Parrots struggle when told to do something other than mimic their peers
There have been many studies on the capability of non-human animals to mimic transitive actions—actions that have a purpose. Hardly any studies have shown that animals are also capable of intransitive actions. Even though intransitive actions have no particular purpose, imitating these non-conscious movements is still thought to help with socialization and strengthen bonds for both animals and humans.
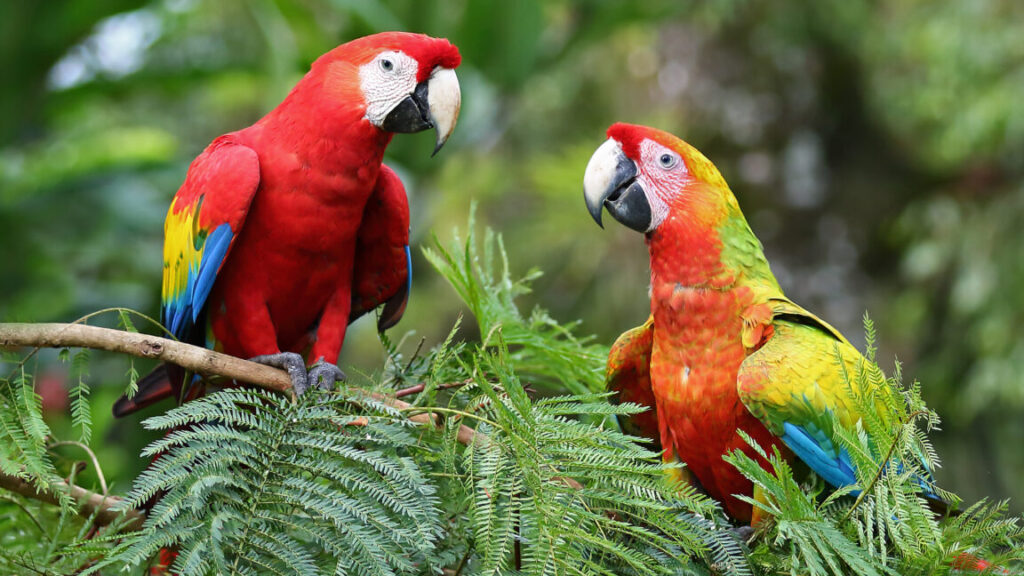
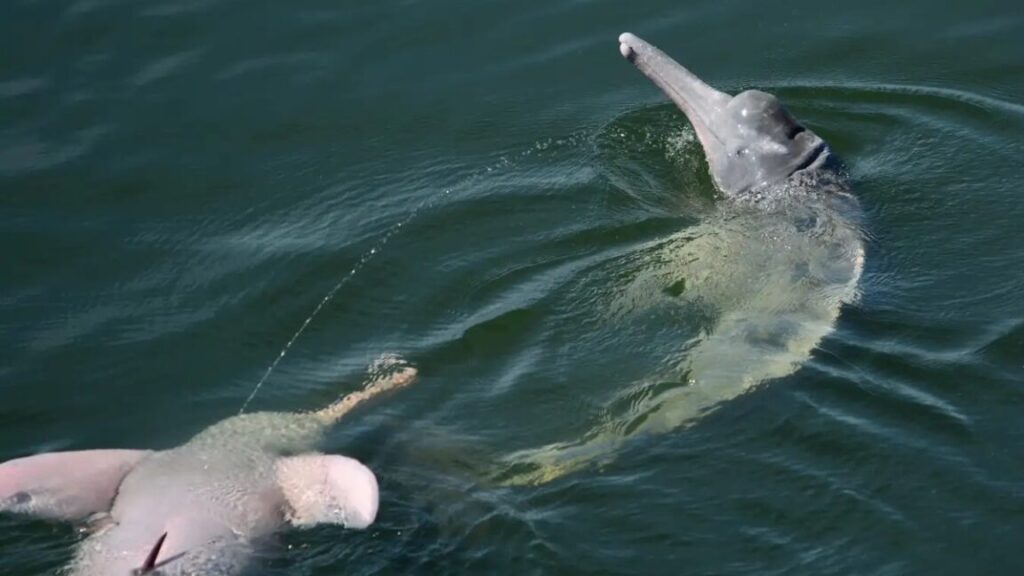
Zoologist Esha Haldar and colleagues from the Comparative Cognition Research group worked with blue-throated macaws, which are critically endangered, at the Loro Parque Fundación in Tenerife. They trained the macaws to perform two intransitive actions, then set up a conflict: Two neighboring macaws were asked to do different actions.
What Haldar and her team found was that individual birds were more likely to perform the same intransitive action as a bird next to them, no matter what they’d been asked to do. This could mean that macaws possess mirror neurons, the same neurons that, in humans, fire when we are watching intransitive movements and cause us to imitate them (at least if these neurons function the way some think they do).
But it wasn’t on purpose
Parrots are already known for their mimicry of transitive actions, such as grabbing an object. Because they are highly social creatures with brains that are large relative to the size of their bodies, they made excellent subjects for a study that gauged how susceptible they were to copying intransitive actions.
Mirroring of intransitive actions, also called automatic imitation, can be measured with what’s called a stimulus-response-compatibility (SRC) test. These tests measure the response time between seeing an intransitive movement (the visual stimulus) and mimicking it (the action). A faster response time indicates a stronger reaction to the stimulus. They also measure the accuracy with which they reproduce the stimulus.
Until now, there have only been three studies that showed non-human animals are capable of copying intransitive actions, but the intransitive actions in these studies were all by-products of transitive actions. Only one of these focused on a parrot species. Haldar and her team would be the first to test directly for animal mimicry of intransitive actions.
Parrots struggle when told to do something other than mimic their peers Read More »