After seeing Wi-Fi network named “STINKY,” Navy found hidden Starlink dish on US warship
I need that sweet, sweet wi-fi —
To be fair, it’s hard to live without Wi-Fi.

Enlarge / The USS Manchester. Just the spot for a Starlink dish.
Department of Defense
It’s no secret that government IT can be a huge bummer. The records retention! The security! So government workers occasionally take IT into their own hands with creative but, err, unauthorized solutions.
For instance, a former US Ambassador to Kenya in 2015 got in trouble after working out of an embassy compound bathroom—the only place where he could use his personal computer (!) to access an unsecured network (!!) that let him log in to Gmail (!!!), where he did much of his official business—rules and security policies be damned.
Still, the ambassador had nothing on senior enlisted crew members of the littoral combat ship USS Manchester, who didn’t like the Navy’s restriction of onboard Internet access. In 2023, they decided that the best way to deal with the problem was to secretly bolt a Starlink terminal to the “O-5 level weatherdeck” of a US warship.
They called the resulting Wi-Fi network “STINKY”—and when officers on the ship heard rumors and began asking questions, the leader of the scheme brazenly lied about it. Then, when exposed, she went so far as to make up fake Starlink usage reports suggesting that the system had only been accessed while in port, where cybersecurity and espionage concerns were lower.
Rather unsurprisingly, the story ends badly, with a full-on Navy investigation and court-martial. Still, for half a year, life aboard the Manchester must have been one hell of a ride.
Enlarge / A photo included in the official Navy investigation report, showing the location of the hidden Starlink terminal on the USS Manchester.
DOD (through Navy Times)
One stinky solution
The Navy Times has all the new and gory details, and you should read their account, because they went to the trouble of using the Freedom of Information Act (FOIA) to uncover the background of this strange story. But the basics are simple enough: People are used to Internet access. They want it, even (perhaps especially!) when at sea on sensitive naval missions to Asia, where concern over Chinese surveillance and hacking runs hot.
So, in early 2023, while in the US preparing for a deployment, Command Senior Chief Grisel Marrero—the enlisted shipboard leader—led a scheme to buy a Starlink for $2,800 and to install it inconspicuously on the ship’s deck. The system was only for use by chiefs—not by officers or by most enlisted personnel—and a Navy investigation later revealed that at least 15 chiefs were in on the plan.
The Navy Times describes how Starlink was installed:
The Starlink dish was installed on the Manchester’s O-5 level weatherdeck during a “blanket” aloft period, which requires a sailor to hang high above or over the side of the ship.
During a “blanket” aloft, duties are not documented in the deck logs or the officer of the deck logs, according to the investigation.
It’s unclear who harnessed up and actually installed the system for Marrero due to redactions in the publicly released copy of the probe, but records show Marrero powered up the system the night before the ship got underway to the West Pacific waters of U.S. 7th Fleet.
This was all extremely risky, and the chiefs don’t appear to have taken amazing security precautions once everything was installed. For one thing, they called the network “STINKY.” For another, they were soon adding more gear around the ship, which was bound to raise further questions. The chiefs found that the Wi-Fi signal coming off the Starlink satellite transceiver couldn’t cover the entire ship, so during a stop in Pearl Harbor, they bought “signal repeaters and cable” to extend coverage.
Sailors on the ship then began finding the STINKY network and asking questions about it. Some of these questions came to Marrero directly, but she denied knowing anything about the network… and then privately changed its Wi-Fi name to “another moniker that looked like a wireless printer—even though no such general-use wireless printers were present on the ship, the investigation found.”
Marrero even went so far as to remove questions about the network from the commanding officer’s “suggestion box” aboard ship to avoid detection.
Finding the stench
Ship officers heard the scuttlebutt about STINKY, of course, and they began asking questions and doing inspections, but they never found the concealed device. On August 18, though, a civilian worker from the Naval Information Warfare Center was installing an authorized SpaceX “Starshield” device and came across the unauthorized SpaceX device hidden on the weatherdeck.
Marrero’s attempt to create fake data showing that the system had only been used in port then failed spectacularly due to the “poorly doctored” statements she submitted. At that point, the game was up, and Navy investigators looked into the whole situation.
All of the chiefs who used, paid for, or even knew about the system without disclosing it were given “administrative nonjudicial punishment at commodore’s mast,” said Navy Times.
Marrero herself was relieved of her post last year, and she pled guilty during a court-martial this spring.
So there you go, kids: two object lessons in poor decision-making. Whether working from an embassy bathroom or the deck of a littoral combat ship, if you’re a government employee, think twice before giving in to the sweet temptation of unsecured, unauthorized wireless Internet access.
Update, Sept. 5, 3: 30pm: A reader has claimed that the default Starlink SSID is actually… “STINKY.” This seemed almost impossible to believe, but Elon Musk in fact tweeted about it in 2022, Redditors have reported it in the wild, and back in 2022 (thanks, Wayback Machine), the official Starlink FAQ said that the device’s “network name will appear as ‘STARLINK’ or ‘STINKY’ in device WiFi settings.” (A check of the current Starlink FAQ, however, shows that the default network name now is merely “STARLINK.”)
In other words, not only was this asinine conspiracy a terrible OPSEC idea, but the ringleaders didn’t even change the default Wi-Fi name until they started getting questions about it. Yikes.
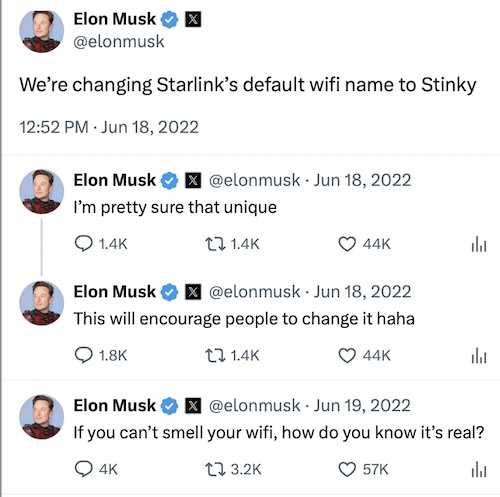
2022 Twitter thread announcing that “STINKY” would be the default SSID for Starlink.
After seeing Wi-Fi network named “STINKY,” Navy found hidden Starlink dish on US warship Read More »



