After a rocky six years, Sony cancels future single-player PC game releases
Finally, Bloomberg’s sources cautioned that Sony’s strategy for single-player releases could change again at some point in the future.
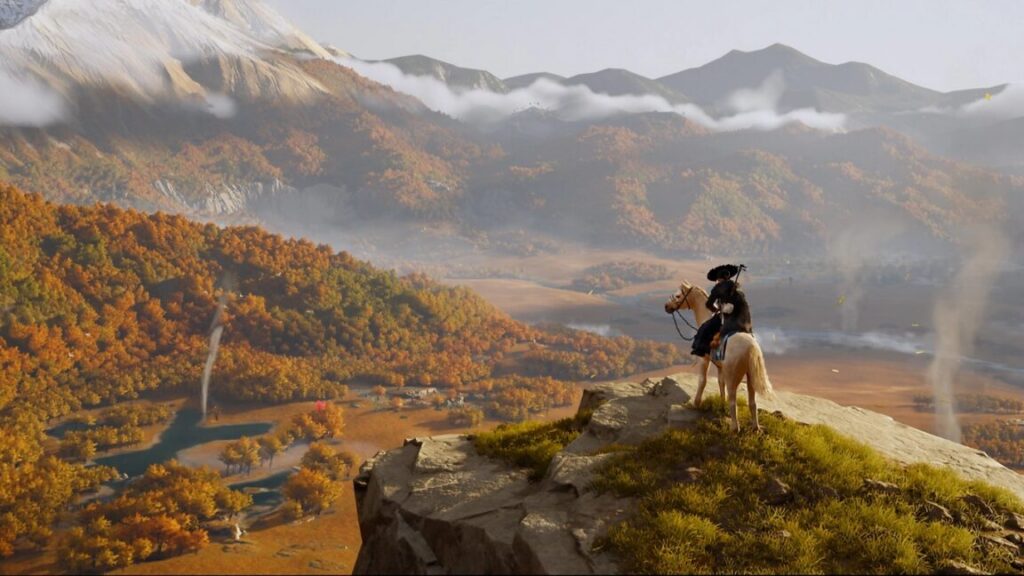
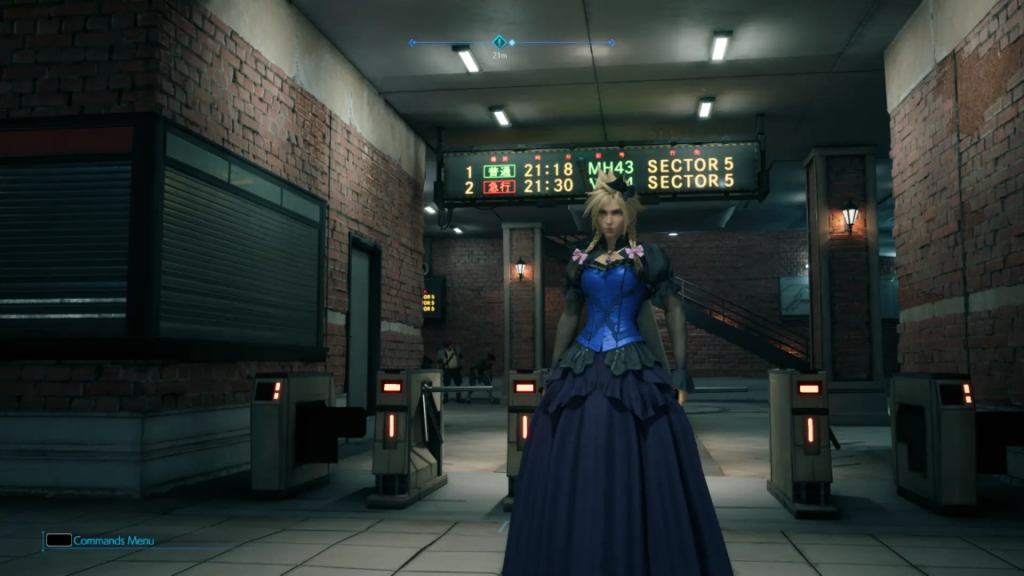
Historically, Sony did not release its first-party games on PCs. That began to change in 2020, and the company has put out titles like Horizon Zero Dawn, Helldivers 2, and Ghost of Tsushima on PCs, among others. Sony’s PC launch experiments haven’t been without confusion or drama, however.
The company was inconsistent about which titles reached the platform and about the timelines for those releases. Single-player titles hit Steam months or even years after their console releases, long after the gaming community buzz around them had died down.
Further, some titles required players sign in to a PlayStation account to access core features, which wasn’t a popular choice with everyone, and the back-and-forth on that policy felt chaotic to many players.
Sony has been less decisive about its PC strategy compared to the other two major console manufacturers. Nintendo simply does not release its games on PC at all, while Microsoft has released all of its first-party Xbox titles on PC.
Bloomberg also notes that some recent releases have not sold as well on PC as hoped, suggesting that Sony’s test-the-waters approach has found said water lukewarm.
After a rocky six years, Sony cancels future single-player PC game releases Read More »