this booster again Tuesday but did not attempt a catch. Credit: SpaceX
After releasing the Starship upper stage to continue its journey into space, the Super Heavy booster flipped around to fly tail-first and reignited 13 of its engines to begin boosting itself back toward the South Texas coast. On this test flight, SpaceX aimed the booster for a hard splashdown in the ocean just offshore from Starbase, rather than a mid-air catch back at the launch pad, which SpaceX accomplished on three of its four most recent test flights.
SpaceX made the change for a few reasons. First, engineers programmed the booster to fly at a higher angle of attack during its descent, increasing the amount of atmospheric drag on the vehicle compared to past flights. This change should reduce propellant usage on the booster’s landing burn, which occurs just before the rocket is caught by the launch pad’s mechanical arms, or “chopsticks,” on a recovery flight.
During the landing burn itself, engineers wanted to demonstrate the booster’s ability to respond to an engine failure on descent by using just two of the rocket’s 33 engines for the end of the burn, rather than the usual three. Instead, the rocket appeared to explode around the beginning of the landing burn before it could complete the final landing maneuver.
Before the explosion at the end of its flight, the booster appeared to fly as designed. Data displayed on SpaceX’s live broadcast of the launch showed all 33 of the rocket’s engines fired normally during its initial ascent from Texas, a reassuring sign for the reliability of the Super Heavy booster.
SpaceX kicked off the year with the ambition to launch as many as 25 Starship test flights in 2025, a goal that now seems to be unattainable. However, an X post by Musk on Tuesday night suggested a faster cadence of launches in the coming months. He said the next three Starships could launch at intervals of about once every three to four weeks. After that, SpaceX is expected to transition to a third-generation, or Block 3, Starship design with more changes.
It wasn’t immediately clear how long it might take SpaceX to correct whatever problems caused Tuesday’s test flight woes. The Starship vehicle for the next flight is already built and completed cryogenic prooftesting April 27. For the last few ships, SpaceX has completed this cryogenic testing milestone around one-and-a-half to three months prior to launch.
A spokesperson for the Federal Aviation Administration said the agency is “actively working” with SpaceX in the aftermath of Tuesday’s test flight but did not say if the FAA will require SpaceX to conduct a formal mishap investigation.
Shana Diez, director of Starship engineering at SpaceX, chimed in with her own post on X. Based on preliminary data from Tuesday’s flight, she is optimistic the next test flight will fly soon. She said engineers still need to examine data to confirm none of the problems from Starship’s previous flight recurred on this launch but added that “all evidence points to a new failure mode” on Tuesday’s test flight.
SpaceX will also study what caused the Super Heavy booster to explode on descent before moving forward with another booster catch attempt at Starbase, she said.
“Feeling both relieved and a bit disappointed,” Diez wrote. “Could have gone better today but also could have gone much worse.”
SpaceX may have solved one problem only to find more on latest Starship flight Read More »