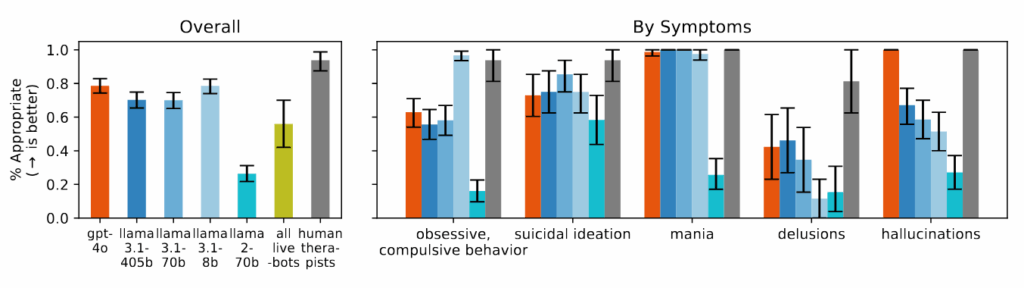
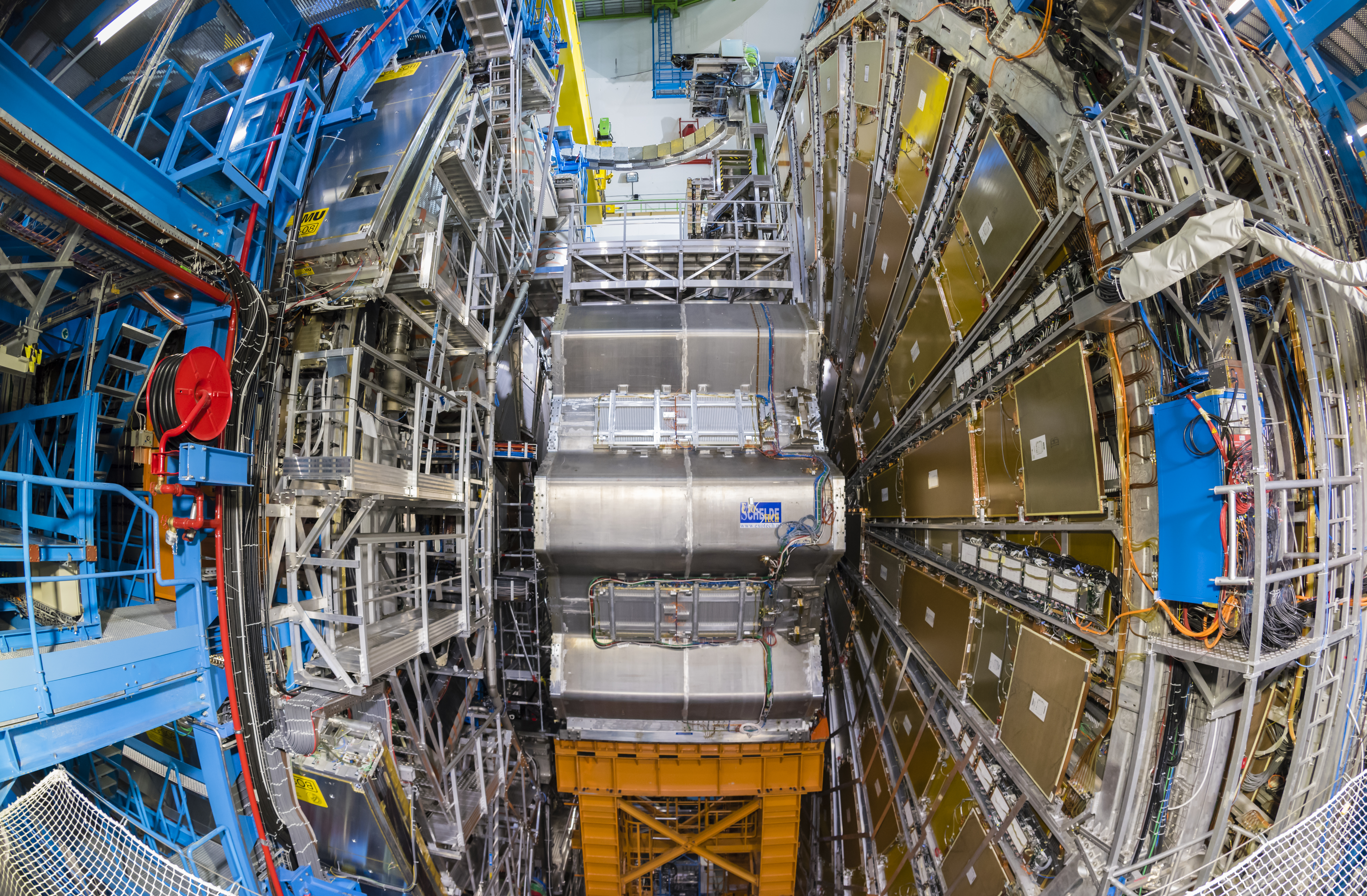
OpenAI and partners are building a massive AI data center in Texas
Stargate moves forward despite early skepticism
When OpenAI announced Stargate in January, critics questioned whether the company could deliver on its ambitious $500 billion funding promise. Trump ally and frequent Altman foe Elon Musk wrote on X that “They don’t actually have the money,” claiming that “SoftBank has well under $10B secured.”
Tech writer and frequent OpenAI critic Ed Zitron raised concerns about OpenAI’s financial position, noting the company’s $5 billion in losses in 2024. “This company loses $5bn+ a year! So what, they raise $19bn for Stargate, then what, another $10bn just to be able to survive?” Zitron wrote on Bluesky at the time.
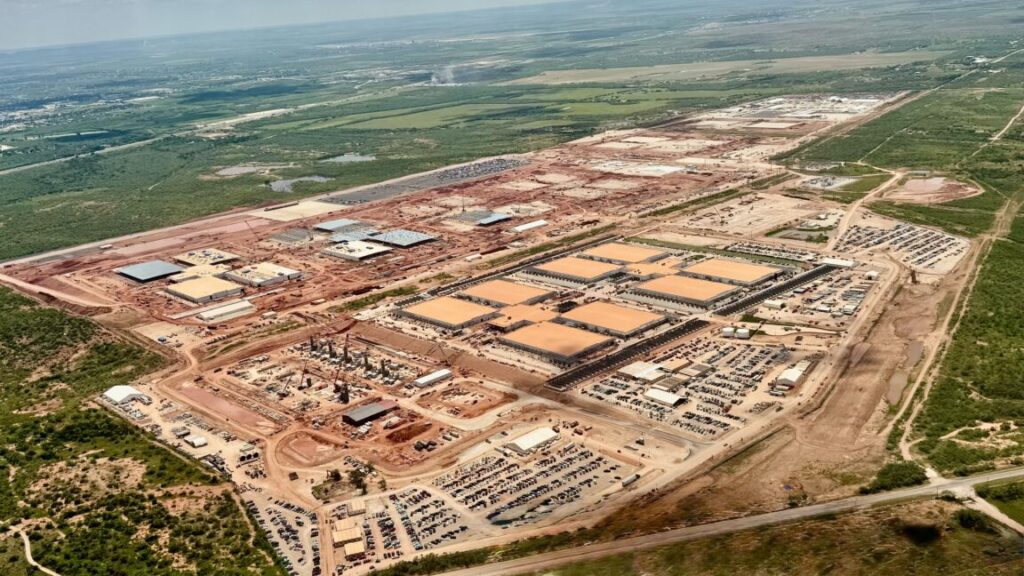
Six months later, OpenAI’s Abilene data center has moved from construction to partial operation. Oracle began delivering Nvidia GB200 racks to the facility last month, and OpenAI reports it has started running early training and inference workloads to support what it calls “next-generation frontier research.”
Despite the White House announcement with President Trump in January, the Stargate concept dates back to March 2024, when Microsoft and OpenAI partnered on a $100 billion supercomputer as part of a five-phase plan. Over time, the plan evolved into its current form as a partnership with Oracle, SoftBank, and CoreWeave.
“Stargate is an ambitious undertaking designed to meet the historic opportunity in front of us,” writes OpenAI in the press release announcing the latest deal. “That opportunity is now coming to life through strong support from partners, governments, and investors worldwide—including important leadership from the White House, which has recognized the critical role AI infrastructure will play in driving innovation, economic growth, and national competitiveness.”
OpenAI and partners are building a massive AI data center in Texas Read More »