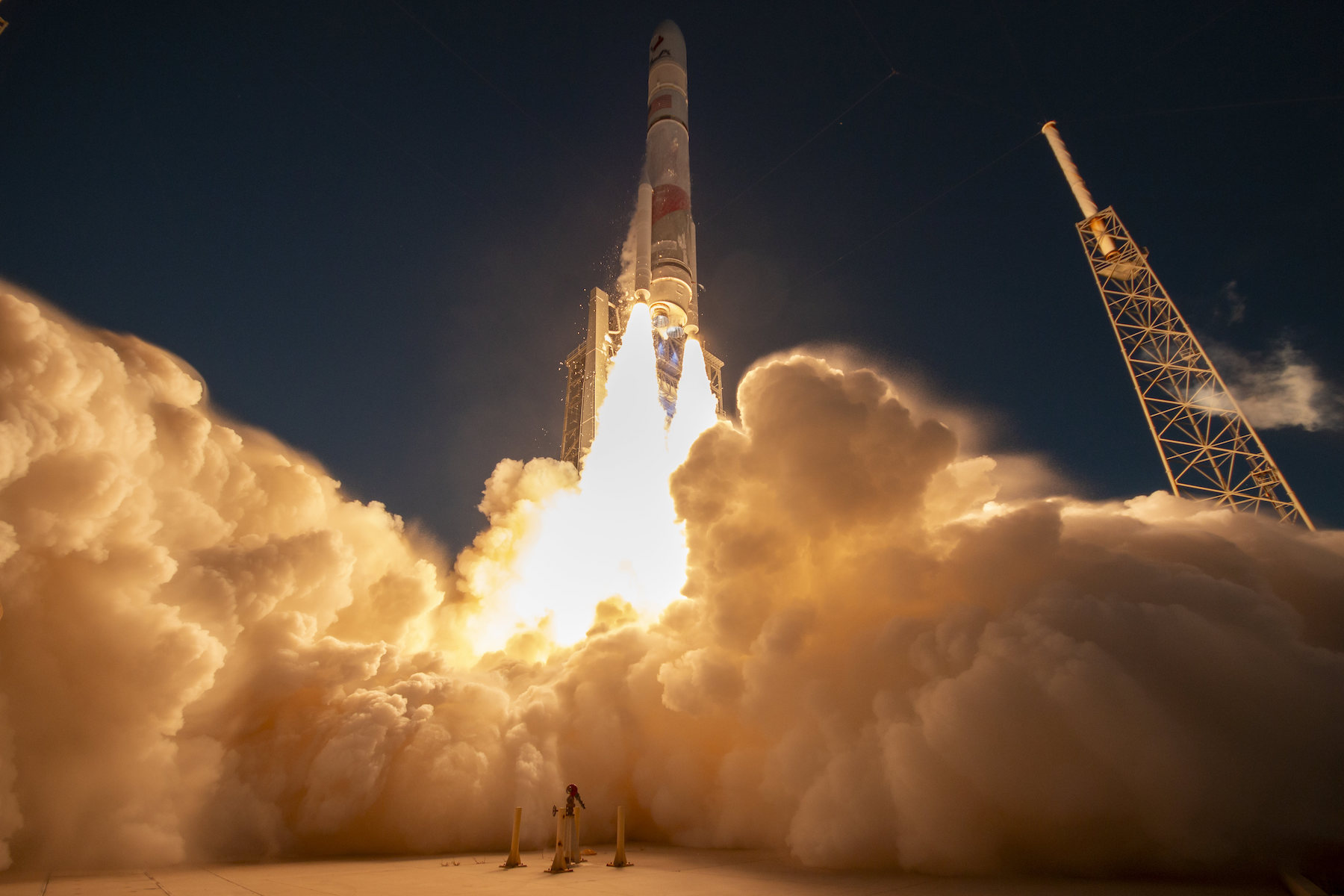
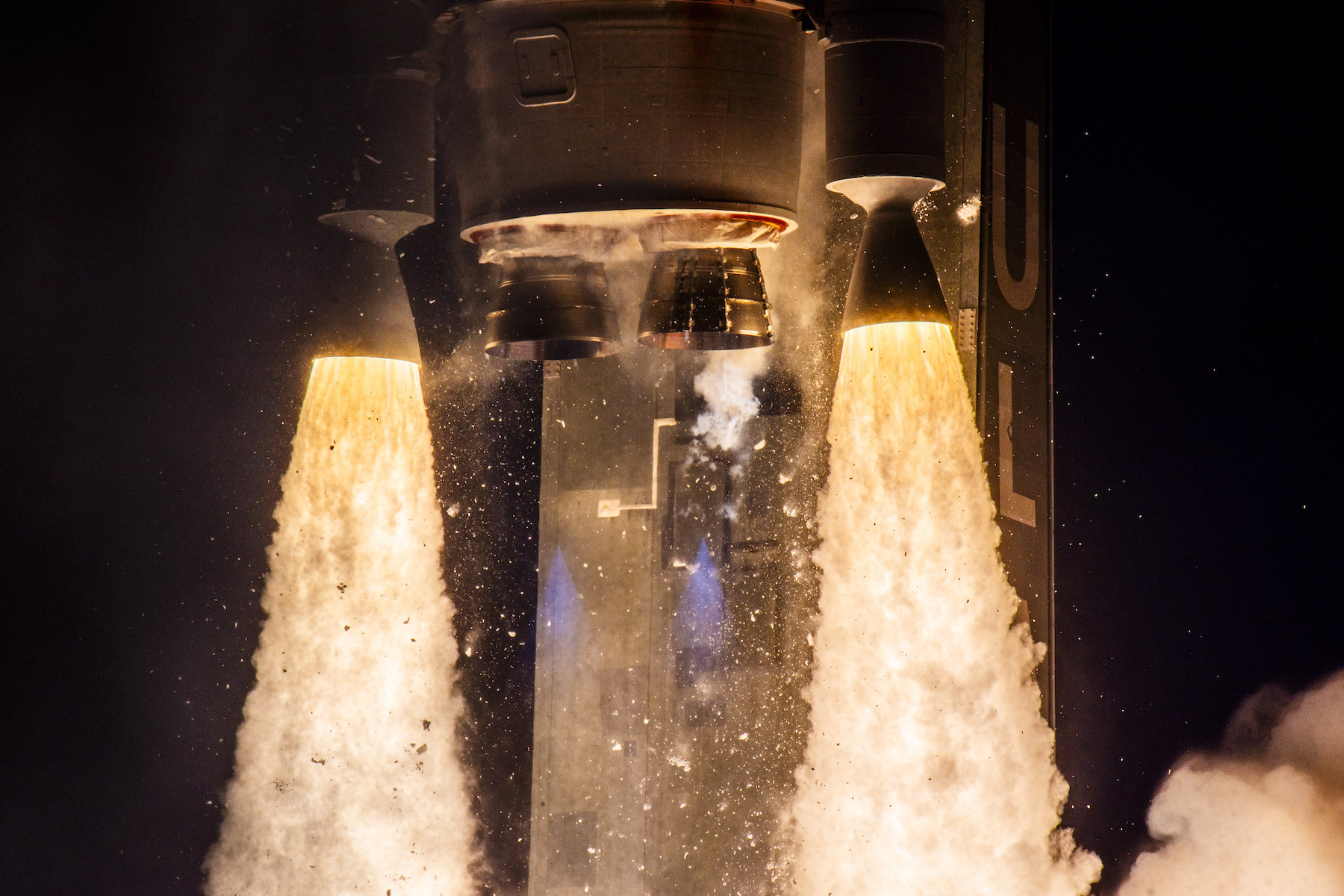
SpaceX’s next Starship launch—and first catch—could happen this weekend
The FAA is still reviewing plans for the fifth Starship test flight, but could approve it soon.
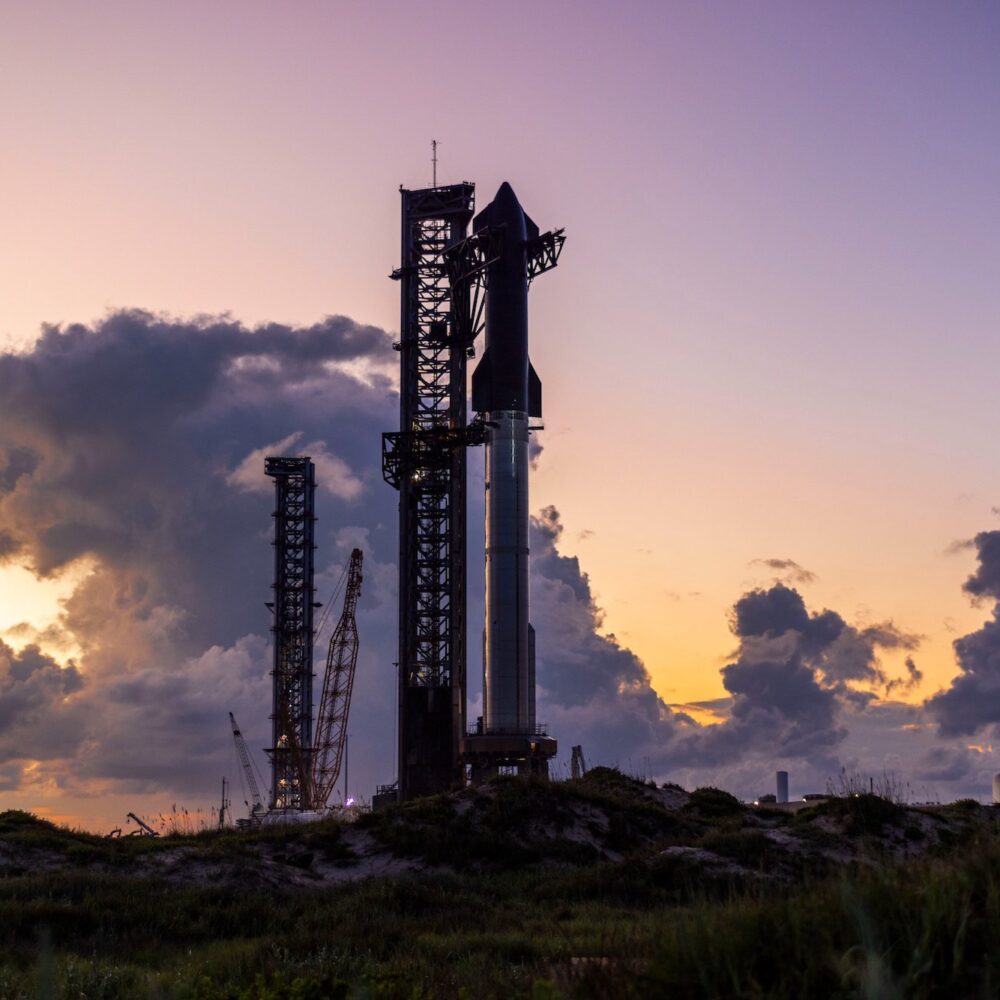

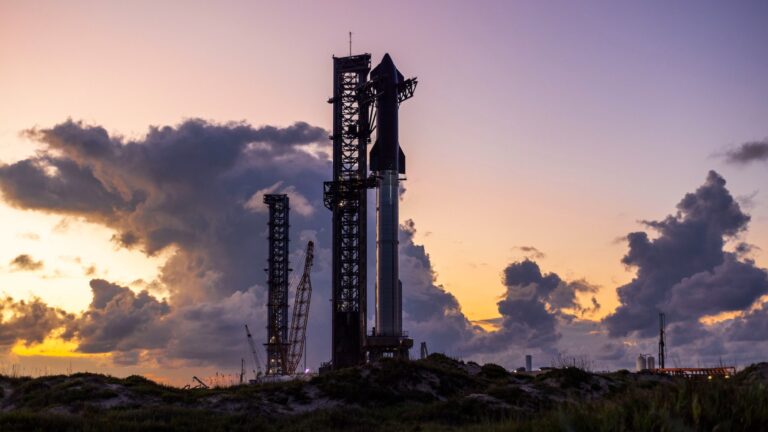
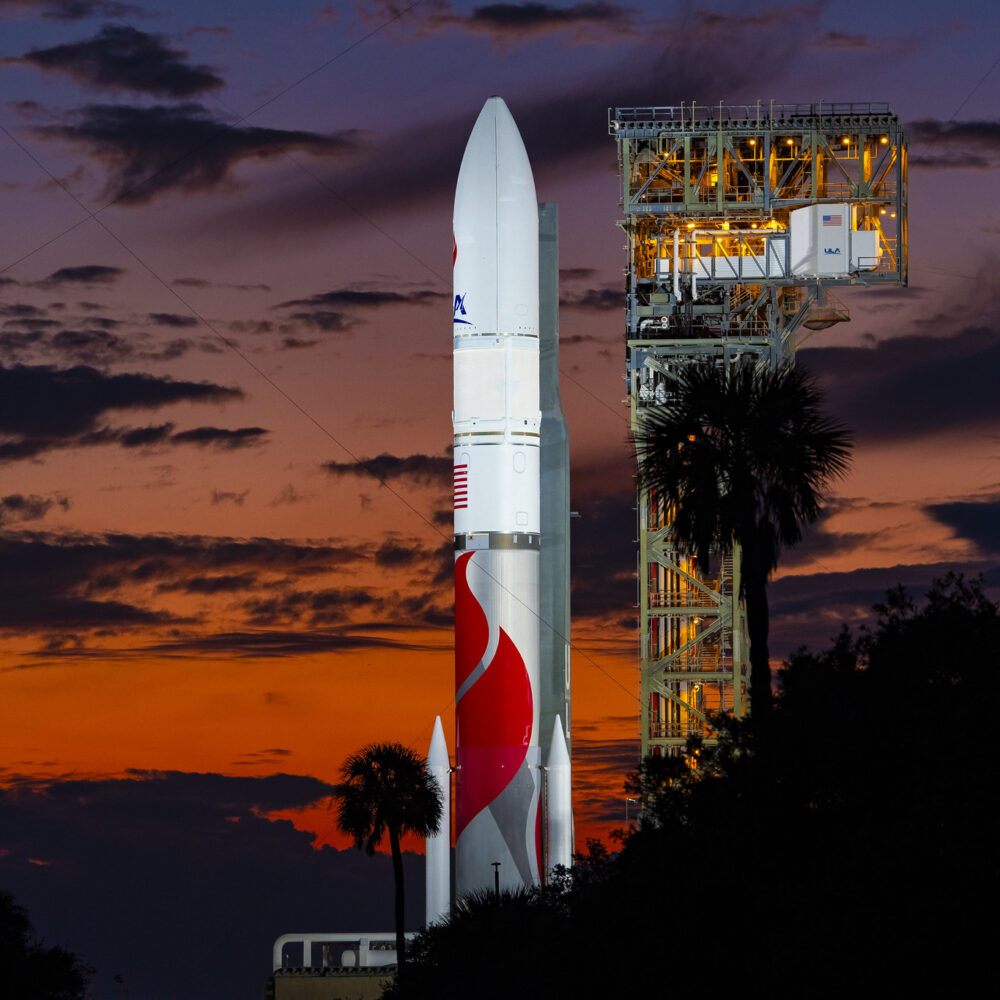
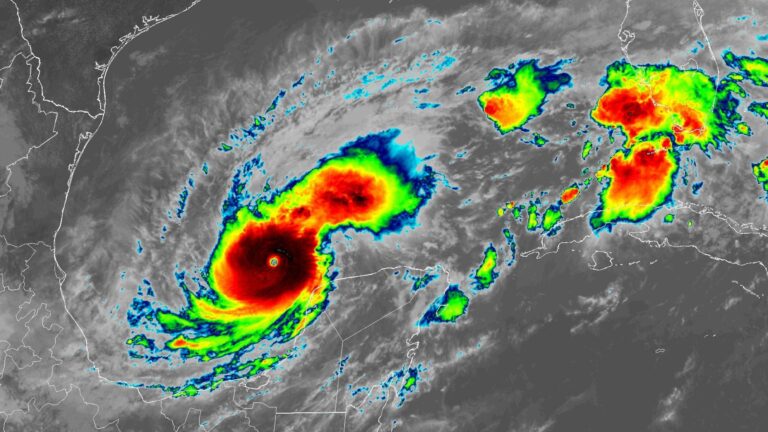
SpaceX’s fully-stacked Super Heavy booster and Starship upper stage at the company’s launch site in South Texas. Credit: SpaceX
We may not have to wait as long as we thought for the next test flight of SpaceX’s Starship rocket.
The world’s most powerful launcher could fly again as soon as Sunday, SpaceX says, assuming the Federal Aviation Administration grants approval. The last public statement released from the FAA suggested the agency didn’t expect to determine whether to approve a commercial launch license for SpaceX’s next Starship test flight before late November.
There’s some optimism at SpaceX that the FAA might issue a launch license much sooner, perhaps in time for Starship to fly this weekend. The launch window Sunday opens at 7 am CDT (8 am EDT; 12: 00 UTC), about a half-hour before sunrise at SpaceX’s Starbase launch site in South Texas.
“The fifth flight test of Starship will aim to take another step towards full and rapid reusability,” SpaceX wrote in an update posted on its website. “The primary objectives will be attempting the first ever return to launch site and catch of the Super Heavy booster and another Starship reentry and landing burn, aiming for an on-target splashdown of Starship in the Indian Ocean.”
Stacked together, the Super Heavy booster, or first stage, and the Starship upper stage stand nearly 400 feet (121 meters) tall. The Super Heavy booster—itself bigger than the fuselage of a 747 jumbo jet—will vertically return to the Starbase launch pad guided by cold gas thrusters, aerodynamic grid fins, and propulsive maneuvers with its methane-fueled Raptor engines.
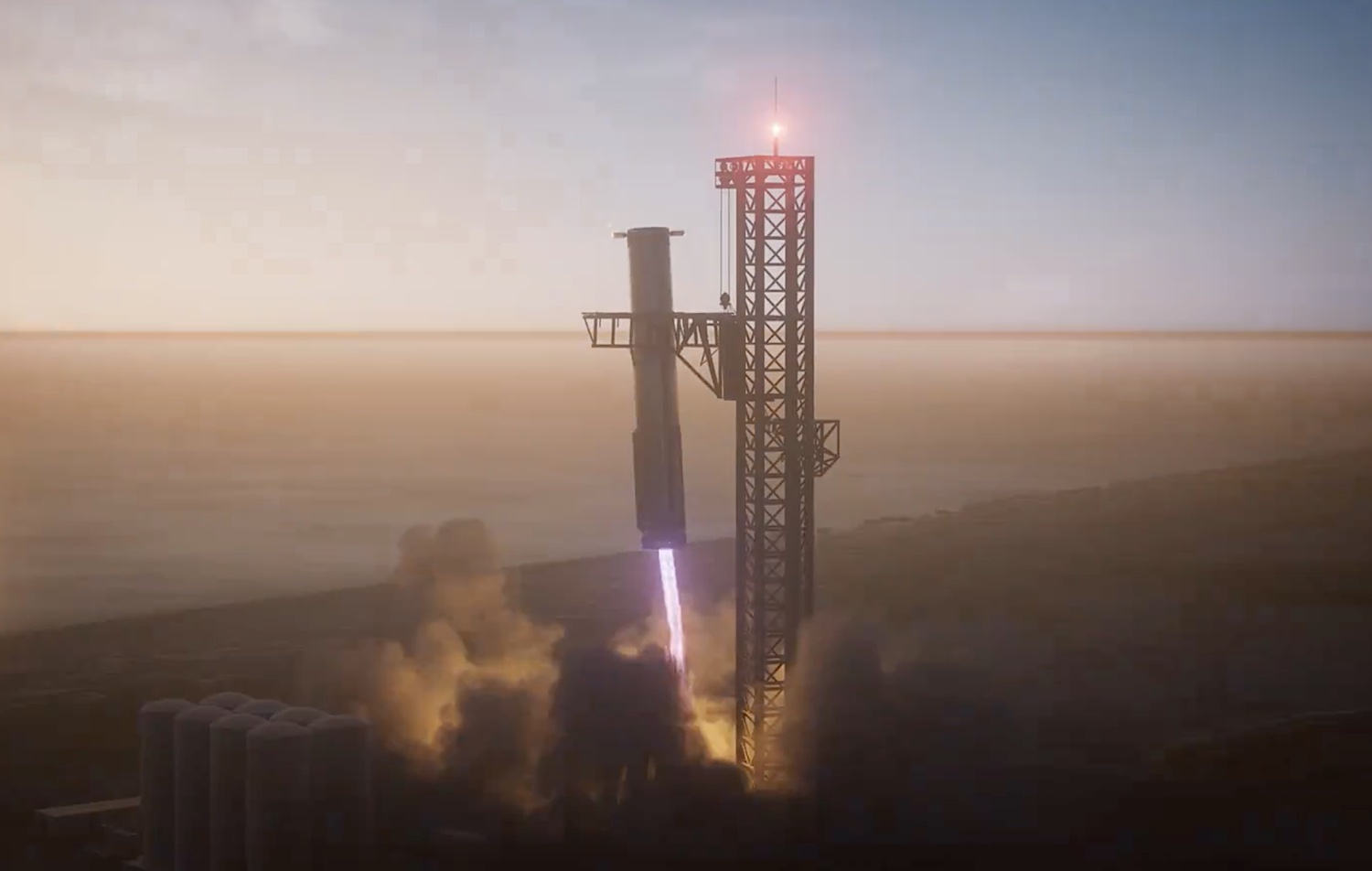
Once the booster’s Raptor engines slow it to a hover, mechanical arms on the launch pad tower will close in around the rocket and capture it in midair. If you’re into rockets, or just want to spice up your morning, you don’t want to miss this. We’ll have a more detailed story before the launch previewing the timeline of events.
Safety measures
The FAA has been reviewing SpaceX’s plans to bring the Super Heavy booster back to the Starbase launch pad for months.
Most recently, the agency’s review of SpaceX’s proposed flight plan has focused on the effects of the rocket’s sonic boom as it comes back to Earth. The FAA and other agencies are also studying how a disposable section of the booster, called a hot-staging ring, might impact the environment when it falls into the sea just offshore from Starbase, located on the Gulf Coast east of Brownsville.
During SpaceX’s most recent Starship test flight in June, the Super Heavy booster completed a control descent to a predetermined location in the Gulf of Mexico, giving engineers enough confidence to try a return to the launch site on the next mission.
SpaceX protested the length of time the FAA said it needed to review the flight plan, after the federal regulator previously told SpaceX it expected to make a license determination in September.
“Unfortunately, instead of focusing resources on critical safety analysis and collaborating on rational safeguards to protect both the public and the environment, the licensing process has been repeatedly derailed by issues ranging from the frivolous to the patently absurd,” SpaceX wrote in a statement last month.
“I think the two-month delay is necessary to comply with the launch requirements, and I think that’s an important part of safety culture,” said Michael Whitaker, the FAA administrator, in a congressional hearing September 24.
The FAA is responsible for ensuring commercial space launches do not endanger the public and comport with the US government’s national security and foreign policy interests. Earlier this year, SpaceX was also fined by the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality and the Environmental Protection Agency for alleged violations of environmental regulations related to the launch pad’s water system, which cools a steel flame deflector under the 33 main engines of Starship’s Super Heavy booster.
Ars contacted an FAA spokesperson Tuesday about the status of the agency’s review of the Starship launch license request, but did not receive a response.
Artist’s illustration of SpaceX’s Super Heavy booster coming in for a catch by the launch pad’s mechanical arms. Credit: SpaceX
Teams at Starbase completed two partial propellant loading tests on the fully stacked Starship rocket in recent days. Early Tuesday, SpaceX tested the water deluge system at the launch pad two times, presumably to check the system’s ability to activate minutes apart to protect the pad during launch and recovery of the Super Heavy booster.
Later Tuesday, SpaceX removed the Starship upper stage from the Super Heavy booster. This is required for technicians to perform one of the final tasks to prepare for launch—installing the rocket’s flight termination system, which would destroy the rocket if it veers off course.
“We accept no compromises when it comes to ensuring the safety of the public and our team, and the return will only be attempted if conditions are right,” SpaceX said.
SpaceX outlined additional human-in-the-loop safety criteria for the upcoming Starship flight. SpaceX launches are typically fully automated from liftoff through the end of the mission.
“Thousands of distinct vehicle and pad criteria must be met prior to a return and catch attempt of the Super Heavy booster, which will require healthy systems on the booster and tower and a manual command from the mission’s flight director,” SpaceX wrote. “If this command is not sent prior to the completion of the boostback burn, or if automated health checks show unacceptable conditions with Super Heavy or the tower, the booster will default to a trajectory that takes it to a landing burn and soft splashdown in the Gulf of Mexico.”
Recovering the Super Heavy booster back at the launch pad is critical for SpaceX’s ambition to rapidly reuse the rocket. Eventually, SpaceX will also recover and reuse the Starship portion of the rocket, but for now, the company is sticking to water landings for the ship.
Extensive upgrades
SpaceX teams in Texas have beefed up the launch tower and catch arms in the last few months, working around the clock to add structural stiffeners and test the arms’ load-carrying capability.
“Extensive upgrades ahead of this flight test have been made to hardware and software across Super Heavy, Starship, and the launch and catch tower infrastructure at Starbase,” SpaceX said. “SpaceX engineers have spent years preparing and months testing for the booster catch attempt, with technicians pouring tens of thousands of hours into building the infrastructure to maximize our chances for success.”
It will take about seven minutes for the Super Heavy booster to climb to the edge of space, separate from the Starship upper stage, and return to Starbase for recovery. While the booster comes back to the ground, Starship will fire its six engines to accelerate to near orbital velocity, fast enough to complete a half-lap around Earth before gravity pulls it toward an atmospheric reentry over the Indian Ocean.
This is a similar trajectory to the one Starship flew in June, when it survived a fiery reentry for a controlled splashdown. It was the first time SpaceX completed an end-to-end Starship test flight.
After analyzing the results from the June mission, SpaceX engineers decided to rework the heat shield for the next Starship vehicle. The company said its technicians spent more than 12,000 hours replacing the entire thermal protection system with new-generation tiles, a backup ablative layer, and additional protections between the ship’s flap structures.
Onboard cameras showed fragments of the heat shield falling off Starship when it reentered the atmosphere in June.
“This massive effort, along with updates to the ship’s operations and software for reentry and landing burn, will look to improve upon the previous flight and bring Starship to a soft splashdown at the target area in the Indian Ocean,” SpaceX said.
Starship won’t attempt to reignite its Raptor engines in space on the upcoming test flight. This is one of the next things SpaceX needs to demonstrate for Starship to soar into a stable orbit around Earth and guide itself to a controlled reentry to ensure it doesn’t become stranded in space or fall over a populated area. SpaceX wanted to relight a Raptor engine in space on Starship’s third test flight in March, but aborted the maneuver.
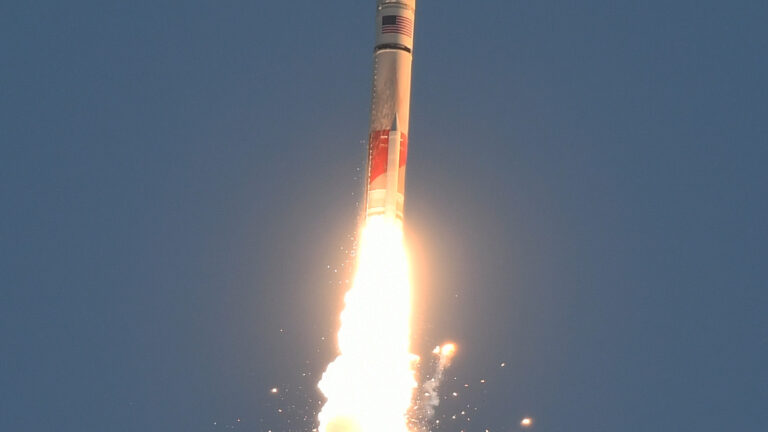
The business end of Starship’s Super Heavy booster during a launch in March. Credit: SpaceX
Once Starship is able to sustain a flight in low-Earth orbit, SpaceX can begin experiments with in-space refueling, which is required to support future Starship flights to the Moon, Mars, and other deep space destinations. Starship is a foundational element of SpaceX’s vision to create a settlement on the red planet.
NASA has a contract with SpaceX to develop a human-rated Starship to land astronauts on the Moon as part of the agency’s Artemis program. NASA’s official schedule calls for the first Artemis crew landing in September 2026. Realistically, the landing will probably happen later in the decade because the Starship lander and new lunar spacesuits likely won’t be ready in two years.
Starships will likely fly many dozens of times, if not more, before NASA approves it to land astronauts on the Moon. These flights will test the rocket’s ability to repeatedly and reliably fly to space and back, transfer cryogenic propellants in orbit, and safely land on the lunar surface without a crew.
As we’ve seen with SpaceX’s workhorse Falcon 9 rocket, rapidly reusing elements of a launch vehicle can enable rapid-fire launch cadences. Validating the architecture for recovering the Super Heavy booster directly on the launch pad, as SpaceX intends to do quite soon, is a key step on this path.
SpaceX’s next Starship launch—and first catch—could happen this weekend Read More »