I threw away Audible’s app, and now I self-host my audiobooks
Stream your DRM-free audiobooks to devices yourselves, without the cloud’s chains.
We’re an audiobook family at House Hutchinson, and at any given moment my wife or I are probably listening to one while puttering around. We’ve collected a bit over 300 of the things—mostly titles from web sources (including Amazon’s Audible) and from older physical “books on tape” (most of which are actually on CDs). I don’t mind doing the extra legwork of getting everything into files and then dragging-n-dropping those files into the Books app on my Mac, but my wife prefers to simply use Audible’s app to play things directly—it’s (sometimes) quick, it’s (generally) easy, and it (occasionally) works.
But a while back, the Audible app stopped working for her. Tapping the app’s “Library” button would just show a spinning loading icon, forever. All the usual troubleshooting (logging in and out in various ways, removing and reinstalling the app, other familiar rituals) yielded no results; some searching around on Google and DuckDuckGo led me to nothing except a lot of other people having the same problem and a whole lot of silence from Audible and Amazon.
So, having put in the effort to do things the “right” way and having that way fail, I changed tacks and fixed the problem, permanently, with Audiobookshelf.
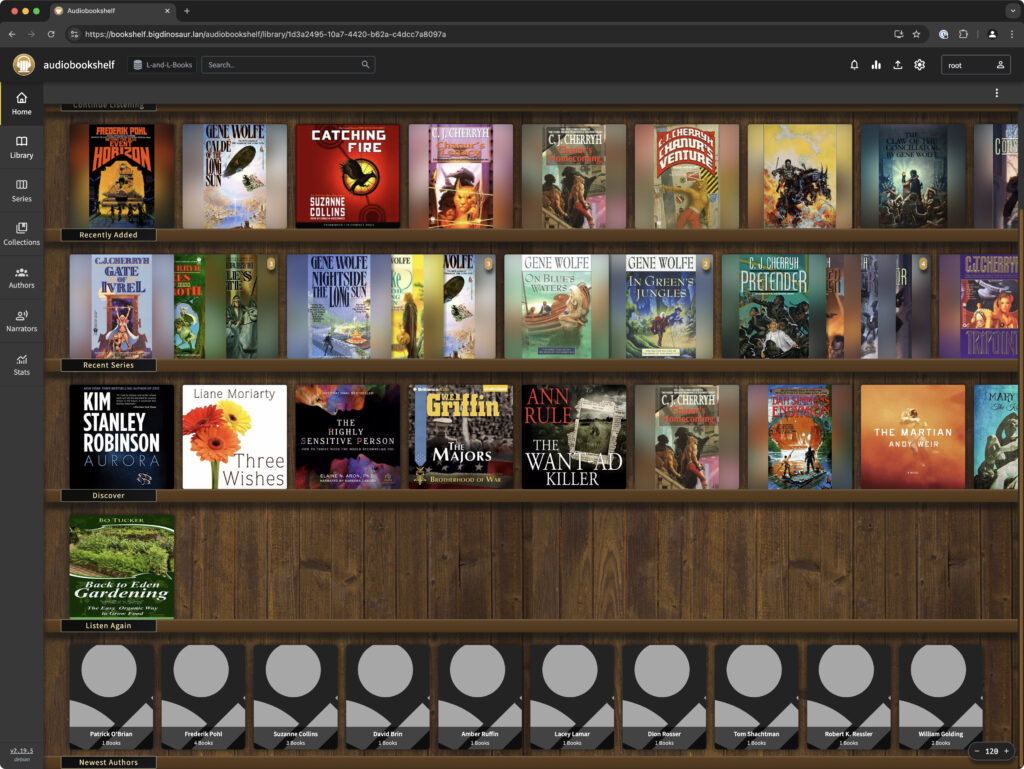
Audiobookshelf! Behold, the unholy melding together of my wife’s and my audiobooks. Credit: Lee Hutchinson
Audiobookshelf
Audiobookshelf is a self-hosted audiobook and podcast server, and after two weeks of use, so far it works vastly better than trying to stream within Audible’s app. My wife can now actually listen to audiobooks instead of staring at a spinning loading icon forever.
To get Audiobookshelf running, you need something to run it on—a spare desktop or other computer you’re not using should fit the bill, as Audiobookshelf’s requirements are relatively meager. You can either install it via a Docker image, or on bare metal on Windows or several different Linux distros. (The Linux distro installations include a repository for handling updates via your system’s update method, so you won’t have to be manually installing releases willy-nilly.)
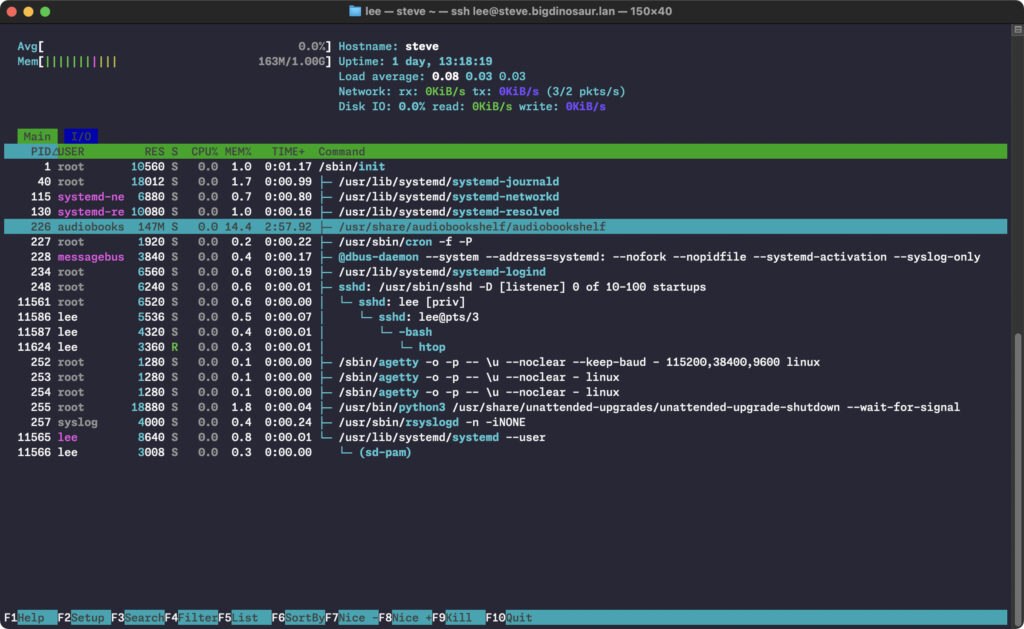
Since I already have a Proxmox instance up and running on my LAN, I chose to install Audiobookshelf inside an Ubuntu 24.04 LXC container using the “bare metal” method. It’s not particularly resource-intensive, using about 150MB of RAM at idle; as noted above, if you don’t have a server handy, running Audiobookshelf via Docker on your desktop or laptop shouldn’t be much of a burden on your memory or CPU. (It does suck up a fair amount of processing power when it’s bulk-importing or matching books in your library, but these aren’t things you’ll be doing terribly often.)
Audiobookshelf process resource utilization in htop. Credit: Lee Hutchinson
Getting it going
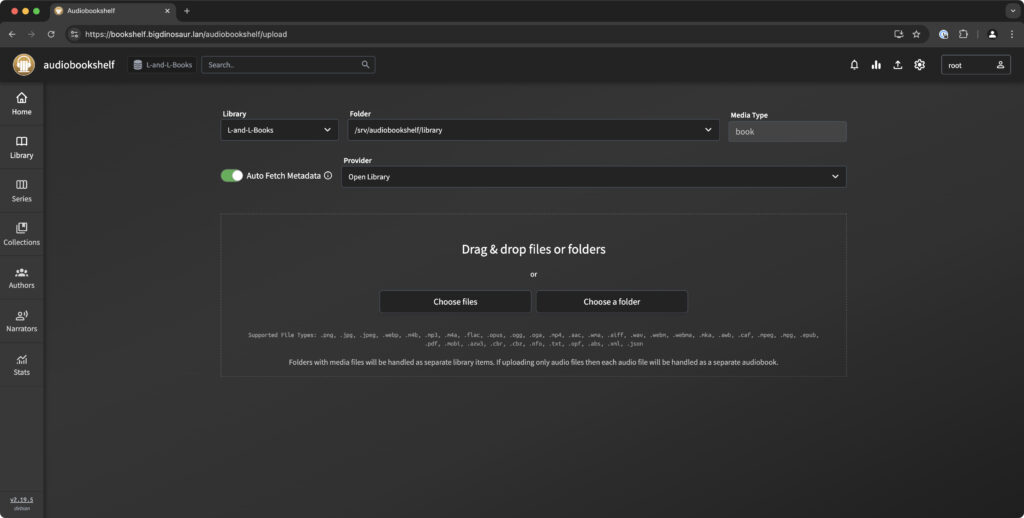
Once you’ve got Audiobookshelf installed via your preferred method, your next stop is creating and then populating your library. You can do this directly in the application’s web interface, if desired:
You can populate your library via Audiobookshelf’s upload page, if desired. Credit: Lee Hutchinson
I chose to do it the old-fashioned way and copy files into the library location myself, which also works.
There are a number of ways to make sure Audiobookshelf properly ingests and categorizes your books; first, it is aware of and respects metadata tags if your books have them. If your files lack tags, the Audiobookshelf docs provide several other methods of organization using file and directory structure. Between tags and being able to just name things per the guide, I had no problem uploading all 300-ish of my books into Audiobookshelf, with no misses or mismatches.
Of course, this all presupposes that you’ve got some DRM-free audiobooks. There are plenty of sources where you can get books free of charge—like Librivox, for example. If you’re using pay sites like Audible, you’ll want to actually log in to your library via a web browser and download each audiobook locally; this will give you a pile of files in .AAX format or something similar—which leads to a significant caveat.
The DRM elephant in the room
While books that come on audio CDs don’t have DRM embedded in them, files downloaded from Audible or other for-pay sources often do. Audiobookshelf won’t play books with DRM, which means you need a method of stripping that DRM out.
Unfortunately, here’s where we run into a problem: removing DRM from your audiobooks is not universally legal. “In the US, the law against ‘circumventing’ effective DRM has no personal-use exemption. In Europe, it varies by country,” explained the Electronic Frontier Foundation’s Competition and IP Litigation Director Mitch Stoltz when Ars reached out for advice. “That’s as silly as it sounds—stripping DRM from one’s own copy of an audiobook in order to listen to it privately through different software doesn’t threaten the author or publisher, except that it makes it harder for them to charge you twice for the same audiobook. It’s another example of how anti-circumvention laws interfere with consumers’ rights of ownership over the things they buy.”
And that means you’re kind of on your own for this step. Should you live in a jurisdiction where DRM removal from audiobooks for personal use is legal—which includes some but not all European countries—then sites like this one can assist in the process; for the rest of us, the only advice I can give is to simply proceed in a legal manner and use DRM-free audiobooks to start with.
Playing things
Once you’ve got Audiobookshelf set up and your DRM-free books stuffed into it, the last piece of the puzzle is an app to actually listen to books with. There is an official Audiobookshelf app, and if you’re an Android user you can grab it right here. The iOS app is perpetually stuck in beta and requires Test Flight, but there are third-party alternatives.
Personally, I’ve been using Plappa, and I’ve found it to be not just perfectly acceptable, but also more responsive and less prone to crashing than Apple’s own Books app (not to mention there’s no annoying in-app audiobook store page always trying to get in my face!).
Administrating things
Audiobookshelf itself has plenty of tunable options for the home system administrator who just can’t leave well enough alone; I’ve found most of the defaults are exactly what I want, but there’s tons of stuff to tweak if you want to do the tweaking.
Notably, Audiobookshelf supports multiple libraries if you want more organizational options. It has accounts you can set up for different listeners, logging options, notification options, RSS support, and a whole mess of other things I honestly haven’t even looked at yet. The good news for me is that you don’t have to look at any of that stuff if you don’t want to—Audiobookshelf is set up to be workable right out of the box.
But what if I’m not home?
Sharper readers might already have spotted a major problem with self-hosting audiobooks on one’s LAN: How do you listen when you’re not on the LAN?
This is probably worth another article, but the way I’m tackling this particular problem is with a local instance of Wireguard and a VPN profile on my mobile devices. When I’m out and about or in the car or whatever, I can tap the “VPN” shortcut on my iOS home screen, and boom—Plappa is now able to see Audiobookshelf, and streaming works just as well as it does at home.
One potential concern for doing this is cellular data usage, but this fear seems minor. The biggest audiobook I’ve got is a cool multicast recording of Frank Herbert’s Dune, which weighs in at about 2.4GB—so, the most data I’m going to transfer even for my biggest audiobook is 2.4GB max, and that’d only be if I listened to all hillion-jillion hours of Dune at the same time. And depending on the app you’re using for playback, you’ll likely also have the option to download the books to your device and listen to them locally, without streaming. (This is true for Plappa, at least.)
Self-hosting happiness achieved
I glossed over a lot of the setup steps to keep this a relatively short piece, but even so, getting Audiobookshelf going is a relatively simple self-hosting task, as self-hosting tasks go.
We also haven’t talked about Audiobookshelf’s other major feature: podcast hosting. I’m not a big podcast kind of guy (I tend to prefer audiobooks if I have time to listen to something), but Audiobookshelf is also (purportedly) great for hosting a giant pile of podcasts. If those are your jam, then that’s another point for Audiobookshelf.
I can’t vouch for the podcasting bits, but I can say that it’s gratifying to have solved a problem—especially one that was driving my wife crazy, and any day I can solve a problem for her via nerdery and server-wrangling is a good day. At least as of right now, the Audible app on her phone remains nonfunctional for reasons that are beyond me, but with luck—and a bit of ongoing care and maintenance for the server in the closet where this stuff all lives now—neither of us will ever have to deal with that app again.
I threw away Audible’s app, and now I self-host my audiobooks Read More »