15 state attorneys general sue RFK Jr. over “anti-science” vaccine policy
This administration may be hazardous to your health
Trump administration’s reduced vaccine schedule “throws science out the window.”
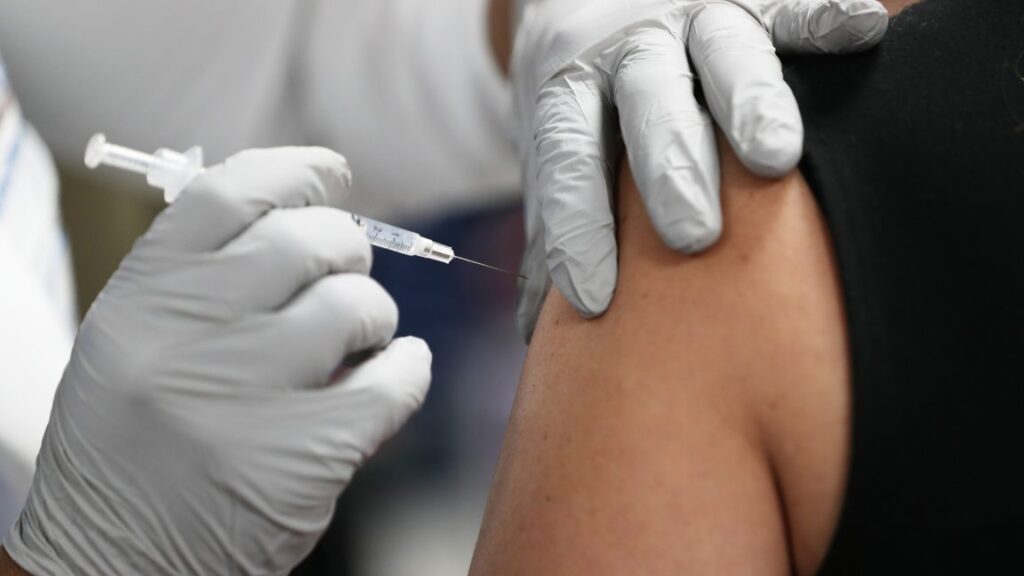
A healthcare worker receives a Pfizer-BioNtech Covid-19 vaccine at Jackson Memorial Hospital on December 15, 2020 in Miami, Florida. Credit: Getty Images | Joe Raedle
Scientists have long warned that a warming world is likely to hasten the spread of infectious diseases, making vaccination even more critical to safeguard public health.
And though most scientists hail vaccines as one of public health’s greatest achievements, they have provoked fear, distrust, and contentious resistance since Edward Jenner invented the first vaccine, to prevent smallpox, in the late 1700s.
Yet, until now, the United States never installed an outspoken vaccine critic like Robert F. Kennedy Jr. as a top health official with the power to upend federal childhood vaccine recommendations. Health and Human Services Secretary Kennedy and other top officials in the Trump administration have waged an “unprecedented attack on the nation’s evidence-based childhood immunization schedule,” a lawsuit, filed by 15 states, charged on Tuesday. Their actions will make people sicker and strain state resources, the suit claims.
A coalition of 14 attorneys general and Pennsylvania Governor Josh Shapiro, led by California Attorney General Rob Bonta and Arizona Attorney General Kris Mayes, is suing Kennedy, who has long promoted debunked theories linking vaccines to autism, as well as HHS, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, and its acting director, Jay Bhattacharya.
The multistate coalition is suing the agencies and their leaders, Mayes said in a press briefing Tuesday, “over their needlessly confusing, scientifically unsound, and unlawful revision of America’s immunization schedule.”
The suit also challenges Kennedy’s abrupt firing and “unlawful replacement” of 17 experts on the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP), which recommends which vaccines children and adults should receive, “with unqualified individuals whose minority anti-vaccine views align with Kennedy’s.”
In January, the CDC, with advice from the reconstituted ACIP, took seven childhood shots off the list of vaccines routinely recommended for all children, rescinding the CDC’s established guidance that vaccines protecting against rotavirus, meningococcal disease, hepatitis A, hepatitis B, influenza, COVID-19, and respiratory syncytial virus should be universally administered.
All the “demoted” vaccines, as the lawsuit calls them, prevent diseases that carry the risk of death. The January CDC memo recommends that parents consult with doctors for these vaccines, “taking the risk profile of each unique child into account.”
It does not make provisions for the millions of Americans who lack access to health providers who would provide such consultations.
ACIP’s vaccine recommendations have traditionally guided US health insurance coverage decisions, state school vaccine requirements, and physicians’ advice to parents and patients, Bonta said at the briefing. But Kennedy fired all the voting ACIP members four months after he promised Congress during his confirmation hearing that he’d leave the panel intact, Bonta said, noting that the suit is the 59th California has filed against the second Trump administration.
Kennedy said his unprecedented removal of the ACIP experts was “prioritizing the restoration of public trust above any specific pro- or anti-vaccine agenda,” in a press release in June.
Yet Kennedy’s picks include vaccine skeptics who “lack the requisite scientific knowledge and expertise to advise HHS and CDC on the ‘use of vaccines and related agents for effective control of vaccine-preventable diseases,’” as required by the committee’s charter, the suit argues.
“What Secretary Kennedy has done and what the Trump administration has enabled, throws science out the window, replaces qualified experts with unqualified ideologues, and then uses the resulting confusion to undermine public confidence in vaccines that have saved millions of lives,” Mayes said.
Stoking vaccine doubts leads to lower vaccination rates, which leads to more disease outbreaks—such as the hundreds of measles cases reported in 26 states over the past two months—more children in hospitals and greater strain on state Medicaid systems and public health infrastructure, Mayes said.
Democratic states are doing everything they can to fill the gaps left by this administration’s policies, she said. “But diseases cross state lines.”
Sowing doubt and confusion
The administration cited Denmark’s more limited childhood immunization schedule to justify its changes, but the Scandinavian country has fewer circulating infectious diseases and universal health care for a population that is tiny compared to the United States, the suit notes.
“Copying Denmark’s vaccine schedule without copying Denmark’s healthcare system doesn’t give families more options,” Mayes said, noting that millions of Americans lack access to health care, particularly in rural areas. “It just leaves kids unprotected from serious diseases.”
Inside Climate News asked HHS how it will ensure that parents without access to health care get their children the vaccines they need and how the administration plans to protect vulnerable populations as climate change fuels the spread of infectious diseases.
“This is a publicity stunt dressed up as a lawsuit,” said HHS press secretary Emily Hilliard, ignoring the questions. “By law, the health secretary has clear authority to make determinations on the CDC immunization schedule and the composition of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices. The CDC immunization schedule reforms reflect common-sense public health policy shared by peer, developed countries.”
The revised childhood immunization schedule wasn’t based on new science or expert consensus, Mayes said. “It was based on an ideological agenda, one that Secretary Kennedy has been pushing for years.”
Kennedy has been at the forefront of a dangerous movement that has significantly eroded trust in safe and effective vaccines, Bonta said. “While RFK Jr. is entitled to his own personal opinions, opinions, mind you, not facts, he isn’t entitled to use his opinions as the basis for breaking the law and endangering our children.”
The actions that RFK Jr. and ACIP have taken flout decades of scientific research, harm public health, and strain state resources by sowing doubt and confusion in vaccines and in science, Bonta said.
“California will be forced to expend resources to treat once rare diseases, to respond to outbreaks, and to combat misinformation,” he said. “I refuse to allow RFK Jr. to threaten the health and well being of the more than eight million young people who call the Golden State home, the 400,000 babies that are born here in California each year.”
Routine childhood vaccinations will prevent approximately 508 million cases of illness, 32 million hospitalizations, and 1,129,000 deaths among US children born between 1994 and 2023, scientists with the CDC reported in August 2024, before Donald Trump returned to office. The immunizations resulted in direct savings of $540 billion and societal savings of $2.7 trillion, they concluded.
“Without these vaccines, not only will our children and vulnerable individuals get sick, but our healthcare systems will have to shoulder the burden of increased preventable illnesses, preventable hospital visits, and avoidable costs,” Bonta said. “Vaccines save lives and save our states money. To get rid of them is illogical and unconscionable.”
Climate-fueled outbreaks
Two weeks before Bonta filed his latest lawsuit against the Trump administration, he denounced the Environmental Protection Agency’s repeal of the 2009 endangerment finding that recognized climate change as a threat to public health and welfare and provided the legal grounds to regulate greenhouse gases under the Clean Air Act.
The Trump administration’s endangerment finding recision, like its overhaul of the vaccine schedule, “is completely divorced from and untethered from science and facts and data and evidence,” Bonta said at the briefing Tuesday, noting that California will continue to push back against the EPA’s action.
“We must follow the facts, the science, the evidence and data, including the interconnectivity between climate change and the spread of vaccine-preventable diseases,” Bonta said.
Climate hazards such as drought, floods, and heatwaves have exacerbated outbreaks of more than half of human infectious diseases, researchers reported in Nature Climate Change in 2022, either by impairing people’s resistance or bolstering transmission of pathogens. The team warned that the number of pathogenic diseases and transmission pathways worsened by climatic hazards “are too numerous for comprehensive societal adaptations,” underscoring the urgent need to address the source of the problem: greenhouse gases.
Arizona is seeing more extreme heat events as a result of climate change, leaving people with underlying conditions at greater risk of heat-related illness and death.
“A lack of vaccines, a lack of access to vaccines starting at birth, will make our population sicker and more vulnerable to extreme heat and to climate-related disasters,” Mayes said. “And that will be sort of a self-perpetuating cycle where you have a less healthy population that is less capable of withstanding the impacts of climate change, and then you have climate change that is expanding and growing ever-more dangerous, having a greater and greater impact on a less healthy society.”
The only bodies that are capable of providing scientific guidance and advice on vaccines to the entire country are the CDC and ACIP, Mayes said. “And we now basically don’t have that across a number of these diseases and vaccines,” she said. “So we’re not protected, and we’re going to continue to see these outbreaks across the country, including in our states, even though we’re doing everything we can to protect ourselves.”
Liza Gross is a reporter for Inside Climate News based in Northern California. She is the author of The Science Writers’ Investigative Reporting Handbook and a contributor to The Science Writers’ Handbook, both funded by National Association of Science Writers’ Peggy Girshman Idea Grants. She has long covered science, conservation, agriculture, public and environmental health and justice with a focus on the misuse of science for private gain. Prior to joining ICN, she worked as a part-time magazine editor for the open-access journal PLOS Biology, a reporter for the Food & Environment Reporting Network and produced freelance stories for numerous national outlets, including The New York Times, The Washington Post, Discover, and Mother Jones. Her work has won awards from the Association of Health Care Journalists, American Society of Journalists and Authors, Society of Professional Journalists NorCal, and Association of Food Journalists.
This story originally appeared on Inside Climate News.
15 state attorneys general sue RFK Jr. over “anti-science” vaccine policy Read More »