Perplexity will come to Moto phones after exec testified Google limited access
Shevelenko was also asked about Chrome, which the DOJ would like to force Google to sell. Like an OpenAI executive said on Monday, Shevelenko confirmed Perplexity would be interested in buying the browser from Google.
Motorola has all the AI
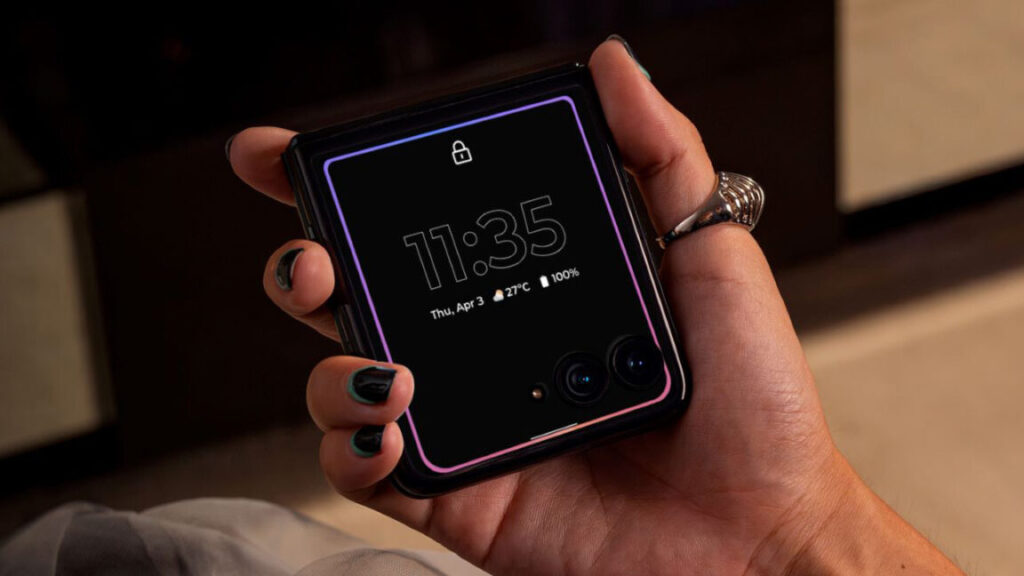
There were some vague allusions during the trial that Perplexity would come to Motorola phones this year, but we didn’t know just how soon that was. With the announcement of its 2025 Razr devices, Moto has confirmed a much more expansive set of AI features. Parts of the Motorola AI experience are powered by Gemini, Copilot, Meta, and yes, Perplexity.
While Gemini gets top billing as the default assistant app, other firms have wormed their way into different parts of the software. Perplexity’s app will be preloaded, and anyone who buys the new Razrs. Owners will also get three free months of Perplexity Pro. This is the first time Perplexity has had a smartphone distribution deal, but it won’t be shown prominently on the phone. When you start a Motorola device, it will still look like a Google playground.
While it’s not the default assistant, Perplexity is integrated into the Moto AI platform. The new Razrs will proactively suggest you perform an AI search when accessing certain features like the calendar or browsing the web under the banner “Explore with Perplexity.” The Perplexity app has also been optimized to work with the external screen on Motorola’s foldables.
Moto AI also has elements powered by other AI systems. For example, Microsoft Copilot will appear in Moto AI with an “Ask Copilot” option. And Meta’s Llama model powers a Moto AI feature called Catch Me Up, which summarizes notifications from select apps.
It’s unclear why Motorola leaned on four different AI providers for a single phone. It probably helps that all these companies are desperate to entice users to bulk up their market share. Perplexity confirmed that no money changed hands in this deal—it’s on Moto phones to acquire more users. That might be tough with Gemini getting priority placement, though.
Perplexity will come to Moto phones after exec testified Google limited access Read More »