Mozilla’s privacy service drops a provider with ties to people-search sites
People search —
Owner of Onerep removal service launched “dozens of people-search services.”
Mozilla
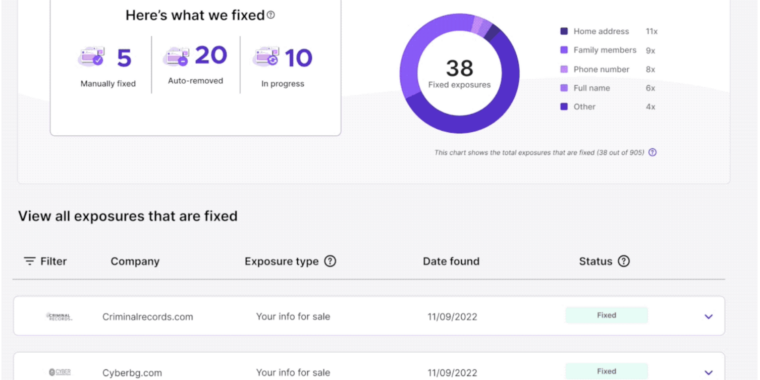
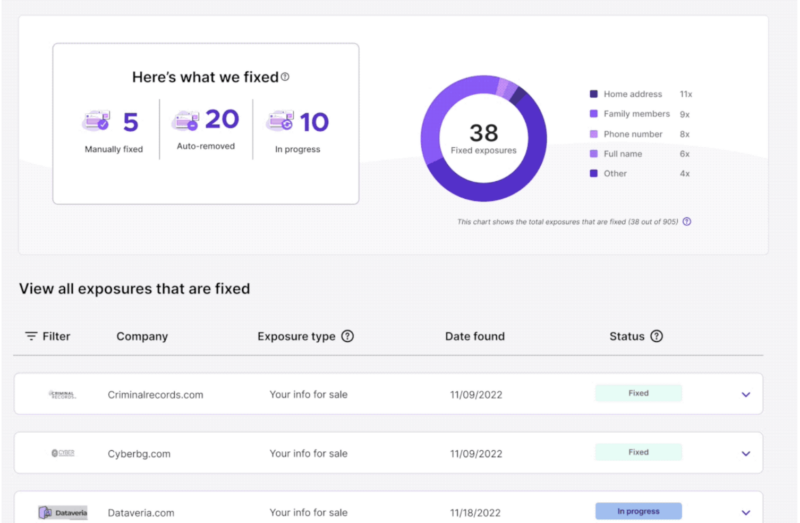
Mozilla’s Monitor Plus, a service launched by the privacy-minded tech firm in February, notes on its pitch page that there is “a $240 billion industry of data brokers selling your private information for profit” and that its offering can “take back your privacy.”
Mozilla’s most recent move to protect privacy has been to cut out one of the key providers of Monitor Plus’ people-search protections, Onerep. That comes after reporting from security reporter Brian Krebs, who uncovered Onerep CEO and founder Dimitri Shelest as the founder of “dozens of people-search services since 2010,” including one, Nuwber, that still sells the very kind of “background reports” that Monitor Plus seeks to curb.
Shelest told Krebs in a statement (PDF) that he did have an ownership stake in Nuwber, but that Nuwber has “zero cross-over or information-sharing with Onerep” and that he no longer operates any other people-search sites. Shelest admitted the bad look but said that his experience with people search gave Onerep “the best tech and team in the space.”
Brandon Borrman, vice president of communications at Mozilla, said in a statement that while “customer data was never at risk, the outside financial interests and activities of Onerep’s CEO do not align with our values.” Mozilla is “working now to solidify a transition plan,” Borrman said. A Mozilla spokesperson confirmed to Ars today that Mozilla is continuing to offer Monitor Plus, suggesting no pause in subscriptions, at least for the moment.
Monitor Plus also kept track of a user’s potential data breach exposures in partnership with HaveIBeenPwned. Troy Hunt, founder of HaveIBeenPwned, told Krebs that aside from Onerep’s potential conflict of interest, broker removal services tend to be inherently fraught. “[R]emoving your data from legally operating services has minimal impact, and you can’t remove it from the outright illegal ones who are doing the genuine damage.”
Still, every bit—including removing yourself from the first page of search results—likely counts. Beyond sites that scrape public records and court documents for your information, there are the other data brokers selling barely anonymized data from web browsing, app sign-ups, and other activity. A recent FTC settlement with antivirus and security firm Avast highlighted the depth of identifying information that often is available for sale to both commercial and government entities.
Mozilla’s privacy service drops a provider with ties to people-search sites Read More »