Estate of woman who died in 2021 heat dome sues Big Oil for wrongful death
At least 100 heat-related deaths in Washington state came during the unprecedented heat wave.
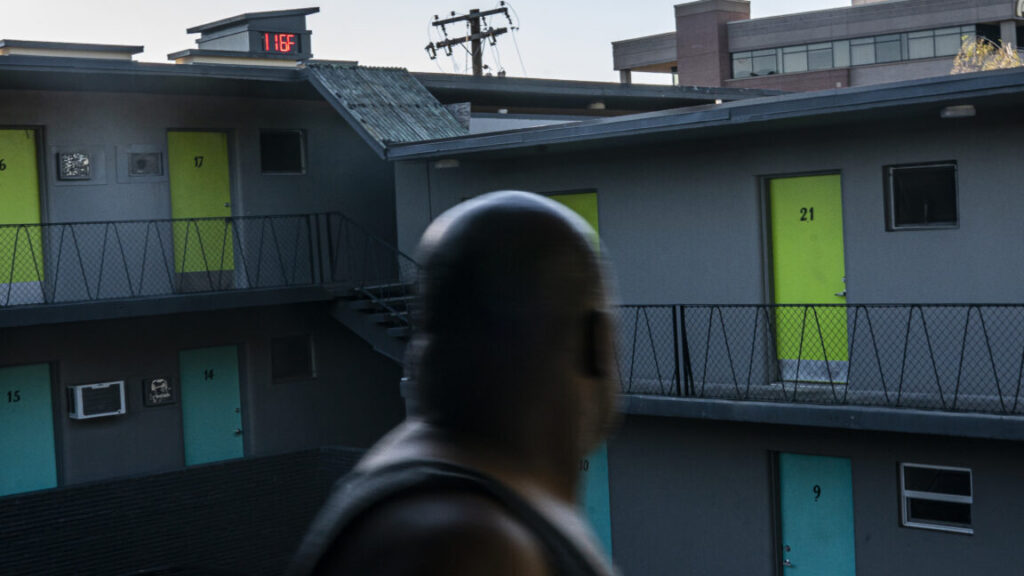
Everett Clayton looks at a digital thermometer on a nearby building that reads 116 degrees while walking to his apartment on June 27, 2021 in Vancouver, Washington. Credit: Nathan Howard/Getty Images
This article originally appeared on Inside Climate News, a nonprofit, non-partisan news organization that covers climate, energy, and the environment. Sign up for their newsletter here.
The daughter of a woman who was killed by extreme heat during the 2021 Pacific Northwest heat dome has filed a first-of-its-kind lawsuit against major oil companies claiming they should be held responsible for her death.
The civil lawsuit, filed on May 29 in King County Superior Court in Seattle, is the first wrongful death case brought against Big Oil in the US in the context of climate change. It attempts to hold some of the world’s biggest fossil fuel companies liable for the death of Juliana Leon, who perished from overheating during the heat dome event, which scientists have determined would have been virtually impossible absent human-caused climate change.
“The extreme heat that killed Julie was directly linked to fossil fuel-driven alteration of the climate,” the lawsuit asserts. It argues that fossil fuel defendants concealed and misrepresented the climate change risks of their products and worked to delay a transition to cleaner energy alternatives. Furthermore, oil companies knew decades ago that their conduct would have dangerous and deadly consequences, the case alleges.
“Defendants have known for all of Julie’s life that their affirmative misrepresentations and omissions would claim lives,” the complaint claims. Leon’s daughter, Misti, filed the suit on behalf of her mother’s estate.
At 65, Juliana Leon was driving home from a medical appointment in Seattle on June 28, 2021, a day when the temperature peaked at 108° Fahrenheit (42.2° Celsius). She had the windows rolled down since the air conditioner in her car wasn’t working, but with the oven-like outdoor temperatures she quickly succumbed to the stifling heat. A passerby found her unresponsive in her car, which was pulled over on a residential street. Emergency responders were unable to revive her. The official cause of death was determined to be hyperthermia, or overheating.
There were at least 100 heat-related deaths in the state from June 26 to July 2, 2021, according to the Washington State Department of Health. That unprecedented stretch of scorching high temperatures was the deadliest weather-related event in Washington’s history. Climate change linked to the burning of fossil fuels intensified this extreme heat event, scientists say.
Misti Leon’s complaint argues that big oil companies “are responsible” for her mother’s climate change-related death. “Through their failure to warn, marketing, distribution, extraction, refinement, transport, and sale of fossil fuels, defendants each bear responsibility for the spike in atmospheric CO2 levels that have resulted in climate change, and thus the occurrence of a virtually impossible weather event and the extreme temperatures of the Heat Dome,” the suit alleges.
Defendants include ExxonMobil, BP, Chevron, Shell, ConocoPhillips, and Phillips 66. Phillips 66 declined to comment; the rest of the companies did not respond to requests for comment.
The plaintiff is represented by the Bechtold Law Firm, based in Missoula, Montana. The lawsuit brings state tort law claims of wrongful death, failure to warn, and public nuisance, and seeks relief in the form of damages as well as a public education campaign to “rectify defendants’ decades of misinformation.”
Major oil and gas companies are currently facing more than two dozen climate damages and deception cases brought by municipal, state, and tribal governments, including a case filed in 2023 by Multnomah County, Oregon, centered around the 2021 Pacific Northwest heat dome. The Leon case, however, is the first climate liability lawsuit filed by an individual against the fossil fuel industry.
“This is the first case that is directly making the connection between the misconduct and lies of big oil companies and a specific, personalized tragedy, the death of Julie Leon,” said Aaron Regunberg, accountability director for Public Citizen’s climate program.
“It puts a human face on it,” Pat Parenteau, emeritus professor of law at Vermont Law and Graduate School, told Inside Climate News.
Climate accountability advocates say the lawsuit could open up a new front for individuals suffering from climate change-related harms to pursue justice against corporate polluters who allegedly lied about the risks of their products.
“Big Oil companies have known for decades that their products would cause catastrophic climate disasters that would become more deadly and destructive if they didn’t change their business model. But instead of warning the public and taking steps to save lives, Big Oil lied and deliberately accelerated the problem,” Richard Wiles, president of the Center for Climate Integrity, said in a statement. “This latest case—the first filed on behalf of an individual climate victim—is another step toward accountability.”
“It’s a model for victims of climate disasters all across the country,” said Regunberg. “Anywhere there’s an extreme weather event with strong attribution science connecting it to climate change, families experiencing a tragedy can file a very similar case.”
Regunberg and several other legal experts have argued that Big Oil could face criminal prosecution for crimes such as homicide and reckless endangerment in the context of climate change, particularly given evidence of internal industry documents suggesting companies like Exxon knew that unabated fossil fuel use could result in “catastrophic” consequences and deaths. A 1996 presentation from an Exxon scientist, for example, outlines projected human health impacts stemming from climate change, including “suffering and death due to thermal extremes.”
The Leon case could “help lay the groundwork” for potential climate homicide cases, Regunberg said. “Wrongful death suits are important. They provide a private remedy to victims of wrongful conduct that causes a death. But we also think there’s a need for public justice, and that’s the role that criminal prosecution is supposed to have,” he told Inside Climate News.
The lawsuit is likely to face a long uphill battle in the courts. Other climate liability cases against these companies brought by government entities have been tied up in procedural skirmishes, some for years, and no case has yet made it to trial.
“In this case we have a grieving woman going up against some of the most powerful corporations in the world, and we’ve seen all the legal firepower they are bringing to bear on these cases,” Regunberg said.
But if the case does eventually make it to trial, it could be a game-changer. “That’s going to be a jury in King County, Washington, of people who probably experienced and remember the Pacific heat dome event, and maybe they know folks who were impacted. I think that’s going to be a compelling case that has a good chance of getting an outcome that provides some justice to this family,” Regunberg said.
Even if it doesn’t get that far, the lawsuit still “marks a significant development in climate liability,” according to Donald Braman, an associate professor of criminal law at Georgetown University and co-author of a paper explaining the case for prosecuting Big Oil for climate homicide.
“As climate attribution science advances, linking specific extreme weather events to anthropogenic climate change with greater confidence, the legal arguments for liability are strengthening. This lawsuit, being the first of its kind for wrongful death in this context, will be closely watched and could set important precedents, regardless of its ultimate outcome,” he said. “It reflects a growing societal demand for accountability for climate-related harms.”
Estate of woman who died in 2021 heat dome sues Big Oil for wrongful death Read More »