Android apps are blocking sideloading and forcing Google Play versions instead
Only way in now is through the roof —
“Select Play Partners” can block unofficial installation of their apps.
Enlarge / It’s never explained what this collection of app icons quite represents. A disorganized app you tossed together by sideloading? A face that’s frowning because it’s rolling down a bar held up by app icons? It’s weird, but not quite evocative.
You might sideload an Android app, or manually install its APK package, if you’re using a custom version of Android that doesn’t include Google’s Play Store. Alternately, the app might be experimental, under development, or perhaps no longer maintained and offered by its developer. Until now, the existence of sideload-ready APKs on the web was something that seemed to be tolerated, if warned against, by Google.
This quiet standstill is being shaken up by a new feature in Google’s Play Integrity API. As reported by Android Authority, developer tools to push “remediation” dialogs during sideloading debuted at Google’s I/O conference in May, have begun showing up on users’ phones. Sideloaders of apps from the British shop Tesco, fandom app BeyBlade X, and ChatGPT have reported “Get this app from Play” prompts, which cannot be worked around. An Android gaming handheld user encountered a similarly worded prompt from Diablo Immortal on their device three months ago.
Google’s Play Integrity API is how apps have previously blocked access when loaded onto phones that are in some way modified from a stock OS with all Google Play integrations intact. Recently, a popular two-factor authentication app blocked access on rooted phones, including the security-minded GrapheneOS. Apps can call the Play Integrity API and get back an “integrity verdict,” relaying if the phone has a “trustworthy” software environment, has Google Play Protect enabled, and passes other software checks.
Graphene has questioned the veracity of Google’s Integrity API and SafetyNet Attestation systems, recommending instead standard Android hardware attestation. Rahman notes that apps do not have to take an all-or-nothing approach to integrity checking. Rather than block installation entirely, apps could call on the API only during sensitive actions, issuing a warning there. But not having a Play Store connection can also deprive developers of metrics, allow for installation on incompatible devices (and resulting bad reviews), and, of course, open the door to paid app piracy.
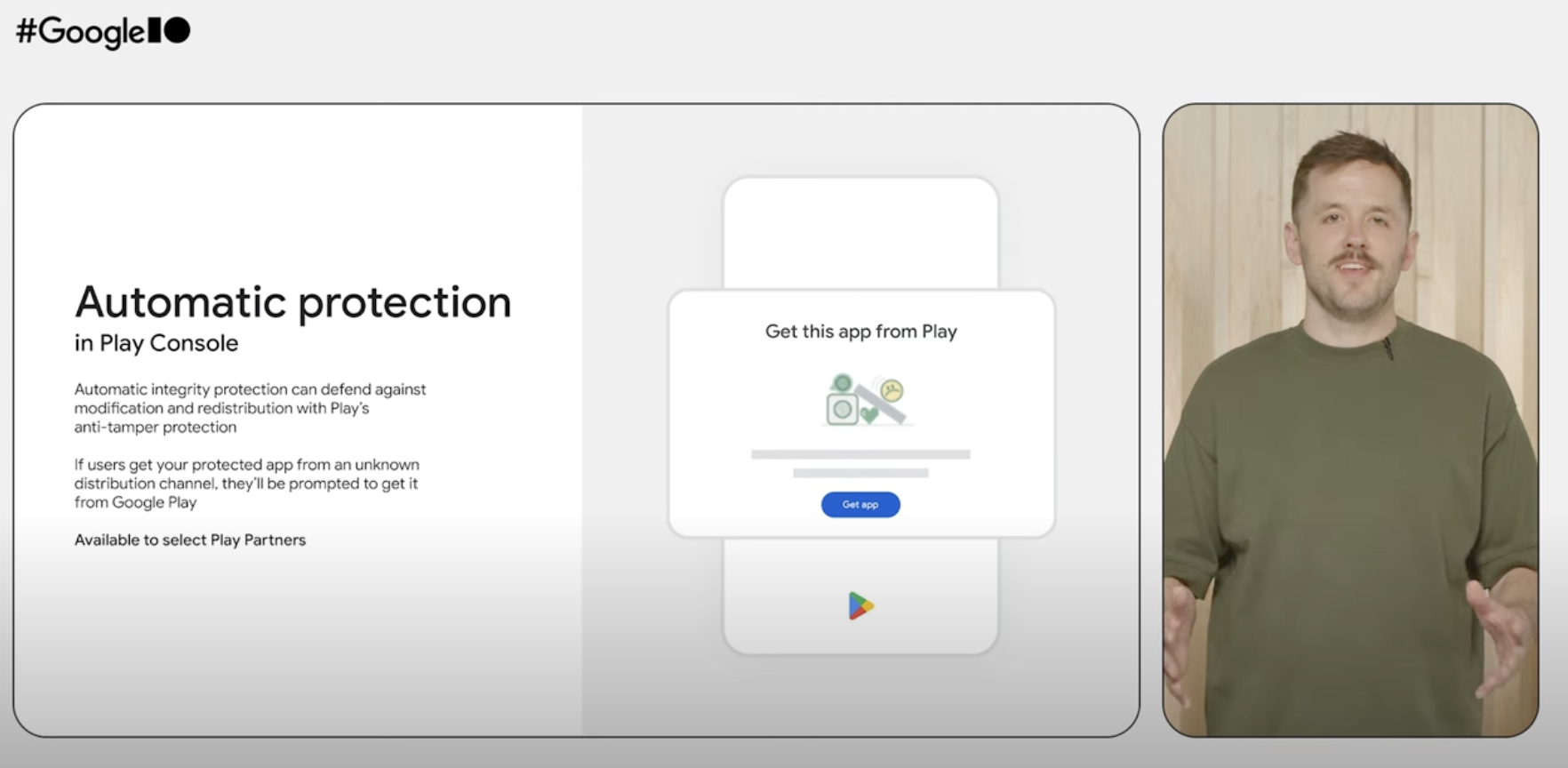
“Unknown distribution channels” blocked
Google’s developer video about “Automatic integrity protection” (at the 12-minute, 24-second mark on YouTube) notes that “select” apps have access to automatic protection. This adds an automatic checking tool to your app and the “strongest version of Google Play’s anti-tamper protection.” “If users get your protected app from an unknown distribution channel,” a slide in the presentation reads, “they’ll be prompted to get it from Google Play,” available to “select Play Partners.”
Last year, Google introduced malware scanning of sideloaded apps at install time. Google and Apple have come out against legislation that would broaden sideloading rights for smartphone owners, citing security and reliability concerns. European regulators forced Apple earlier this year to allow for sideloading apps and app stores, though with fees and geographical restrictions in place.
Android apps are blocking sideloading and forcing Google Play versions instead Read More »


