Oklahoma’s big “TV nudes” scandal was… a Jackie Chan movie on a Samsung streaming service
News 4 watched the movie and confirmed it contains several scenes that match the description given by board members, including one where a group of fully nude women [!] work inside a factory [!!] packaging cocaine [!!!], some wearing only lab coats [!!!!].
Another scene shows a fully nude woman giving a man a massage, eventually moving under the table while the dialogue strongly suggests sexual activity.
But why was The Protector showing on a TV in a state office building at all? Investigators came to find out that the Samsung smart TV in question—recently installed in the office—had been set up in such a way that it defaulted to showing Samsung TV Plus Channel 1204, the “Movie Hub Action.” (You can see Samsung’s full list of TV Plus streaming channels here.) And at the time of the state board meeting, Movie Hub Action was streaming The Protector. How and why the TV was turned on or switched to this streaming channel isn’t clear, but the whole thing appears to be an absolutely bizarre accident.
As part of this important investigation, the sheriff’s office then took clips from The Protector to the board members who complained. According to the Oklahoma Voice, “The board members, Becky Carson and Ryan Deatherage, confirmed to the Sheriff’s Office that the movie was consistent with what they saw on the TV.”
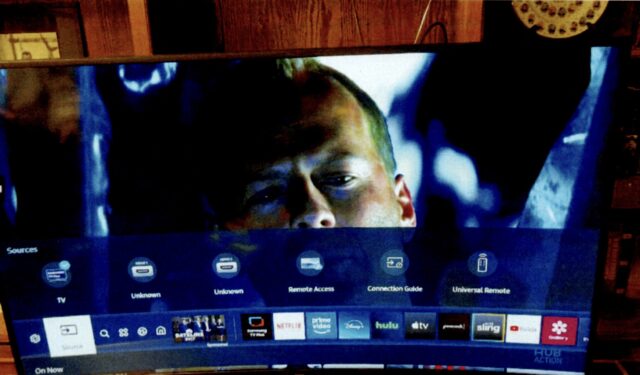
Behold! The actual TV from the incident. Credit: Alias
Hooking smart TVs up to the Internet looks increasingly like a bad idea, though not usually for the reason found in this case. TV manufacturers have taken what should have been a useful feature and turned it into a way to spy on what you’re watching and to push ads to your TV.
Now you can add “showing naked, cocaine-packaging factory workers to Oklahoma Board of Education members” to the list of grievances.