If you thought Astra was going to go away quietly, you were wrong
On Wednesday morning, a surprising email popped into my inbox with the following subject line: “Astra announces Department of Defense contract valued up to $44 Million.”
I had to read it a second time to make sure I got it right. Astra, the launch company? Astra, whose valuation went from $2.6 billion to $25 million after a series of launch failures? Astra, the company that was taken private in July at 50 cents a share?
Yes, it was that Astra.
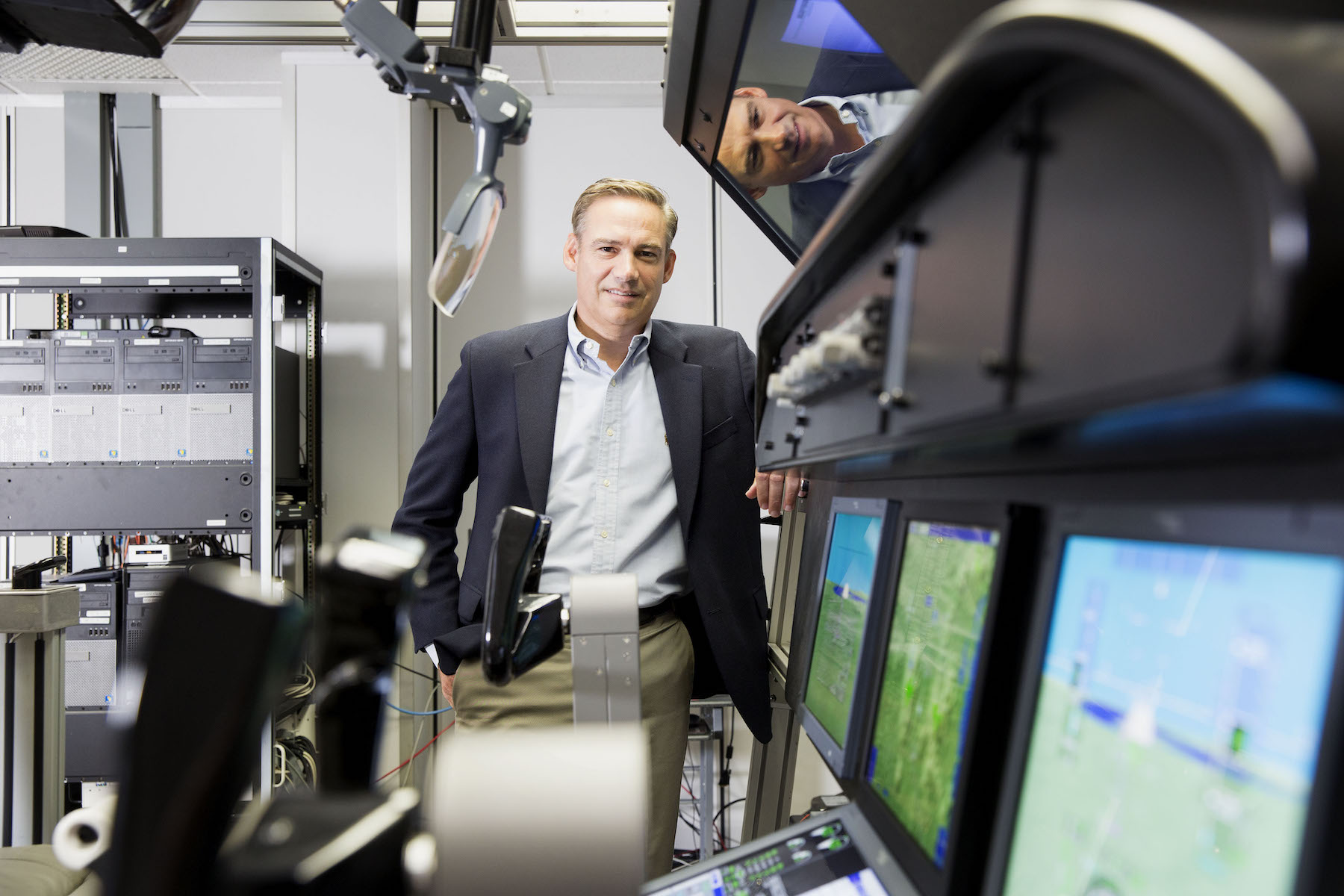
This was curious, indeed. To get some answers, I spoke with the cofounder of Astra, Chris Kemp, who remains the company’s chief executive.
“If I have learned anything, it’s that you just don’t give up,” Kemp said. “You know, if you give up easily, this is not the place to be. Fortunately, I am surrounded by a team that has chosen not to give up.”
Rocket 4 becomes more real
I’ll be frank: When Kemp and his co-founder, Adam London, took Astra private this summer, I never expected to hear from the company again. Astra certainly was not the first launch company to fail, and it won’t be the last. But it is the first to seemingly resurrect itself in such a dramatic way.
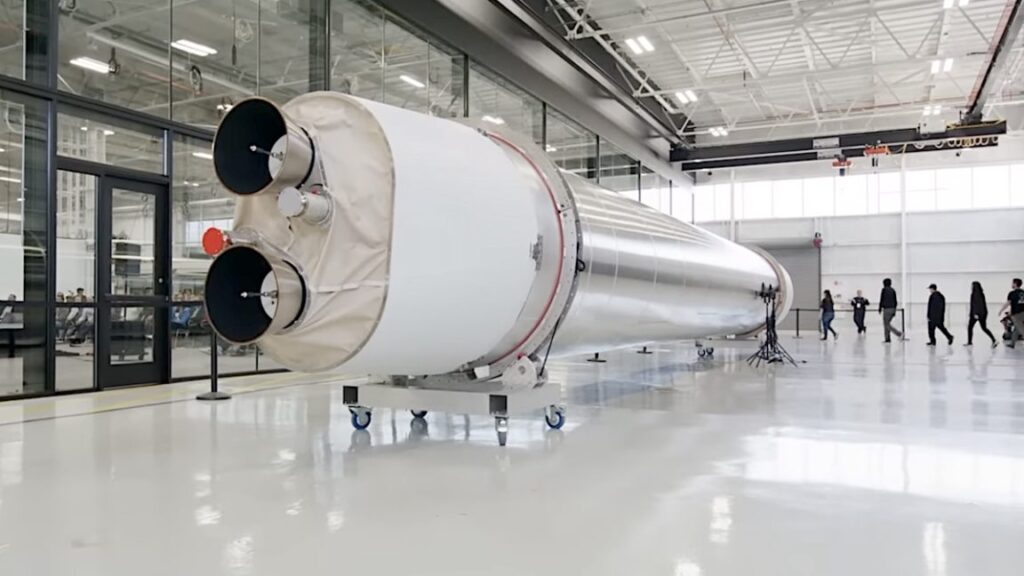
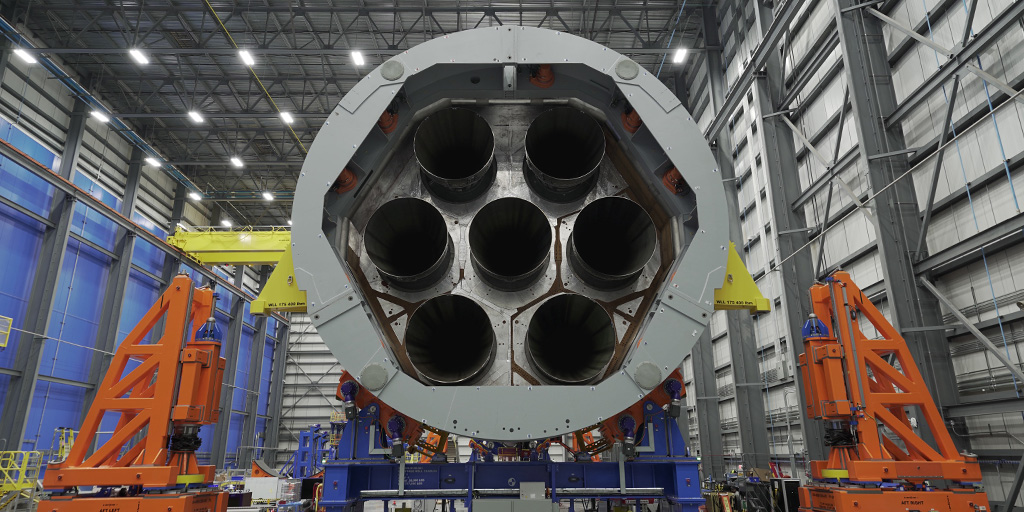
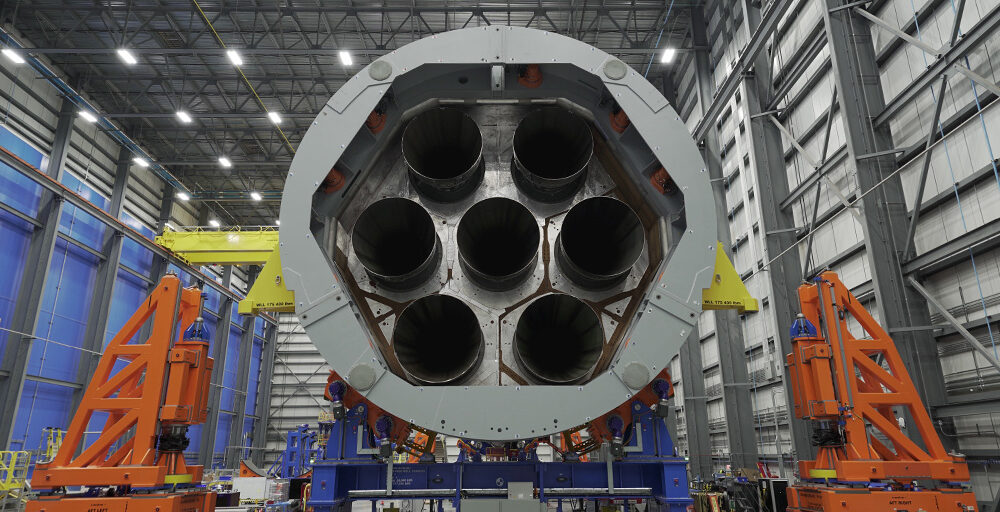
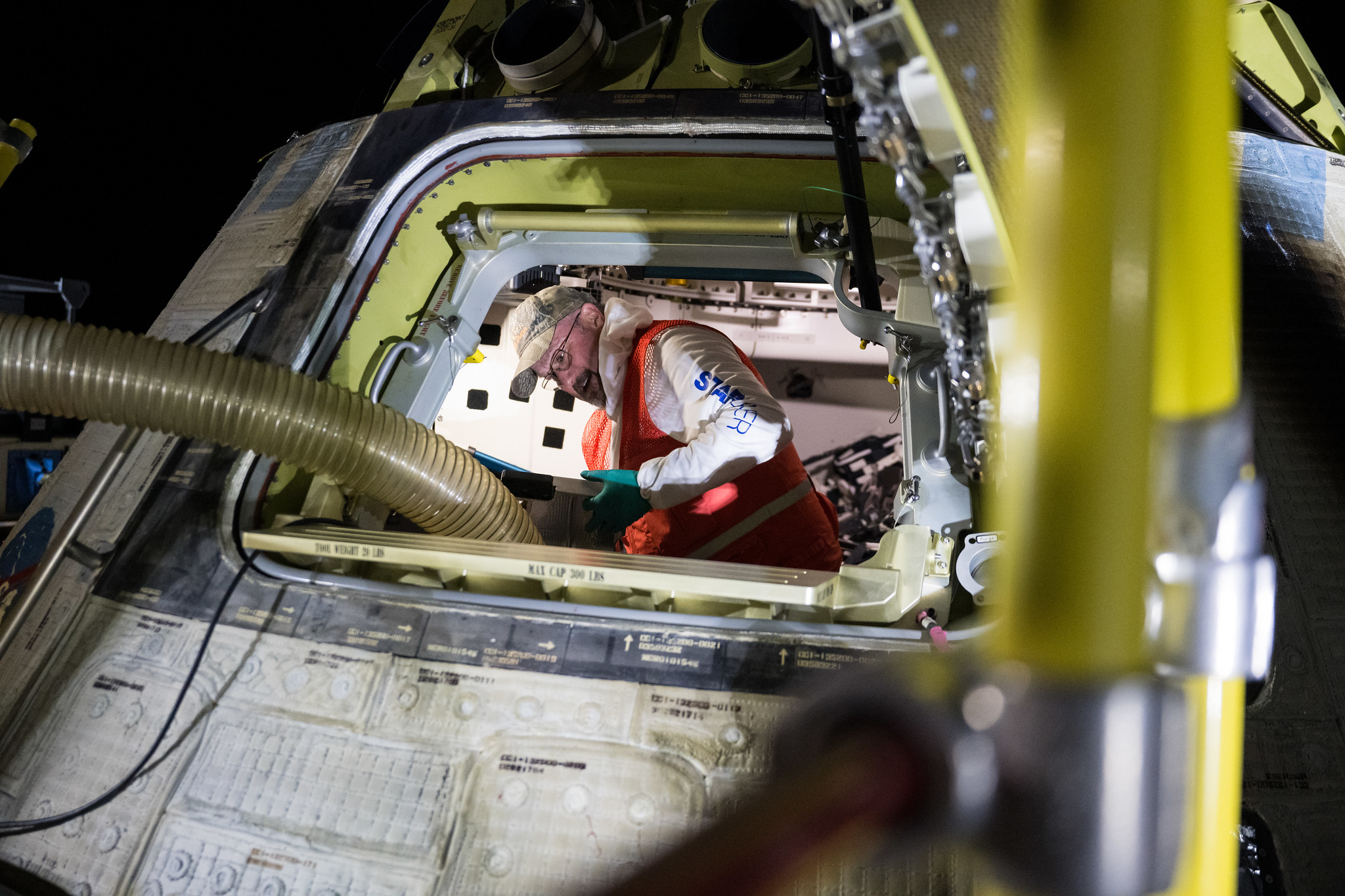
To be clear, Astra is not back yet. The company remains in the phase of building and testing rocket stages and engines and does not have a launch vehicle ready to go. Its new booster, Rocket 4, will launch no earlier than the fourth quarter of 2025, Kemp said. (That date should probably be viewed with some skepticism).
The company has previously discussed Rocket 4, which is intended to carry 600 kg to low-Earth orbit, as far back as August 2022. But at the time, most of the launch industry, including this reporter, shrugged and moved along. After all, the company’s smaller vehicle, Rocket 3, failed on five of its seven orbital launch attempts. The general sentiment was that the new rocket would never fly.
However, even as Astra’s finances worsened and the company had to stave off bankruptcy by being taken private, not everyone dismissed the vision. In April 2023, the US Space Force awarded a task order for Rocket 4 to launch the STP-S29B mission. That was interesting, but it was just a single data point. Then came this week’s announcement that the US Department of Defense’s “Defense Innovation Unit” had awarded a grant worth up to $44 million to Astra for a “tactically responsive launch system.”
If you thought Astra was going to go away quietly, you were wrong Read More »