What did Google announce on I/O day? Quite a lot of things. Many of them were genuinely impressive. Google is secretly killing it on the actual technology front.
Logan Kilpatrick (DeepMind): Google’s progress in AI since last year:
– The worlds strongest models, on pareto frontier
– Gemini app: has over 400M monthly active users
– We now process 480T tokens a month, up 50x YoY
– Over 7M developers have built with the Gemini API (4x)
Much more to come still!
I think? It’s so hard to keep track. There’s really a lot going on right now, not that most people would have any idea. Instead of being able to deal with all these exciting things, I’m scrambling to get to it all at once.
Google AI: We covered a LOT of ground today. Fortunately, our friends at @NotebookLM put all of today’s news and keynotes into a notebook. This way, you can listen to an audio overview, create a summary, or even view a Mind Map of everything from #GoogleIO 2025.
That’s actually a terrible mind map, it’s missing about half of the things.
As in, you follow their CEO’s link to a page that tells you everything that happened, and it’s literally a link bank to 27 other articles. I did not realize one could fail marketing forever this hard, and this badly. I have remarkably little idea, given how much effort I am willing to put into finding out, what their products can do.
The market seems impressed, with Google outperforming, although the timing of it all was a little weird. I continue to be deeply confused about what the market is expecting, or rather not expecting, out of Google.
Ben Thompson has a gated summary post, Reuters has a summary as well.
I share Ben’s feeling that I’m coming away less impressed than I should be, because so many things were lost in the shuffle. There’s too much stuff here. Don’t announce everything at once like this if you want us to pay attention. And he’s right to worry that it’s not clear that Google, despite doing all the things, can develop compelling products.
I do think it can, though. And I think it’s exactly right to currently produce a bunch of prototypical not-yet-compelling products that aren’t compelling because they aren’t good enough yet… and then later make them good enough.
Except that you need people to actually then, you know, realize the products exist.
This post covers what I could figure out on a deadline. As for why I didn’t simply give this a few more days, well, I had a reason.
-
The TLDR.
-
Flow, Veo 3 and Imagen 4.
-
Gmail Integration That’s Actually Good?
-
Gemini 2.5 Flash.
-
Gemma 3n.
-
Gemini Diffusion.
-
Jules.
-
We’re in Deep Research.
-
Google Search ‘AI Mode’.
-
AI Shopping.
-
Agent Mode.
-
Project Astra or is it Google Live?.
-
Android XR Glasses.
-
Gemini For Your Open Tabs In Chrome.
-
Google Meet Automatic Translation.
-
We Have Real 3D At Home, Oh No.
-
You Will Use the AI.
-
Our Price Cheap.
-
What To Make Of All This.
Or the ‘too many announcements, lost track.’
Google announced:
-
Veo 3, which generates amazing eight second videos now with talk and sound.
-
Flow, designed to tie that into longer stuff, but that doesn’t work right yet.
-
Various new GMail and related integrations and other ways to spread context.
-
Gemini 2.5 Flash, and Gemini 2.5 Pro Deep Thinking. They’re good, probably.
-
Gemma 3n, open source runs on phones with 2GB ram.
-
Gemini Diffusion as a text model, very intriguing but needs work.
-
Jules, their answer to Codex, available for free.
-
They’re going to let you go Full Agent, in Agent Mode, in several places.
-
Gemini using your open tabs as context, available natively in Chrome.
-
AI Search, for everyone, for free, as a search option, including a future agent mode and a specialized shopping mode.
-
Automatic smooth translation for real-time talk including copying tone.
-
A weird Google Beam thing where you see people in 3D while talking.
-
They did an Android XR demo, but it’s going to be a while.
-
For now you use your phone camera for a full Google Live experience, it’s good.
-
Their new premium AI subscription service is $250/month.
A lot of it is available now, some of it will be a few months. Some of it is free, some of it isn’t, or isn’t after a sample. Some of it is clearly good, some is still buggy, some we don’t know yet. It’s complicated.
Also I think there was a day two?
The offering that got everyone excited and went viral was Veo 3.
They also updated their image generation to Imagen 4 and it’s up to 2k resolution with various improvements and lots of ability to control details. It’s probably pretty good but frankly no one cares.
Did you want an eight second AI video, now with sound, maybe as something you could even extend? They got you. We can talk (cool video). Oh, being able to talk but having nothing to say.
Sundar Pichai (CEO Google): Veo 3, our SOTA video generation model, has native audio generation and is absolutely mindblowing.
For filmmakers + creatives, we’re combining the best of Veo, Imagen and Gemini into a new filmmaking tool called Flow.
Ready today for Google AI Pro and Ultra plan subscribers.
People really love the new non-silent video generation capabilities.
Here’s Bayram Annakov having a guy wake up in a cold sweat. Here’s Google sharing a user extending a video of an eagle carrying a car. Here’s fofr making a man run while advertising replicate, which almost works, and also two talking muffins which totally worked. Here’s Pliny admiring the instruction handling.
And here’s Pliny somewhat jailbreaking it, with videos to show for it. Except, um, Google, why do any of these require jailbreaks? They’re just cool eight second videos. Are they a little NSFW? I mean sure, but we’re strictly (if aggressively) PG-13 here, complete with exactly one F-bomb. I realize this is a negotiation, I realize why we might not want to go to R, but I think refusing to make any of these is rather shameful behavior.
I would say that Flow plus Veo 3 is the first video generation product that makes me think ‘huh, actually that’s starting to be cool.’ Coherence is very strong, you have a lot of tools at your disposal, and sound is huge. They’re going to give you the power to do various shots and virtual camera movements.
I can see actually using this, or something not too different from this. Or I can see someone like Primordial Soup Labs, which formed a partnership with DeepMind, creating an actually worthwhile short film.
Steven McCulloch: Veo 3 has blown past a new threshold of capability, with the ability to one-shot scenes with full lip sync and background audio. What used to be a 4-step workflow with high barrier to entry has been boiled down into a single, frictionless prompt.
This is huge.
They also refer to their music sandbox, powered by Lyria 2, but there’s nothing to announce at this time.
They’re launching SynthID Detector, a tool to detect AI-generated content.
They remind us of Google Vids to turn your slides into videos, please no. Don’t. They’re also offering AI avatars in Vids. Again, please, don’t, what fresh hell is this.
Also there’s Stitch to generate designs and UIs from text prompts?
I keep waiting for it, it keeps not arriving, is it finally happening soon?
Sundar Pichai: With personal smart replies in Gmail, you can give Gemini permission to pull in details from across your Google apps and write in a way that sounds like you.
Rolling out in the coming weeks to subscribers.
I’ve been disappointed too many times at this point, so I will believe it when I see it.
The part that I want most is the pulling in of the details, the ability to have the AI keep track of and remind me of the relevant context, including pulling from Google Drive which in turn means you can for example pull from Obsidian since it’s synced up. They’re also offering ‘source-grounded writing help’ next quarter in Google Docs (but not GMail?) where you have it pull only from particular sources, which is nice if it’s easy enough to use.
I want GMail to properly populate Calendar rather than its current laughably silly hit-and-miss actions (oh look, at movie that runs from 3-4 on Thursday, that’s how that works!), to pull out and make sure I don’t miss key information, to remind me of dropped balls and so on.
They’re offering exactly this with ‘inbox cleanup,’ as in ‘delete all of my unread emails from The Groomed Paw from the last year.’ That’s a first step. We need to kick that up at least a notch, starting with things such as ‘set up an AI filter so I never see another damned Groomed Paw email again unless it seems actually urgent or offers a 50% or bigger sale’ and ‘if Sarah tells me if she’s coming on Friday ping me right away.’
Another offering that sounds great is ‘fast appointment scheduling integrated into GMail,’ in the video it’s a simple two clicks which presumably implies you’ve set things up a lot already. Again, great if it works, but it has to really work and know your preferences and adjust to your existing schedule. If it also reads your other emails and other context to include things not strictly in your calendar, now we’re really talking.
Do I want it to write the actual emails after that? I mean, I guess, sometimes, if it’s good enough. Funnily enough, when that happens, that’s probably exactly the times I don’t want it to sound like me. If I wanted to sound like me I could just write the email. The reason I want the AI to write it is because I need to be Performing Class, or I want to sound like a Dangerous Professional a la Patio11, or I want to do a polite formality. Or when I mostly need to populate the email with a bunch of information.
Of course, if it gets good enough, I’ll also want it to do some ‘sound like me’ work too, such as responding to readers asking questions with known answers. Details are going to matter a ton, and I would have so many notes if I felt someone was listening.
In any case, please, I would love a version of this that’s actually good in those other ways. Are the existing products good enough I should be using them? I don’t know. If there’s one you use that you think I’d want, share in the comments.
I/O Day mostly wasn’t about the actual models or the API, but we do have some incremental changes here thrown into the fray.
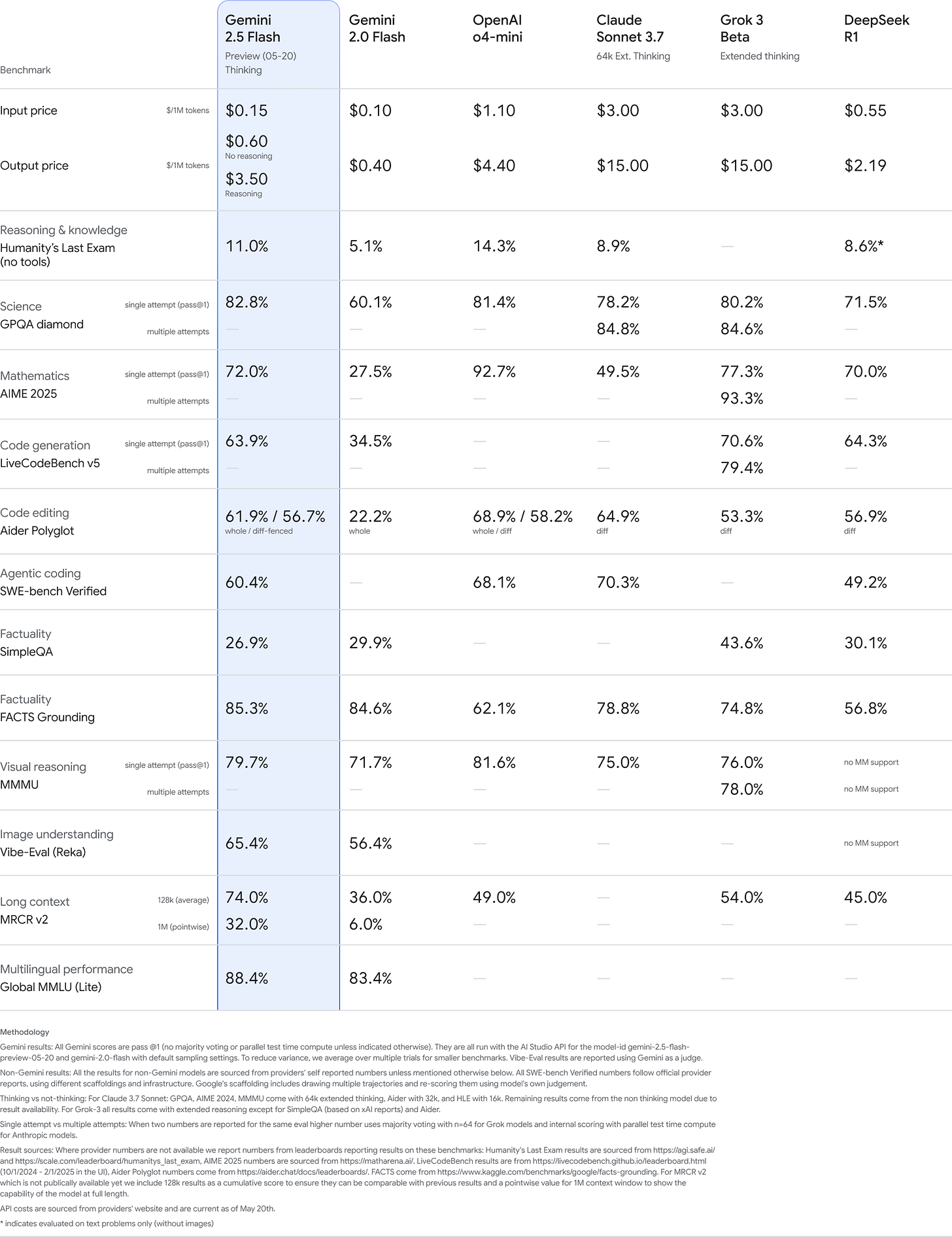
Gemini 2.5 Flash is technically still in preview, but it’s widely available including in the Gemini app, and I’d treat it as de facto released. It’s probably the best fast and cheap model, and the best ‘fast thinking’ model if you use that mode.
Also, yes, of course Pliny pwned it, why do we even ask, if you want to use it you set it as the system prompt.
Pliny: ah forgot to mention, prompt is designed to be set as system prompt. a simple obfuscation of any trigger words in your query should be plenty, like “m-d-m-a” rather than “mdma”
Sundar Pichai (CEO Google): Our newest Gemini 2.5 Flash is better on nearly every dimension: reasoning, multimodality, code, long context. Available for preview in the Gemini app, AI Studio and Vertex AI.
And with Deep Think mode, Gemini 2.5 Pro is getting better, too. Available to trusted testers.
Demis Hassabis: Gemini 2.5 Flash is an amazing model for its speed and low-cost.
Logan Kilpatrick: Gemini 2.5 Flash continues to push the pareto frontier, so much intelligence packed into this model, can’t wait for GA in a few weeks!
Peter Wildeford: LLMs are like parrots except the parrots are very good at math
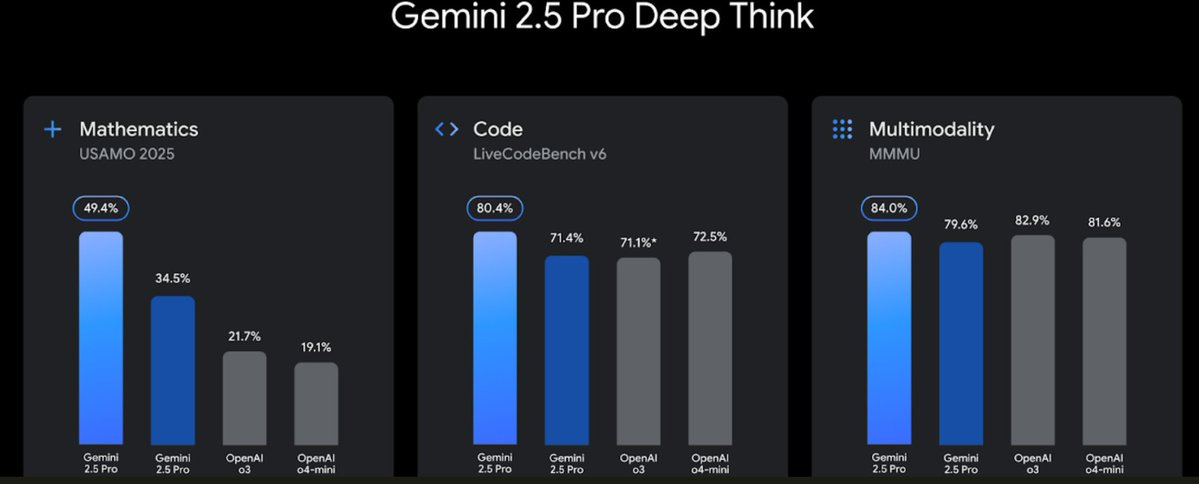
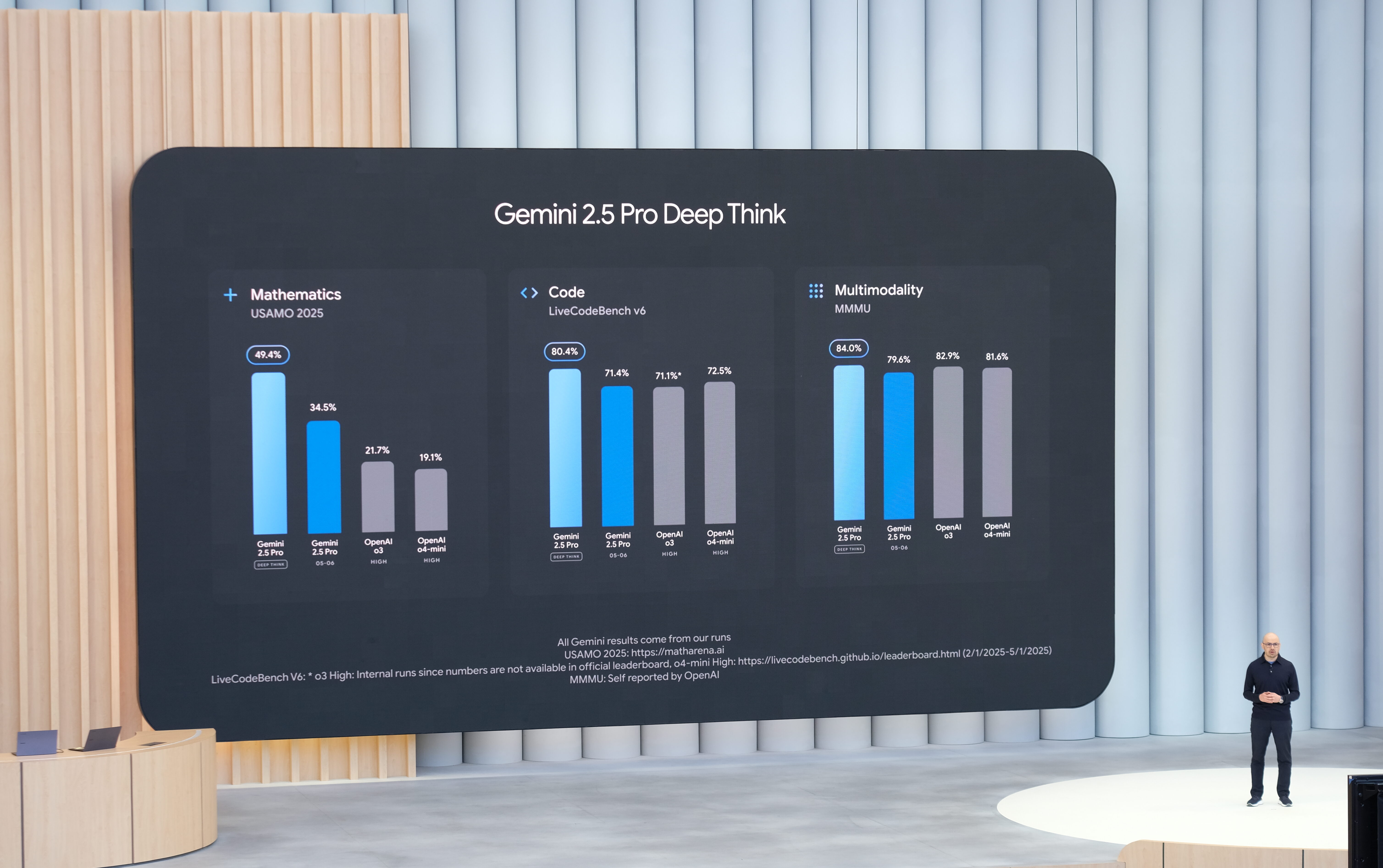
On that last one, the light blue is Deep Thinking, dark blue is regular 2.5 Pro.
Peter Wildeford: It’s pretty confusing that the graphs compare “Gemini 2.5 Pro” to “Gemini 2.5 Pro”
Alex Friedland: The fundamental issue is that numbers are limited and they might run out.
Gemini 2.5 Flash is in second place on (what’s left of) the Arena leaderboard, behind only Gemini 2.5 Pro.
Hasan Can: I wasn’t going to say this at first, because every time I praised one of Google’s models, they ruined it within a few weeks but the new G.2.5 Flash is actually better than the current 2.5 Pro in the Gemini app. It reminds me of the intelligence of the older 2.5 Pro from 03.25.
The Live API will now have audio-visual input and native audio out dialogue with ability to steer tone, accent and style off speaking, ability to respond to user tone of voice, as well as tool use. They’re also adding computer use to the API, and are adding native SDK support for Model Context Protocol (MCP).
There’s a white paper on how they made Gemini secure, and their safeguards, but today is a day that I have sympathy for the ‘we don’t have time for that’ crowd and I’m setting it aside for later. I’ll circle back.
Gemma 3n seems to be a substantial improvement in Google’s open model on-device performance. I don’t know whether it is better than other open alternatives, there’s always a bizarre ocean of different models claiming to be good, but I would be entirely unsurprised if this was very much state of the art.
Google AI Developers: Introducing Gemma 3n, available in early preview today.
The model uses a cutting-edge architecture optimized for mobile on-device usage. It brings multimodality, super fast inference, and more.
Key features include:
-Expanded multimodal understanding with video and audio input, alongside text and images
-Developer-friendly sizes: 4B and 2B (and many in between!)
-Optimized on-device efficiency for 1.5x faster response on mobile compared to Gemma 3 4B
Build live, interactive apps and sophisticated audio-centric experiences, including real-time speech transcription, translation, and rich voice-driven interactions
…
Gemma 3n leverages a Google DeepMind innovation called Per-Layer Embeddings (PLE) that delivers a significant reduction in RAM usage. While the raw parameter count is 5B and 8B, this innovation allows you to run larger models on mobile devices or live-stream from the cloud, with a memory overhead comparable to a 2B and 4B model, meaning the models can operate with a dynamic memory footprint of just 2GB and 3GB. Learn more in our documentation.
Oh, and also they just added MedGemma for health care, SignGemma for ASL and DolphinGemma for talking to dolphins. Because sure, why not?
This quietly seems like it could turn out to be a really big deal. We have an actually interesting text diffusion model. It can do 2k tokens/second.
Alexander Doria: Gemini Diffusion does pass honorably my nearly impossible OCR correction benchmark: Plainly, “can you correct the OCR of this text.”
Meanwhile, here’s a cool finding, ‘what like it’s hard’ department:
Earlence: Gemini diffusion is cool! Really fast and appears capable in coding tasks. But what is interesting is that one of @elder_plinius jailbreaks (for 2.5) appears to have worked on the diffusion model as well when I used it to ask about Anthrax.
Remember when I spent a day covering OpenAI’s Codex?
Well, Google announced Jules, its own AI coding agent. Context-aware, repo-integrated, ready to ship features. The quick video looks like a superior UI. But how good is it? So far I haven’t seen much feedback on that.
So instead of a detailed examination, that’s all I have for you on this right now. Jules exists, it’s Google’s answer to Codex, we’ll have to see if it is good.
But, twist! It’s free. Right now it’s reporting heavy use (not a shock) so high latency.
In addition to incorporating Gemini 2.5, Deep Research will soon let you connect your Google Drive and GMail, choose particular sources, and integrate with Canvas.
This is pretty exciting – in general any way to get deep dives to use your extensive context properly is a big game and Google is very good with long context.
If you don’t want to wait for Deep Research, you can always Deep Think instead. Well, not yet unless you’re a safety researcher (and if you are, hit them up!) but soon.
JJ Hughes notes how exciting it will be to get true long context into a top level deep reasoning model to unlock new capabilities such as for lawyers like himself, but notes the UI remains terrible for this.
Also, remember NotebookLM? There’s now An App For That and it’s doing well.
Google Search AI Overviews have been a bit of a joke for a while. They’re the most common place people interact with AI, and yet they famously make obvious stupid mistakes, including potentially harmful ones, constantly. That’s been improving, and now with 2.5 powering them it’s going to improve again.
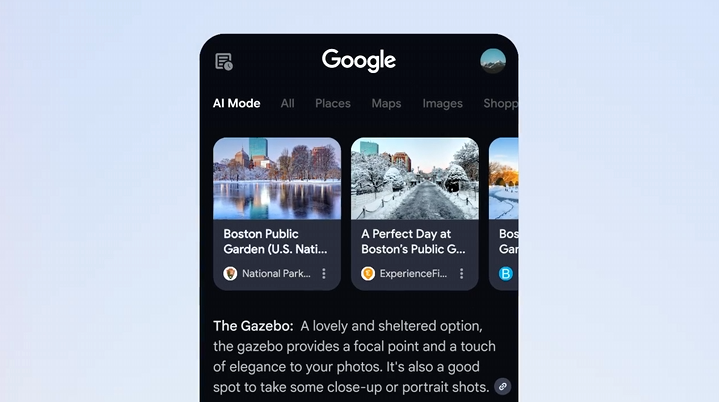
AI Mode is going to be (future tense because it’s not there for me yet) something different from Overviews, but one might ask isn’t it the same as using Gemini? What’s the difference? Is this a version of Perplexity (which has fallen totally out of my rotation), or what?
They’re doing a terrible job explaining any of that, OpenAI is perhaps secretly not the worst namer of AI services.
Sundar Pichai: AI Mode is rolling out to everyone in the US. It’s a total reimagining of Search with more advanced reasoning so you can ask longer, complex queries.
AI Overviews are now used by 1.5B people a month, in 200+ countries and territories.
And Gemini 2.5 is coming to both this week.
My understanding is that the difference is that AI Mode in search will have better integrations for various real time information systems, especially shopping and other commonly accessed knowledge, and has the ability to do a lot of Google searches quickly to generate its context, and also it is free.
They plan on merging ‘Project Mariner’ or ‘Agent Mode’ into it as well, and you’ll have the option to do a ‘deep search.’ They say they’re starting with ‘event tickets, restaurant reservations and local appointments.’ I actually think this is The Way. You don’t try to deploy an agent in general. It’s not time for that yet. You deploy an agent in specific ways where you know it works, on a whitelisted set of websites where you know what it’s doing and that this is safe. You almost don’t notice there’s an agent involved, it feels like using the Web but increasingly without the extra steps.
If they do a decent job of all this, ‘Google Search AI Mode’ is going to be the actually most useful way to do quite a lot of AI things. It won’t be good for jobs that require strong intelligence, but a large percentage of tasks are much more about search. Google has a huge edge there if they execute, including in customization.
They also plan to incorporate AI Search Mode advances directly into regular Google Search, at least in the overviews and I think elsewhere as well.
What I worry about here is it feels like multiple teams fighting over AI turf. The AI Search team is trying to do things that ‘naturally’ fall to Gemini and also to regular Search, and Gemini is trying to do its own form of search, and who knows what the Overviews team is thinking, and so on.
An important special case for Google Search AI Mode (beware, your computer might be accessing GSAM?) will (in a few months) be Shopping With Google AI Mode, I don’t even know what to call anything anymore. Can I call it Google Shopping? Gemini Shopping?
It actually seems really cool, again if executed well, allowing you to search all the sites at once in an AI-powered way, giving you visuals, asking follow ups. It can track prices and then automatically buy when the price is right.
They have a ‘try it on’ that lets you picture yourself in any of the clothing, which is rolling out now to search labs. Neat. It’s double neat if it automatically only shows you clothing that fits you.
Sundar Pichai (CEO Google): Agent Mode in the @Geminiapp can help you get more done across the web – coming to subscribers soon.
Plus a new multi-tasking version of Project Mariner is now available to Google AI Ultra subscribers in the US, and computer use capabilities are coming to the Gemini API.
It will also use MCP, which enshrines MCP as a standard across labs.
The example here is to use ‘agent mode’ to find and go through apartment listings and arrange tours. They say they’re bringing this mode to the Gemini app and planning on incorporating it into Chrome.
I like the idea of their feature ‘teach and repeat.’ As in, you do a task once, and it learns from what you did so it can do similar tasks for you in the future.
Alas, early reports are that Project Mariner is not ready for prime time.
As an example, Bayram Annakov notes it failed on a simple task. That seems to be the norm.
You now can get this for free in Android and iOS, which means sharing live camera feeds while you talk to Gemini and it talks back, now including things like doing Google searches on your behalf, calling up YouTube videos and so on, even making its own phone calls.
I’m not even sure what exactly Project Astra is at this point. I’ve been assuming I’ve been using it when I put Gemini into live video mode, so now it’s simply Google Live, but I’m never quite sure?
Roward Cheung: [Google] revamped project Astra with native audio dialogue, UI control, content retrieval, calling, and shopping.
The official video he includes highlights YouTube search, GMail integration and the ability to have Gemini call a shop (in the background while you keep working) and ask what they have in stock. They’re calling it ‘action intelligence.’
In another area they talk about extending Google Live and Project Astra into search. They’re framing this as you point the camera at something and then you talk and it generates a search, including showing you search results traditional Google style. So it’s at least new in that it can make that change.
If you want to really unlock the power of seeing your screen, you want the screen to see what you see. Thus, Android XR Glasses. That’s a super exciting idea and a long time coming. And we have a controlled demo.
But also, not so fast. We’re talking 2026 at the earliest, probably 18+ months, and we have no idea what they are going to cost. I also got strong ‘not ready for prime time’ vibes from the demo, more of the ‘this is cool in theory but won’t work in practice.’ My guess is that if I had these in current form, I’d almost entirely use them for Google Live purposes and maybe chatting with the AI, and basically nothing else, unless we got better agentic AI that could work with various phone apps?
There’s another new feature where you can open up Gemini in Chrome and ask questions not only about the page, but all your other open pages, which automatically are put into context. It’s one of those long time coming ideas, again if it works well. This one should be available by now.
This is one of many cases where it’s going to take getting used to it so you actually think to use it when this is the right modality, and you have confidence to turn to it, but if so, seems great.
It’s hard to tell how good translation is from a sample video, but I find it credible that this is approaching perfect and means you can pull off free-flowing conversations across languages, as long as you don’t mind a little being lost in translation. They’re claiming they are preserving things like tone of voice.
Sundar Pichai: Real-time speech translation directly in Google Meet matches your tone and pattern so you can have free-flowing conversations across languages
Launching now for subscribers. ¡Es mágico!
Rob Haisfield: Now imagine this with two people wearing AR glasses in person!
They show this in combination with their 3D conferencing platform Google Beam, but the two don’t seem at all related. Translation is for audio, two dimensions are already two more than you need.
Relatedly, Gemini is offering to do automatic transcripts including doing ‘transcript trim’ to get rid of filler words, or one-click balancing your video’s sound.
They’re calling it Google Beam, downwind of Project Starline.
This sounds like it is primarily about 3D video conferencing or some form of AR/VR, or letting people move hands and such around like they’re interacting in person?
Sundar Pichai: Google Beam uses a new video model to transform 2D video streams into a realistic 3D experience — with near perfect headtracking, down to the millimeter, and at 60 frames per second, all in real-time.
The result is an immersive conversational experience. HP will share more soon.
It looks like this isn’t based on the feed from one camera, but rather six, and requires its own unique devices.
This feels like a corporate ‘now with real human physical interactions, fellow humans!’ moment. It’s not that you couldn’t turn it into something cool, but I think you’d have to take it pretty far, and by that I mean I think you’d need haptics. If I can at least shake your hand or hug you, maybe we’ve got something. Go beyond that and the market is obvious.
Whereas the way they’re showing it seems to me to be the type of uncanny valley situation I very much Do Not Want. Why would actually want this for a meeting, either of two people or more than two? I’ve never understood why you would want to have a ‘virtual meeting’ where people were moving in 3D in virtual chairs, or you seemed to be moving in space, it seems like not having to navigate that is one of the ways Google Meet is better than in person.
I can see it if you were using it to do something akin to a shared VR space, or a game, or an intentionally designed viewing experience including potentially watching a sporting event. But for the purposes they are showing off, 2D isn’t a bug. It’s a feature.
On top of that, this won’t be cheap. We’re likely talking $15k-$30k per unit at first for the early devices from HP that you’ll need. Hard pass. But even Google admits the hardware devices aren’t really the point. The point is that you can beam something in one-to-many mode, anywhere in the world, once they figure out what to do with that.
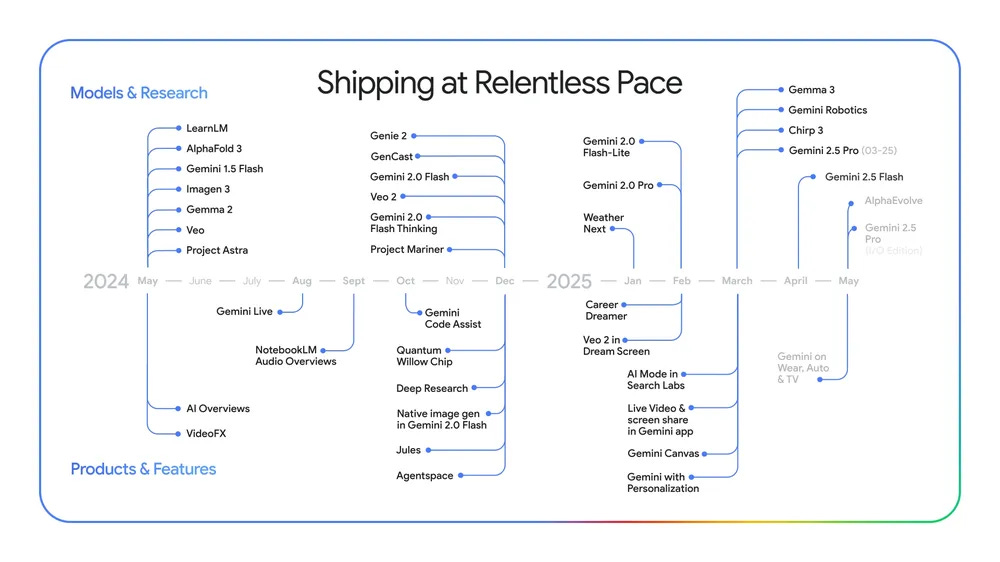
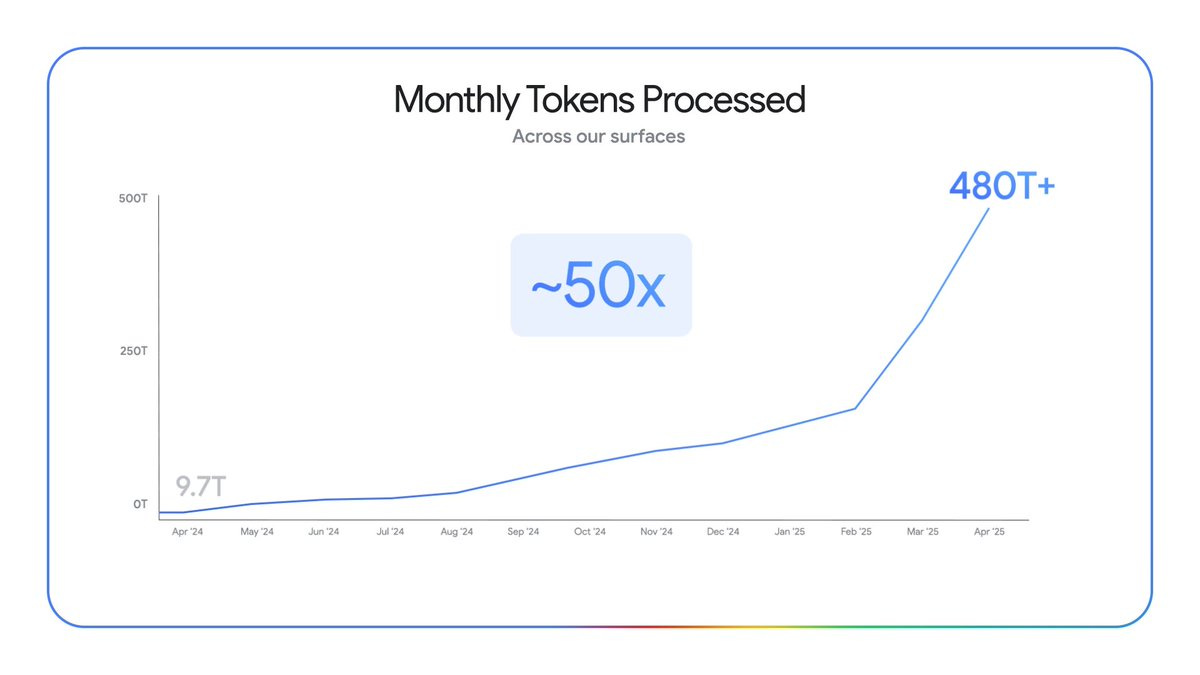
Google’s AI use is growing fast. Really fast.
Sundar Pichai: The world is adopting AI faster than ever before.
This time last year we were processing 9.7 trillion tokens a month across our products and APIs.
Today, that number is 480 trillion. That’s a 50X increase in just a year. 🤯
Gallabytes: I wonder how this breaks down flash versus pro
Peter Wildeford: pinpoint the exact moment Gemini became good
I had Claude estimate similar numbers for other top AI labs. At this point Claude thinks Google is probably roughly on par with OpenAI on tokens processed, and well ahead of everyone else.
But of course you can get a lot of tokens when you throw your AI into every Google search whether the user likes it or not. So the more meaningful number is likely the 400 million monthly active users for Gemini, with usage up 45% in the 2.5 era, but again I don’t think the numbers for different services are all that comparable, but note that ChatGPT’s monthly user count is 1.5 billion, about half of whom use it any given week. The other half have to be some strange weeks, given most of them aren’t exactly switching over to Claude.
Google offers a lot of things for free. That will also be true in AI. In particular, AI Search will stay free, as will basic functionality in the Gemini app. But if you want to take full advantage, yep, you’re going to pay.
They have two plans: The Pro plan at $20/month, and the Ultra plan at $250/month, which includes early access to new features including Agent Mode and much higher rate limits. This is their Ultra pitch.
Hensen Juang: Wait they are bundling YouTube premium?
MuffinV: At this point they will sell every google product as a single subscription.
Hensen Juang: This is the way.
It is indeed The Way. Give me the meta subscription. Google Prime.
For most people, the Pro plan looks like it will suffice. Given everything Google is offering, a lot of you should be giving up your $20/month, even if that’s your third $20/month after Claude and ChatGPT. The free plan is actually pretty solid too, if you’re not going to be that heavy a user because you’re also using the competition.
The $250/month Ultra plan seems like it’s not offering that much extra. The higher rate limits are nice but you probably won’t run into them often. The early access is nice, but the early access products are mostly rough around the edges. It certainly isn’t going to be ‘ten times better,’ and it’s a much worse ‘deal’ than the Pro $20/month plan. But once again, looking at relative prices is a mistake. They don’t matter.
What matters is absolute price versus absolute benefit. If you’re actually getting good use out of the extra stuff, it can easily be well in excess of the $250/month.
If your focus is video, fofr reports you get 12k credits per month, and it costs 150 credits per 8 second Veo 3 video, so with perfect utilization you pay $0.39 per second of video, plus you get the other features. A better deal, if you only want video, is to buy the credits directly, at about $0.19 per second. That’s still not cheap, but it’s a lot better, and this does seem like a big quality jump.
Another key question is, how many iterations does it take to get what you want? That’s a huge determinant of real cost. $0.19 per second is nothing if it always spits out the final product.
For now I don’t see the $250/month being worth it for most people, especially without Project Mariner access. And as JJ Hughes says, add up all these top level subscriptions and pretty soon you’re talking real money. But I’d keep an eye.
Knud Berthelsen: There is so much and you know they will eventually integrate it in their products that actually have users. There needs to be something between the $20/month tier and the $250 for those of us who want an AI agent but not a movie studio.
It’s a lot. Google is pushing ahead on all the fronts at once. The underlying models are excellent. They’re making it rain. It’s all very disjointed, and the vision hasn’t been realized, but there’s tons of potential here.
Pliny: Ok @GoogleDeepMind, almost there. If you can build a kick-ass agentic UI to unify everything and write a half-decent system prompt, people will call it AGI.
Justin Halford: They’re clearly the leading lab at this point.
Askwho: Veo 3’s hyped high-fidelity videos w/ sound are dazzling, but still feel like an advanced toy. Gemini Diffusion shows immense promise, though its current form is weak. Jules is tough to assess fully due to rate limits, but it’s probably the most impactful due to wide availability
Some people will call o3 AGI. I have little doubt some (more) people would call Google Gemini AGI if you made everything involved work as its best self and unified it all.
I wouldn’t be one of those people. Not yet. But yeah, interesting times.
Demis Hassabis does say that unification is the vision, to turn the Gemini app into a universal AI assistant, including combining Google Live for real time vision with Project Mariner for up to ten parallel agent actions.
Ben Thompson came away from all this thinking that the only real ‘products’ here were still Google search and Google Cloud, and that remains the only products that truly matter or function at Google. I get why one would come away with that impression, but again I don’t agree. I think that the other offerings won’t all hit, especially at first, but they’ll get better quickly as AI advances and as the productization and iterations fly by.
He has some great turns of phrase. Here, Ben points out that the problem with AI is that to use it well you have to think and figure out what to do. And if there’s one thing users tend to lack, it would be volition. Until Google can solve volition, the product space will largely go to those who do solve it, which often means startups.
Ben Thompson: Second, the degree to which so many of the demoes yesterday depend on user volition actually kind of dampened my enthusiasm for their usefulness.
It has long been the case that the best way to bring products to the consumer market is via devices, and that seems truer than ever: Android is probably going to be the most important canvas for shipping a lot of these capabilities, and Google’s XR glasses were pretty compelling (and, in my opinion, had a UX much closer to what I envision for XR than Meta’s Orion did).
Devices drive usage at scale, but that actually leaves a lot of room for startups to build software products that incorporate AI to solve problems that people didn’t know they had; the challenge will be in reaching them, which is to say the startup problem is the same as ever.
…
Google is doing a good job at making Search better; I see no reason to be worried about them making any other great product, even as the possibility of making something great with their models seems higher than ever. That’s good for startups!
I’m excited for it rather than worried, but yes, if you’re a startup, I would worry a bit.
What will we see tomorrow?