Achieving lasting remission for HIV
Promising trials using engineered antibodies suggest that “functional cures” may be in reach.
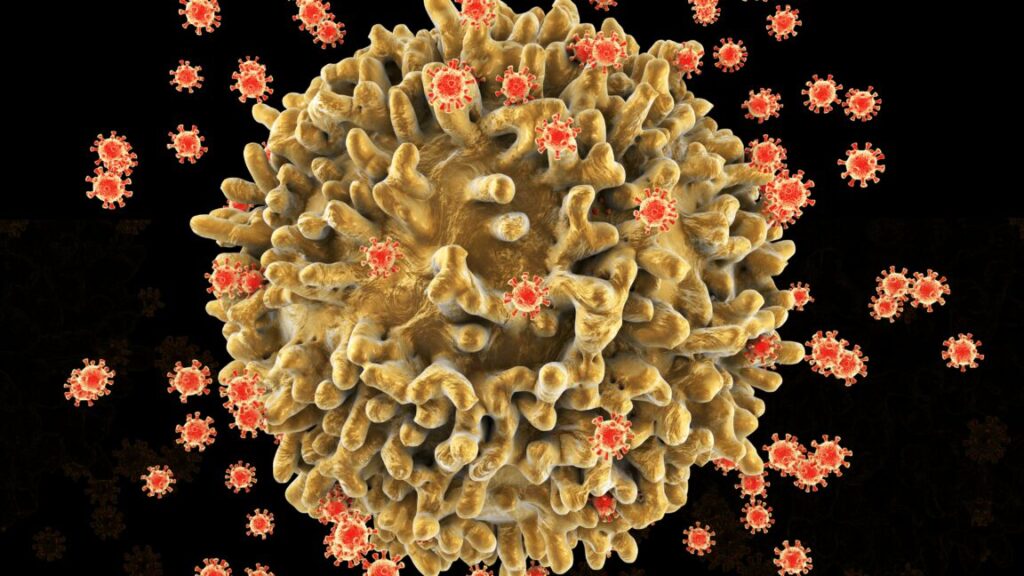
A digital illustration of an HIV-infected T cell. Once infected, the immune cell is hijacked by the virus to produce and release many new viral particles before dying. As more T-cells are destroyed, the immune system is progressively weakened. Credit: Kateryna Kon/Science Photo Library via Getty Images
Around the world, some 40 million people are living with HIV. And though progress in treatment means the infection isn’t the death sentence it once was, researchers have never been able to bring about a cure. Instead, HIV-positive people must take a cocktail of antiretroviral drugs for the rest of their lives.
But in 2025, researchers reported a breakthrough that suggests that a “functional” cure for HIV—a way to keep HIV under control long-term without constant treatment—may indeed be possible. In two independent trials using infusions of engineered antibodies, some participants remained healthy without taking antiretrovirals, long after the interventions ended.
In one of the trials—the FRESH trial, led by virologist Thumbi Ndung’u of the University of KwaZulu-Natal and the Africa Health Research Institute in South Africa—four of 20 participants maintained undetectable levels of HIV for a median of 1.5 years without taking antiretrovirals. In the other, the RIO trial set in the United Kingdom and Denmark and led by Sarah Fidler, a clinical doctor and HIV research expert at Imperial College London, six of 34 HIV-positive participants have maintained viral control for at least two years.
These landmark proof-of-concept trials show that the immune system can be harnessed to fight HIV. Researchers are now looking to conduct larger, more representative trials to see whether antibodies can be optimized to work for more people.
“I do think that this kind of treatment has the opportunity to really shift the dial,” Fidler says, “because they are long-acting drugs”—with effects that can persist even after they’re no longer in the body. “So far, we haven’t seen anything that works like that.”
People with HIV can live long, healthy lives if they take antiretrovirals. But their lifespans are still generally shorter than those of people without the virus. And for many, daily pills or even the newer, bimonthly injections present significant financial, practical, and social challenges, including stigma. “Probably for the last about 15 or 20 years, there’s been this real push to go, ‘How can we do better?’” says Fidler.
The dream, she says, is “what people call curing HIV, or a remission in HIV.” But that has presented a huge challenge because HIV is a master of disguise. The virus evolves so quickly after infection that the body can’t produce new antibodies quickly enough to recognize and neutralize it.
And some HIV hides out in cells in an inactive state, invisible to the immune system. These evasion tactics have outwitted a long succession of cure attempts. Aside from a handful of exceptional stem-cell transplants, interventions have consistently fallen short of a complete cure—one that fully clears HIV from the body.
A functional cure would be the next best thing. And that’s where a rare phenomenon offers hope: Some individuals with long-term HIV do eventually produce antibodies that can neutralize the virus, though too late to fully shake it. These potent antibodies target critical, rarely changing parts of HIV proteins in the outer viral membrane; these proteins are used by the virus to infect cells. The antibodies, able to recognize a broad range of virus strains, are termed broadly neutralizing.
Scientists are now racing to find the most potent broadly neutralizing antibodies and engineer them into a functional cure. FRESH and RIO are arguably the most promising attempts yet.
In the FRESH trial, scientists chose two antibodies that, combined, were likely to be effective against HIV strains known as HIV-1 clade C, which is dominant in sub-Saharan Africa. The trial enrolled young women from a high-prevalence community as part of a broader social empowerment program. The program had started the women on HIV treatment within three days of their infection several years earlier.
The RIO trial, meanwhile, chose two well-studied antibodies shown to be broadly effective. Its participants were predominantly white men around age 40 who also had gone on antiretroviral drugs soon after infection. Most had HIV-1 clade B, which is more prevalent in Europe.
By pairing antibodies, the researchers aimed to decrease the likelihood that HIV would develop resistance—a common challenge in antibody treatments—since the virus would need multiple mutations to evade both.
Participants in both trials were given an injection of the antibodies, which were modified to last around six months in the body. Then their treatment with antiviral medications was paused. The hope was that the antibodies would work with the immune system to kill active HIV particles, keeping the virus in check. If the effect didn’t last, HIV levels would rise after the antibodies had been broken down, and the participants would resume antiretroviral treatment.
Excitingly, however, findings in both trials suggested that, in some people, the interventions prompted an ongoing, independent immune response, which researchers likened to the effect of a vaccine.
In the RIO trial, 22 of the 34 people receiving broadly neutralizing antibodies had not experienced a viral rebound by 20 weeks. At this point, they were given another antibody shot. Beyond 96 weeks—long after the antibodies had disappeared — six still had viral levels low enough to remain off antiviral medications.
An additional 34 participants included in the study as controls received only a saline infusion and mostly had to resume treatment in four to six weeks; all but three were back on treatment within 20 weeks.
A similar pattern was observed in FRESH (although, because it was mostly a safety study, this trial did not include control participants). Six of the 20 participants retained viral suppression for 48 weeks after the antibody infusion, and of those, four remained off treatment for more than a year. Two and a half years after the intervention, one remains off antiretroviral medication. Two others also maintained viral control but eventually chose to go back on treatment for personal and logistical reasons.
It’s unknown when the virus might rebound, so the researchers are cautious about calling participants in remission functionally cured. However, the antibodies clearly seem to coax the immune system to fight the virus. Attached to infected cells, they signal to immune cells to come in and kill.
And importantly, researchers believe that this immune response to the antibodies may also stimulate immune cells called CD8+ T cells, which then hunt down HIV-infected cells. This could create an “immune memory” that helps the body control HIV even after the antibodies are gone.
The response resembles the immune control seen in a tiny group (fewer than 1 percent) of individuals with HIV, known as elite controllers. These individuals suppress HIV without the help of antiretrovirals, confining it mostly to small reservoirs. That the trials helped some participants do something similar is exciting, says Joel Blankson, an infectious diseases expert at Johns Hopkins Medicine, who coauthored an article about natural HIV controllers in the 2024 Annual Review of Immunology. “It might teach us how to be able to do this much more effectively, and we might be able to get a higher percentage of people in remission.”
One thing scientists do know is that the likelihood of achieving sustained control is higher if people start antiretroviral treatment soon after infection, when their immune systems are still intact and their viral reservoirs are small.
But post-treatment control can occur even in people who started taking antiretrovirals a long time after they were initially infected: a group known as chronically infected patients. “It just happens less often,” Blankson says. “So it’s possible the strategies that are involved in these studies will also apply to patients who are chronically infected.”
A particularly promising finding of the RIO trial was that the antibodies also affected dormant HIV hiding out in some cells. These reservoirs are how the virus rebounds when people stop treatment, and antibodies aren’t thought to touch them. Researchers speculate that the T cells boosted by the antibodies can recognize and kill latently infected cells that display even trace amounts of HIV on their surface.
The FRESH intervention, meanwhile, targeted the stubborn HIV reservoirs more directly through incorporating another drug, called vesatolimod. It’s designed to stimulate immune cells to respond to the HIV threat, and hopefully to “shock” dormant HIV particles out of hiding. Once that happens, the immune system, with the help of the antibodies, can recognize and kill them.
The results of FRESH are exciting, Ndung’u says, “because it might indicate that this regimen worked, to an extent. Because this was a small study, it’s difficult to, obviously, make very hard conclusions.” His team is still investigating the data.
Once he secures funding, Ndung’u aims to run a larger South Africa-based trial including chronically infected individuals. Fidler’s team, meanwhile, is recruiting for a third arm of RIO to try to determine whether pausing antiretroviral treatment for longer before administering the antibodies prompts a stronger immune response.
A related UK-based trial, called AbVax, will add a T-cell-stimulating drug to the mix to see whether it enhances the long-lasting, vaccine-like effect of the antibodies. “It could be that combining different approaches enhances different bits of the immune system, and that’s the way forward,” says Fidler, who is a co-principal investigator on that study.
For now, Fidler and Ndung’u will continue to track the virally suppressed participants — who, for the first time since they received their HIV diagnoses, are living free from the demands of daily treatment.
This story originally appeared at Knowable Magazine.
Achieving lasting remission for HIV Read More »