The Backbone One would be an ideal game controller—if the iPhone had more games
It works well, but there still aren’t enough modern, console-style games.
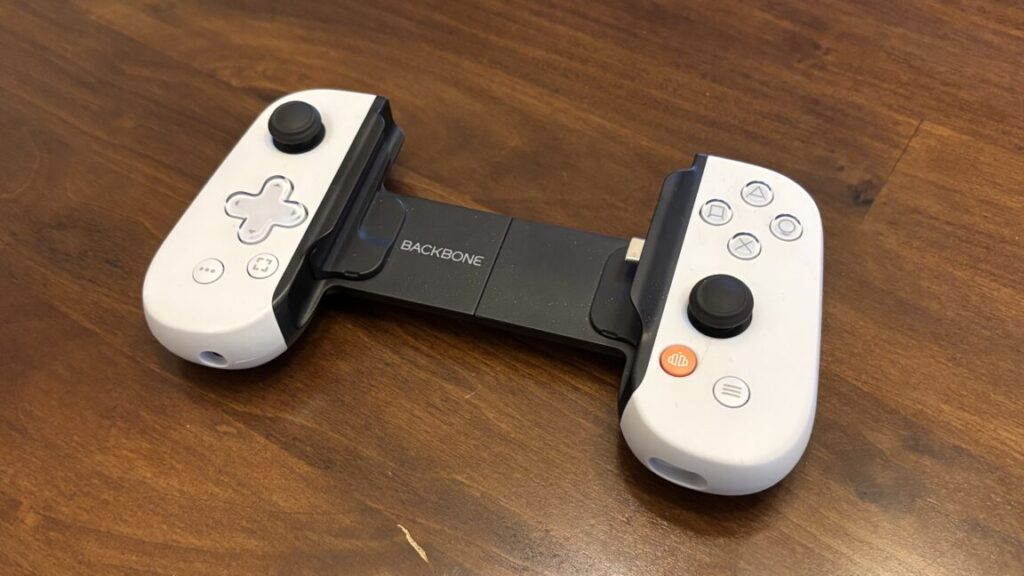
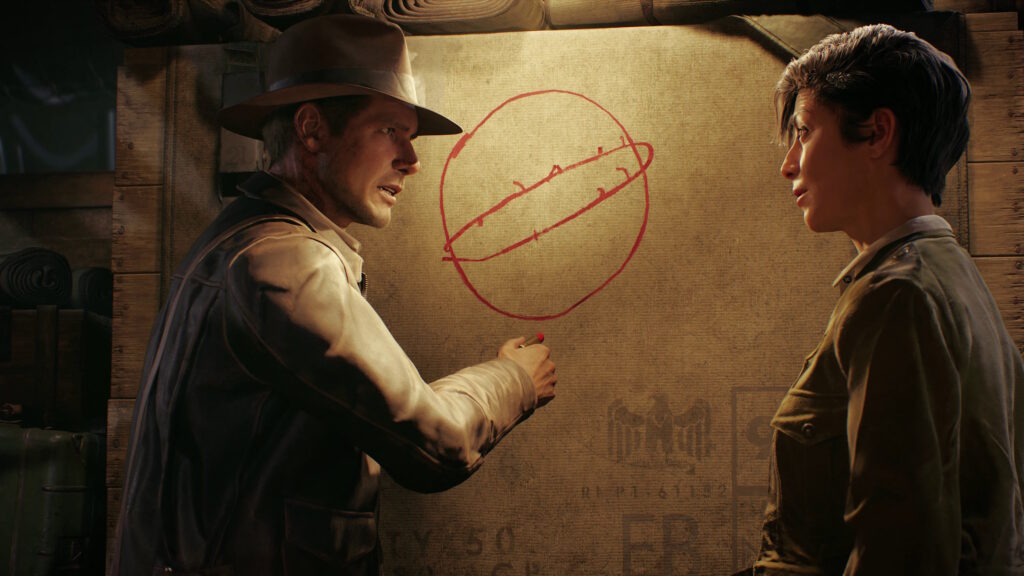
The Backbone One attachable game controller for the iPhone.
In theory, it ought to be as good a time as ever to be a gamer on the iPhone.
Classic console emulators have rolled out to the platform for the first time, and they work great. There are strong libraries of non-skeezy mobile games on Apple Arcade and Netflix Games, streaming via Xbox and PlayStation services is continuing apace, and there are even a few AAA console games now running natively on the platform, like Assassin’s Creed and Resident Evil titles.
Some of those games need a traditional, dual-stick game controller to work well, though, and Apple bafflingly offers no first-party solution for this.
Yes, you can sync popular Bluetooth controllers from Sony, Microsoft, Nintendo, and 8bitdo with your iPhone, but that’s not really the ideal answer—your iPhone isn’t a big TV sitting across the room or a computer monitor propped up on your desk.
A few companies have jumped in to solve this with attachable controllers that give the iPhone a Nintendo Switch or Steam Deck-like form factor (albeit a lot smaller). There’s a wide range of quality, though, and some of the ones you’ll see advertised aren’t very well made.
There’s some debate out there, but there’s one that just about anyone will at least put up for consideration: the Backbone One. That’s the one I picked for my new iPhone 16 Pro Max, which I have loaded with emulators and tons of games.
Since many folks are about to get iPhone 16s for the holidays and might be in the market for something similar, I figured it’d be a good time to write some quick impressions, including pros and cons. Is this thing worth a $99 price tag? What about its subscription-based app?
Switching from the Razer Kishi
Here’s some background, real quick: I previously owned an iPhone 13 Pro, and I played a lot of Diablo Immortal. I wanted to try the controller experience with that game, so I bought a first-generation Razer Kishi—which I liked for the most part. It had excellent thumbsticks that felt similar to those you’d find on an Xbox controller, if a little bit softer.
That said, its design involved a back that loosened up and flexed to fit different kinds of phones, but I found it annoying to take on or off because it immediately crumbled into a folding mess. The big issue that made me go with something else, though, was that the controller worked with a Lightning port, and my new iPhone traded that for USB-C. That’s a good change, overall, but it did mean I had to replace some things.
The Kishi I had is now discontinued, and it’s been replaced with the Kishi V2, which looks… less appealing to me. That’s because it ditches those Xbox-like sticks for ones more similar to what you see with a Nintendo Switch. There’s less range of motion and less stability.
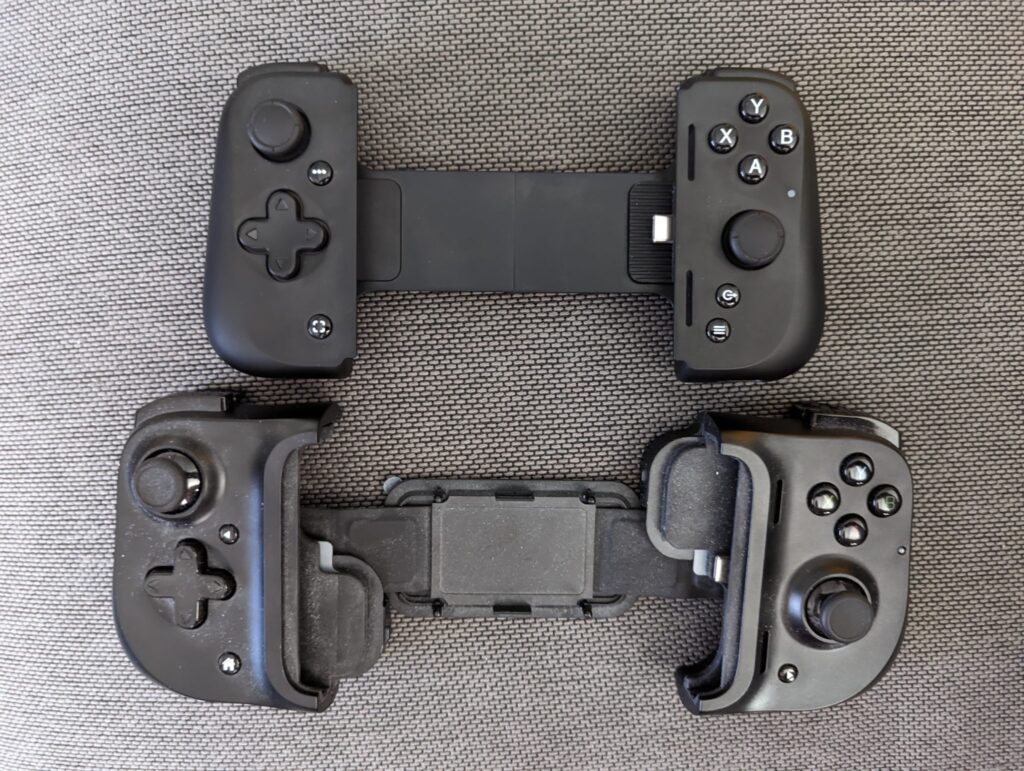

The Razer Kishi V2 (top) and Razer Kishi V1 (bottom). I had the V1. Credit: Ars Technica
The Backbone One has similar drawbacks, but I was drawn to the Backbone as an alternative partly because I had enough complaints about the Kishi that I wanted to roll the dice on something new. I also wanted a change because there’s a version with PlayStation button symbols—and I planned to primarily play PS1 games in an emulator as well as stream PS5 games to the device instead of a PlayStation Portal.
Solid hardware
One of my big complaints about the first-generation Kishi (the folding and flimsy back) isn’t an issue with the Backbone One. It’s right there in the name: This accessory has a sturdy plastic backbone that keeps things nice and stable.
The PlayStation version I got has face buttons and a directional pad that seem like good miniature counterparts to the buttons on Sony’s DualSense controller. The triggers and sticks offer much shallower and less precise control than the DualSense, though—they closely resemble the triggers and sticks on the Nintendo Switch Joy-Cons.
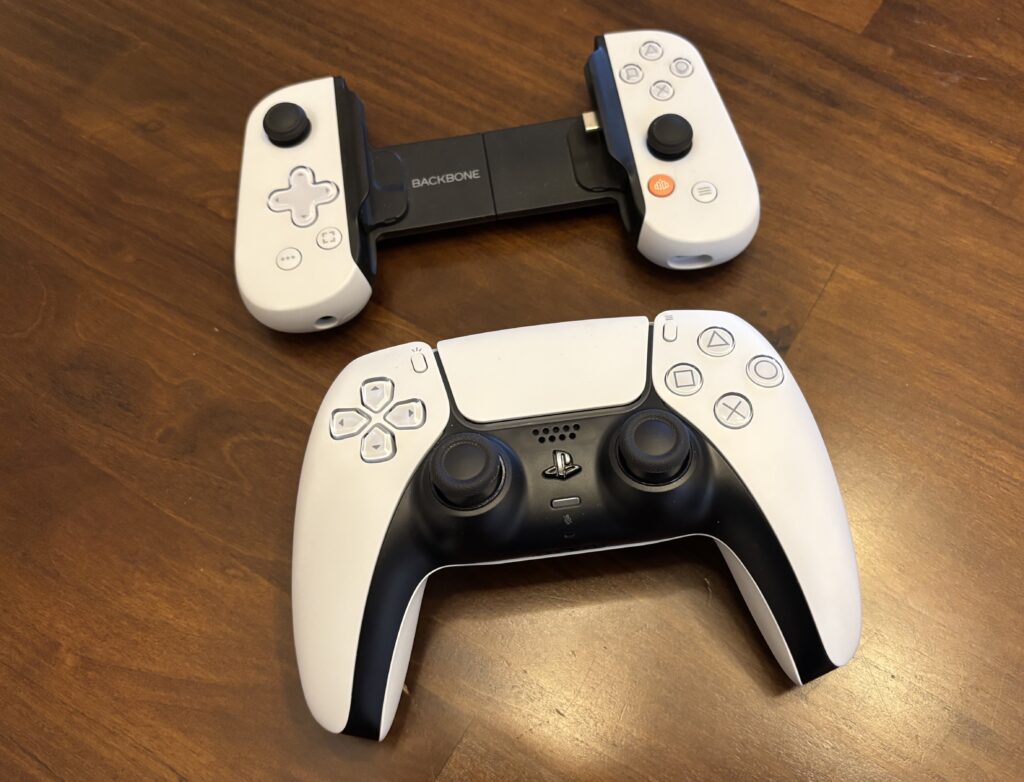

This version of the Backbone One adopts some styling from Sony’s DualSense PS5 controller. Credit: Samuel Axon
I feel that’s a big downside. It’s fine for some games, but if you’re playing any game built around quickly and accurately aiming in a 3D environment, you’ll feel the downgrade compared to a real controller.
The product feels quite sturdy to hold and use, and it doesn’t seem likely to break anytime soon. The only thing that bugs me on that front is that the placement of the USB-C port for connecting to the phone is in a place where it takes enough force to insert or remove it that I’m worried about wear and tear on the ports on either my phone or the controller. Time will tell on that front.
There’s an app, but…
The Backbone One is not just a hardware product, even though I think it’d be a perfectly good product without any kind of software or service component.
There is a Backbone app that closely resembles the PlayStation 5’s home screen interface (this is not just for the PlayStation version of the controller, to be clear). It offers a horizontally scrolling list of games from multiple sources like streaming services, mobile game subscription services, or just what’s installed on your device. It also includes voice chat, multiplayer lobbies, streaming to Twitch, and content like video highlights from games.
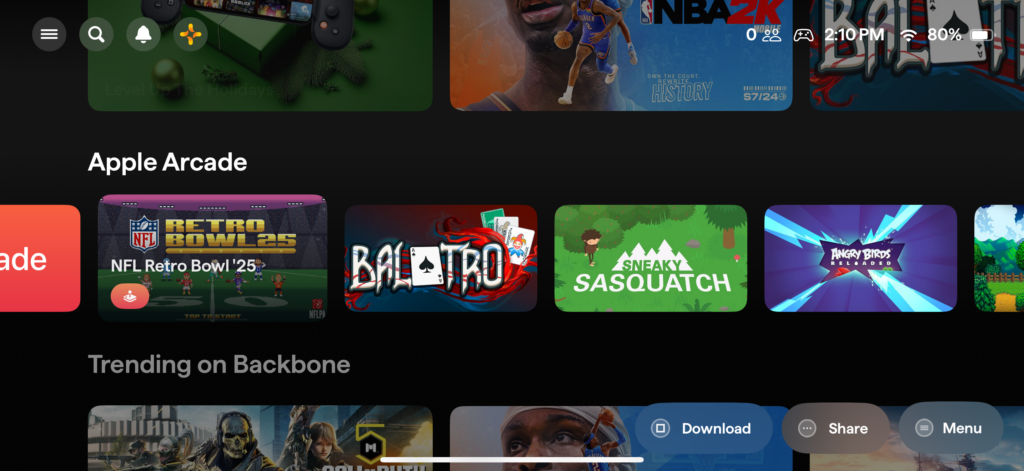
The Backbone One app collects games from different sources into one browsing interface. Credit: Samuel Axon
Unfortunately, all this requires a $40 annual subscription after a one-month trial. The good news is that you don’t have to pay for the Backbone One’s subscription service to use it as a controller with your games and emulators.
I don’t think anyone anywhere was asking for a subscription-based app for their mobile game controller. The fact that one is offered proves two things. First, it shows you just how niche this kind of product still is (and transitively, the current state of playing traditional, console-style games on iPhone) that the company that made it felt this was necessary to make a sufficient amount of money.
Second, it shows how much work Apple still needs to do to bake these features into the OS to make iOS/iPadOS a platform that is competitive with offerings from Sony, Microsoft, or even Nintendo in terms of appeal for core rather than casual gamers. That involves more than just porting a few AAA titles.
The state of iPhone gaming
The Backbone One is a nice piece of hardware, but many games you might be excited to play with it are better played elsewhere or with something else.
Hit games with controller support like Genshin Impact, Call of Duty Mobile, and Infinity Nikki all have excellent touch-based control schemes, making using a gamepad simply a matter of preference rather than a requirement.
While Apple is working with publishers like Capcom and Ubisoft to bring some hardcore console titles to the platform, that all still seems like just dipping toes in the water at this point, because they’re such a tiny slice of what’s on offer for PlayStation, Xbox, PC, or even Nintendo Switch players.
In theory, AAA game developers should be excited at the prospect of having iPhone players as a market—the install base of the iPhone absolutely dwarfs all home and handheld consoles combined. But they’re facing two barriers. The first is a chicken-and-egg problem: Only the most recent iPhones (iPhone 15 Pro and the iPhone 16 series) have supported those console AAA titles, and it will take a few years before most iPhone owners catch up.
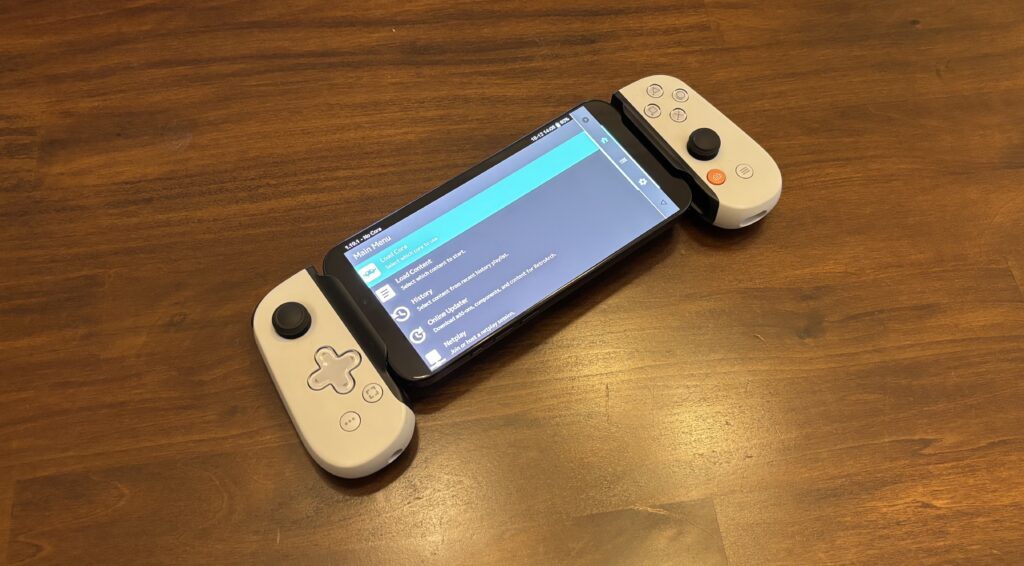

Emulators like RetroArch (seen here running on an iPhone 16 Pro Max) are the main use case of the Backbone One. Credit: Samuel Axon
The second is that modern AAA games are immensely expensive to produce, and they (thankfully) don’t typically have robust enough in-game monetization paths to be distributed for free. That means that to profit and not cannibalize console and PC sales, publishers need to sell games for much higher up-front costs than mobile players are accustomed to.
So if mobile-first hardcore games are best played with touchscreens, and gamepad-first console games haven’t hit their stride on the platform yet, what’s the point of spending $100 on a Backbone One?
The answer is emulators, for both classic and homebrew games. For that, I’ve been pleased with the Backbone One. But if your goal is to play modern games, the time still hasn’t quite come.
Samuel Axon is a senior editor at Ars Technica. He covers Apple, software development, gaming, AI, entertainment, and mixed reality. He has been writing about gaming and technology for nearly two decades at Engadget, PC World, Mashable, Vice, Polygon, Wired, and others. He previously ran a marketing and PR agency in the gaming industry, led editorial for the TV network CBS, and worked on social media marketing strategy for Samsung Mobile at the creative agency SPCSHP. He also is an independent software and game developer for iOS, Windows, and other platforms, and he is a graduate of DePaul University, where he studied interactive media and software development.
The Backbone One would be an ideal game controller—if the iPhone had more games Read More »